You love Coca-Cola, and after discovering its risk factors, you switched to Coke Zero. But still, there are rumors that Coke Zero is no good.
So, now before again giving up on Coke Zero, you might be wanting to know, “Is Coke Zero bad for you”
Unfortunately, the answer is Yes; Coke Zero is bad for you as it has several risk factors for your health. It can increase the risk of heart disease, kidney disease, tooth erosion, etc.
We know you’re not feeling lucky now, but we suggest you review this article and discover some new data on Coke Zero.
Coke Zero Nutritional Value
Before we discuss why coke zero is bad for you, let’s learn about its nutritional value. Here’s a table summarizing the nutritional information for Coca-Cola Zero Sugar (Coke Zero).
|
Nutrition Information |
Per 100ml |
|
Energy |
1.4kJ/0.3 kcal |
|
Fat |
0g |
|
Carbohydrate |
0g |
|
Protein |
0g |
|
Salt |
0.02g |
Note: The values provided are per 100ml of the product.
Is Coke Zero Bad for You? 7 Top Reasons
Now we’ll learn about 7 crucial reasons why coke zero is bad for you.
1. Diabetic Risk
Coke Zero, despite being sugar-free, may not necessarily be a healthier option for individuals seeking to reduce their risk of diabetes due to the sugar substitutes it contains.
A 14-year study involving 66,118 women observed a connection between consuming artificially sweetened beverages and an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Similarly, another study involving 2,019 individuals found a link between sugar-sweetened and artificially sweetened diet beverages and type 2 diabetes, suggesting that switching to diet soda may not lower the risk of diabetes.
In contrast, an 8-year study involving 64,850 women found that consuming artificially sweetened beverages increased the risk of diabetes by 21%, although the risk associated with sugar-sweetened drinks was even higher at 43%.
Interestingly, conflicting results have been found in other studies. For example, a 14-year study of 1,685 middle-aged adults did not establish an association between diet soda consumption and an increased risk of prediabetes.
Due to the conflicting findings, there is currently no exact explanation of how artificially sweetened beverages increase the risk of diabetes. Further research is required to gain a better understanding of this relationship.
2. Gut Microbiome and Disease Risk
Diet sodas, including Coke Zero, have been associated with alterations in the gut microbiome. The gut microbiome plays a crucial role in overall health and digestion. Additionally, some studies suggest that the consumption of diet sodas may be linked to an increased risk of osteoporosis, heart disease, and kidney disease.
However, it’s important to note that these associations do not necessarily imply causation and further research is needed to establish the precise relationship between diet sodas and these health risks.
3. Lack of Nutritional Benefits
Health experts generally do not recommend drinking soda, including Coke Zero, regularly due to their lack of nutritional benefits. These beverages provide no essential nutrients and may contribute to excessive calorie consumption without offering any significant nutritional value.
4. Risk of Enamel and Tooth Erosion
The acidic pH level of Coke Zero, similar to other carbonated beverages, is linked to a heightened risk of enamel and tooth erosion. Acidic drinks can weaken the protective layer of enamel on the teeth, making them more susceptible to damage and erosion over time. However, Coke Zero may have a slightly lower acidity than regular Coke and other acidic beverages.
5. Risk of Heart Disease
A study found a correlation between artificially sweetened beverages and an elevated risk of heart disease among women without a history of heart disease.
6. Risk of Kidney Disease
The high phosphorus content in sodas, including diet sodas, may contribute to kidney damage. Research indicates that individuals who consume more than seven glasses of diet soda per week may double their risk of kidney disease.
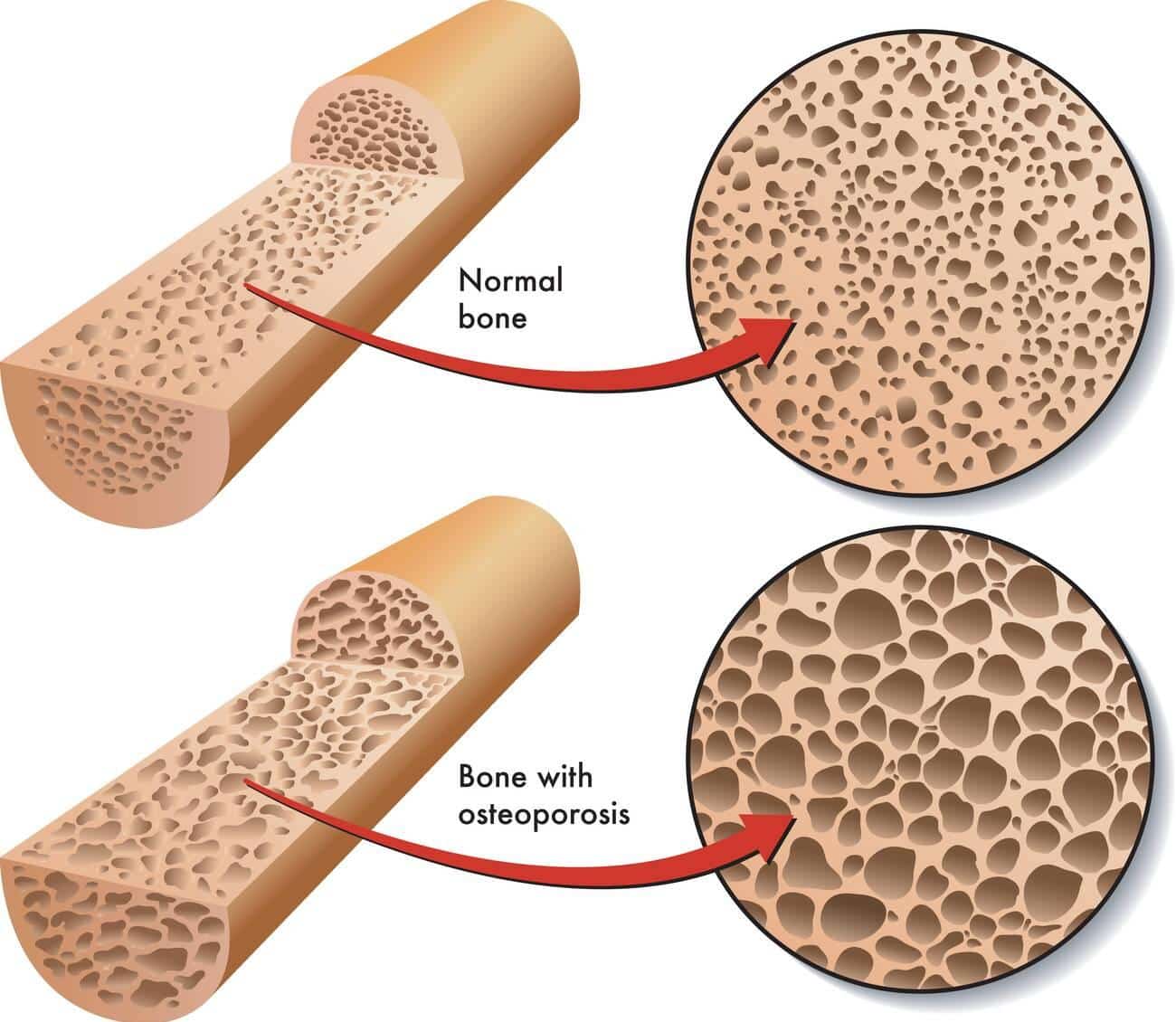
7. Potential Increase in Osteoporosis Risk
Research has shown that daily cola intake and diet beverages may be associated with lower bone mineral density. This suggests a potential increased risk of osteoporosis.
Related Article: Is Ceviche Healthy
Is it OK to Drink Coke Zero Every Day?
Consuming moderate diet soda, such as one or two cans per day, is generally considered safe and unlikely to cause harm. The artificial sweeteners and other chemicals used in diet soda are typically considered safe for most individuals, with no credible evidence linking them to cancer.
Certain types of diet soda are even enriched with vitamins and minerals. However, it’s important to note that diet soda should not be considered a healthy beverage or a magical weight-loss solution.
While switching from regular soda to diet soda may help reduce calorie intake, it remains unclear whether this can effectively prevent obesity and associated health issues in the long run.
There are healthier, low-calorie alternatives available. Below we’ll learn about them.
8 Healthier Low-Calorie Alternatives to Coke Zero
There are several healthier, low-calorie alternatives to Coke Zero That you can consider:
- Water: Water is the ultimate zero-calorie beverage and the best choice for hydration. It does not contain any added sugars or artificial sweeteners.
- Sparkling Water: If you enjoy carbonated beverages, choose plain or flavored sparkling water without added sugars. You can add a squeeze of lemon or lime for extra flavor.
- Unsweetened Tea: Green tea, black tea, herbal tea, or iced tea without added sugars can be refreshing and provide various health benefits.
- Herbal Infusions: Infused water with fruits, herbs, or vegetables can provide a flavorful, low-calorie option. Examples include cucumber-infused water, lemon-mint water, or berry-infused water.
- Unsweetened Coffee: Black coffee or coffee with a small amount of low-fat milk or a sugar substitute can be a low-calorie alternative.
- Skim or Low-Fat Milk: Skim or low-fat milk can be a good choice if you prefer dairy. They provide essential nutrients like calcium and protein while lowering calories than whole milk.
- Coconut Water: Coconut water is a natural, electrolyte-rich beverage that can offer hydration and a subtle sweetness. Look for brands without added sugars.
- Homemade Fruit Smoothies: Create your smoothies using a base of low-fat yogurt or milk and fresh or frozen fruits. Avoid adding additional sugars or sweeteners.
You May Find Interest: Is Coconut Milk Good for Acid Reflux
Is Coke Zero More Bad than Coke?
To understand whether Coke Zero or regular Coke is better, you need to understand the comparison between them. Below let’s check out Coke Zero Vs Regular Coke.
|
Factors |
Coke Zero |
Regular coke |
|
Sugar |
0 grams |
High sugar content (varies by size) |
|
Calories |
0 calories |
High-calorie content (varies by size) |
|
Sweeteners |
Artificial sweeteners (e.g., aspartame, acesulfame potassium) |
Sugar (sucrose or high fructose corn syrup) |
|
Taste |
Similar to regular Coke |
Traditional Coke flavor |
|
Health Effects |
Lower risk of weight gain, obesity, and type 2 diabetes compared to regular Coke |
Higher risk of weight gain, obesity, and type 2 diabetes due to sugar content |
|
Considerations |
Contains artificial sweeteners, which some individuals may want to limit |
The high sugar content can contribute to various health issues |
|
Moderation |
Should be consumed in moderation |
Should be consumed in moderation |
- Sugar Content: Regular Coke contains significant sugar, contributing to its high-calorie content. In contrast, Coke Zero is sugar-free and uses artificial sweeteners to provide a similar taste without the added calories.
- Artificial Sweeteners: Coke Zero contains artificial sweeteners like aspartame and acesulfame potassium, which are considered safe for consumption by regulatory authorities. However, some people may prefer to limit their intake of artificial sweeteners due to personal preferences or concerns.
- Health Effects: Regular consumption of sugary beverages like regular Coke has been associated with weight gain, increased risk of obesity, and chronic health conditions such as type 2 diabetes and heart disease. While Coke Zero is lower in calories and sugar, it is still essential to moderate the consumption of artificially sweetened drinks and prioritizes healthier beverage choices.
- Overall Diet and Lifestyle: Considering the overall dietary and lifestyle factors are crucial. Drinking any soda, whether regular or diet, should be done in moderation. A balanced diet consisting of whole foods and regular physical activity is vital for maintaining good health.
In conclusion, regular Coke and Coke Zero should be consumed in moderation as part of a balanced diet.
Why is Coke Zero so Addicting?
The perception of addiction can vary among individuals. However, according to many people, Coke Zero is highly addicting. Here are the reasons why Coke Zero may be perceived as addictive, presented in bullet points:
- Sugar Substitutes: Coke Zero contains artificial sweeteners that can activate the brain’s reward centers, potentially creating a craving for the sweet taste.
- Flavor and Taste: The combination of flavors and carbonation in Coke Zero can be enjoyable and lead to repeated consumption, potentially resulting in cravings.
- Marketing and Branding: Coca-Cola invests in marketing and branding to create a strong association with Coke Zero, which can contribute to its appeal and perceived addiction.
- Habit Formation: Regular consumption of Coke Zero can lead to the formation of habits, where individuals associate the beverage with certain activities or situations, reinforcing the desire for it.
- Psychological Factors: Personal preferences, psychological factors, and individual susceptibility to cravings can influence the perceived addiction to specific beverages.
Top Picks: Health Benefits of Oatmeal
Does Coke Zero Have Benefits?
There are no significant benefits of Coke Zero except two. Below I’m describing them.
1. Calorie-Free
Coke Zero is a calorie-free beverage that does not contribute to calorie intake. This can benefit those monitoring their caloric information in weight management or calorie-controlled diets. Individuals can enjoy the Coca-Cola flavor without adding extra calories to their diet by choosing Coke Zero instead of regular Coke or other sugary drinks.
2. Zero Sugar
One of the main benefits of Coke Zero is that it contains zero sugar. Instead, it is sweetened with artificial sweeteners like aspartame and acesulfame potassium, which provide the signature Coca-Cola flavor without the sugar content.
This can be particularly appealing to individuals looking to reduce their sugar consumption for various reasons, including weight management, diabetes management, or overall health concerns related to excessive sugar intake.
Final Words
So, in the end, the logic and data say Coke Zero is no good even though it has 0 sugar and calories. I’ve already mentioned 7 risk factors, which should make you more precise. However, I’ve also said a certain amount of Coke Zero is okay if you’re highly addictive. However, it’s the best advice to give up on Coke Zero. All the Best!
Disclaimer: This content is for informational purposes only and does not replace professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. This information is not comprehensive and should not be used to make health or well-being decisions. Consult a qualified healthcare professional with questions about a medical condition, treatment options, or health regimen. This website or the content should never replace professional medical advice.