You know that sinking feeling when you click “I Agree” on a privacy policy you didn’t read? You aren’t the only one. Recent data shows that 92% of Americans are now concerned about their privacy online, yet 62% believe it’s impossible to go through daily life without companies collecting their data. We have accepted that big tech companies own our digital footprints—but that agreement is starting to expire.
Here is the reality: Decentralized Web Hosting (Web3) is shifting the power dynamic. By using blockchain and peer-to-peer networks, this technology ensures your data isn’t stored in a single “honeypot” server owned by one corporation. Instead, it is encrypted, shredded, and distributed across a global network that you control.
In this guide, I’m going to break down exactly how this technology works, compare the real-world costs (hint: it’s drastically cheaper), and show you the specific tools—like IPFS and Filecoin—that are making the internet private again. Ready to take back control of your digital identity? Let’s look at the facts.
What is Decentralized Web Hosting?
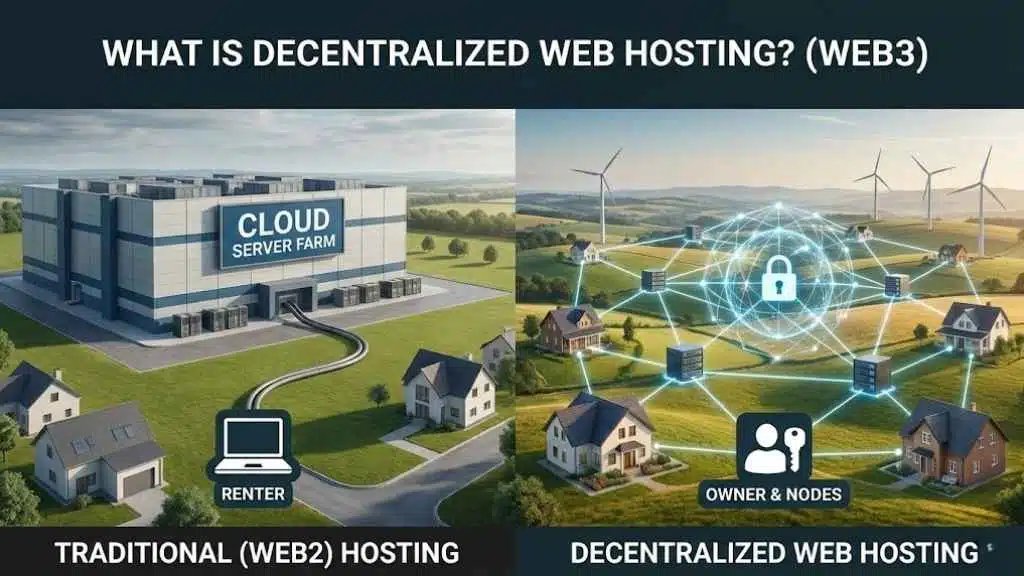
At its core, decentralized web hosting is about removing the “middleman” from the internet equation. Instead of renting space on a server farm owned by Amazon (AWS) or Google, your website lives on a network of independent computers—called nodes—scattered across the globe.
Definition and key principles
Web3 web hosting uses decentralization to store and share data across many computers instead of relying on one main server. This approach gives users more control over their digital identity and personal information. With blockchain technology, every action is recorded in a secure, public ledger that anyone can check for accuracy.
The biggest shift here is data sovereignty. In the traditional model, if you stop paying your bill or violate a term of service, a company can delete your digital existence with one click. In a decentralized model, you own your cryptographic keys. As long as you hold those keys, you own your data. Smart contracts—self-executing code on the blockchain—automate these agreements, ensuring that storage providers get paid and your data stays online without a corporate intermediary.
How it differs from traditional hosting
Traditional web hosting relies on centralized servers. Think of it like renting an apartment: the landlord (Amazon, Microsoft, or Google) has the keys and can enter—or evict you—at any time. Decentralized hosting is more like owning a home; you have the deed and the keys.
To see why this matters, look at the cost and structure differences below:
| Feature | Centralized (Web2) | Decentralized (Web3) |
|---|---|---|
| Data Storage | Single location or cluster (e.g., AWS Data Center) | Distributed across global nodes |
| Monthly Cost (1TB) | ~$23.00 (Standard S3 pricing) | ~$0.19 (Filecoin network average) |
| Censorship Risk | High (Provider can remove content) | Low (Immutable & distributed) |
| Single Point of Failure | Yes (Server outages affect access) | No (Redundant copies exist globally) |
Insider Tip: While the cost savings are massive, the user experience in Web3 is still catching up. Setting up a decentralized site often requires more technical know-how than a simple drag-and-drop website builder.
How Decentralized Web Hosting Works
Decentralized web hosting spreads your website data across many computers, not just one or two central servers. It sounds complex, but it follows a logical three-step process: Sharding (breaking up data), Encryption (locking it), and Distribution (sending it out).
Peer-to-peer (P2P) networks
Peer-to-peer, or P2P, networks connect many computers so each one shares resources with others. No single server holds all the data. Instead, copies of files are stored across many users’ devices around the world.
This means control is spread out and no company can decide what should stay online or be removed—helping to protect against censorship. Think of it like BitTorrent; there is no central computer sending you a movie. Instead, you download tiny pieces of the movie from thousands of other users simultaneously.
Web3 uses P2P networks for hosting websites and apps using blockchain technology. With this setup, your private information does not get funneled into a central database. Instead, encrypted pieces of data travel between users directly, adding stronger privacy and more user control over digital identity and content ownership.
Role of blockchain technology
Blockchain technology acts as the “incentive layer” for these networks. While P2P networks handle the files, the blockchain handles the payments and proof. It ensures that the people storing your data (Storage Providers) are actually keeping it online and unaltered.
For example, the Filecoin network uses a system called “Proof of Spacetime.” Storage providers must mathematically prove to the blockchain, every single day, that they are still storing your data correctly. If they fail, they are fined automatically.
Users get more power over their digital identity and data ownership because blockchain stores records across many computers at once. Each change or upload gets time-stamped on the chain, making it easy to track and very hard to fake. This approach brings stronger privacy and security for everyone involved.
Data encryption and distribution
Data encryption scrambles your files with cryptography before they leave your device. Only people with the right digital key can unlock and read them. This method helps protect your data, even if hackers try to steal it during transfer.
Here is how the secure workflow typically happens:
- Upload & Encrypt: You upload a file, and it is immediately encrypted on your own device (Client-Side Encryption).
- Generate CID: The network assigns a unique fingerprint to your file called a Content Identifier (CID).
- Shard & Disperse: The file is broken into smaller chunks (“shards”) and sent to different nodes globally.
- Retrieval: When you need the file, the network finds the closest nodes with your shards, reassembles them, and decrypts them using your key.
Key Benefits of Decentralized Web Hosting
Decentralized web hosting gives users more power over their data… and that changes how people control information online. Beyond just “owning your data,” there are practical security and uptime benefits that even major corporations are starting to notice.
Enhanced privacy and security
More power shifts to the user with Web3. You control your data using blockchain and cryptography instead of letting big companies store everything on one server. This means hackers have a harder time reaching your private files, since information spreads out across many places.
In a traditional breach—like the massive hacks we’ve seen at T-Mobile or 23andMe—attackers target one central database to steal millions of records. In a decentralized network, there is no central database to target. To steal data, a hacker would need to compromise thousands of independent nodes simultaneously, which is mathematically nearly impossible.
Censorship resistance
Web3 uses decentralization and blockchain to keep content free from censorship. Decentralized web hosting spreads data across many computers, not just a few servers that can be controlled or shut down. This means no single person, company, or government can quickly remove information from the system.
A prime example of this is Mirror.xyz, a publishing platform built on Web3 protocols. Unlike Medium or WordPress, where the platform can suspend your blog, articles published on Mirror are stored permanently on Arweave. As long as the network exists, your words exist.
Improved resilience and uptime
Decentralized web hosting uses peer-to-peer networks and blockchain to spread data across many computers. If one server goes down, others keep the site running. This setup prevents a single point of failure, which is common with traditional web hosts.
“In a decentralized network, ‘Link Rot’ becomes a thing of the past. Because files are requested by their unique content hash (CID) rather than a specific location address, links don’t break just because a server moved or changed its name.”
Protection against DDoS attacks
DDoS attacks flood websites with fake traffic. This slows down or even shuts off access for real users. Web3 uses decentralization and blockchain networks to stop this problem. Data does not sit on one server, making it hard for attackers to target a single place.
Each part of the site exists across many nodes in peer-to-peer networks. If some nodes get hit by bad traffic, other nodes can keep serving content fast and safe. Attackers would need huge resources to take down every node at once—much more than with old web hosting methods. This makes decentralized web hosting much stronger against DDoS threats and helps keep user privacy and data protection top priorities in Web3 systems.
Common Technologies Powering Decentralized Web Hosting
Many smart tools now help people host websites in new ways—using shared systems, not big central servers. Two names dominate this space, and knowing the difference between them is critical for choosing the right tool.
IPFS (InterPlanetary File System)
IPFS, short for InterPlanetary File System, is a Web3 technology. It uses peer-to-peer networks rather than central servers. Files are broken into smaller pieces and stored across many computers worldwide. No one company controls the data; users keep ownership of their files.
The magic of IPFS is Content Addressing. In the old web, you look for a location. In IPFS, you look for the file’s fingerprint (CID). If the content of the file changes even by one pixel, the fingerprint changes. This guarantees you are always getting the exact data you asked for.
Pro-Tip for Users: Until recently, the Brave browser had a built-in IPFS node. However, as of late 2024, this feature was deprecated. To run a true node now, the community recommends downloading IPFS Desktop or using the IPFS Companion browser extension for the best experience.
Filecoin
Filecoin uses blockchain and peer-to-peer networks to store and share data in a decentralized way. Users pay with Filecoin tokens to save files across many independent computers instead of one central server. It essentially acts as the “Airbnb for data storage”—renting out unused hard drive space globally.
The scale here is massive. As of 2025, the Filecoin network has a storage capacity of over 23 exbibytes. To put that in perspective, that’s enough space to store thousands of copies of the entire Internet Archive. Because supply is so high, prices remain incredibly low compared to AWS or Google Cloud.
Blockchain for data integrity
Blockchain helps protect data integrity by storing records in a public digital ledger. This means once information goes on the blockchain, no one can secretly change or delete it. Each new block of data links to the last one using cryptography, making it easy to track any changes and keep them honest.
Web3 technology uses blockchain to give users more control over their own content and privacy online. With this system, your website files stay safe from tampering because many copies exist across a network. No single person or company can take down or quietly edit your content.
Use Cases of Decentralized Web Hosting
Decentralized hosting opens doors for new types of websites and online services, built with privacy at their core. It is not just for tech demos anymore; real-world organizations are using it to solve specific problems.
Decentralized applications (DApps)
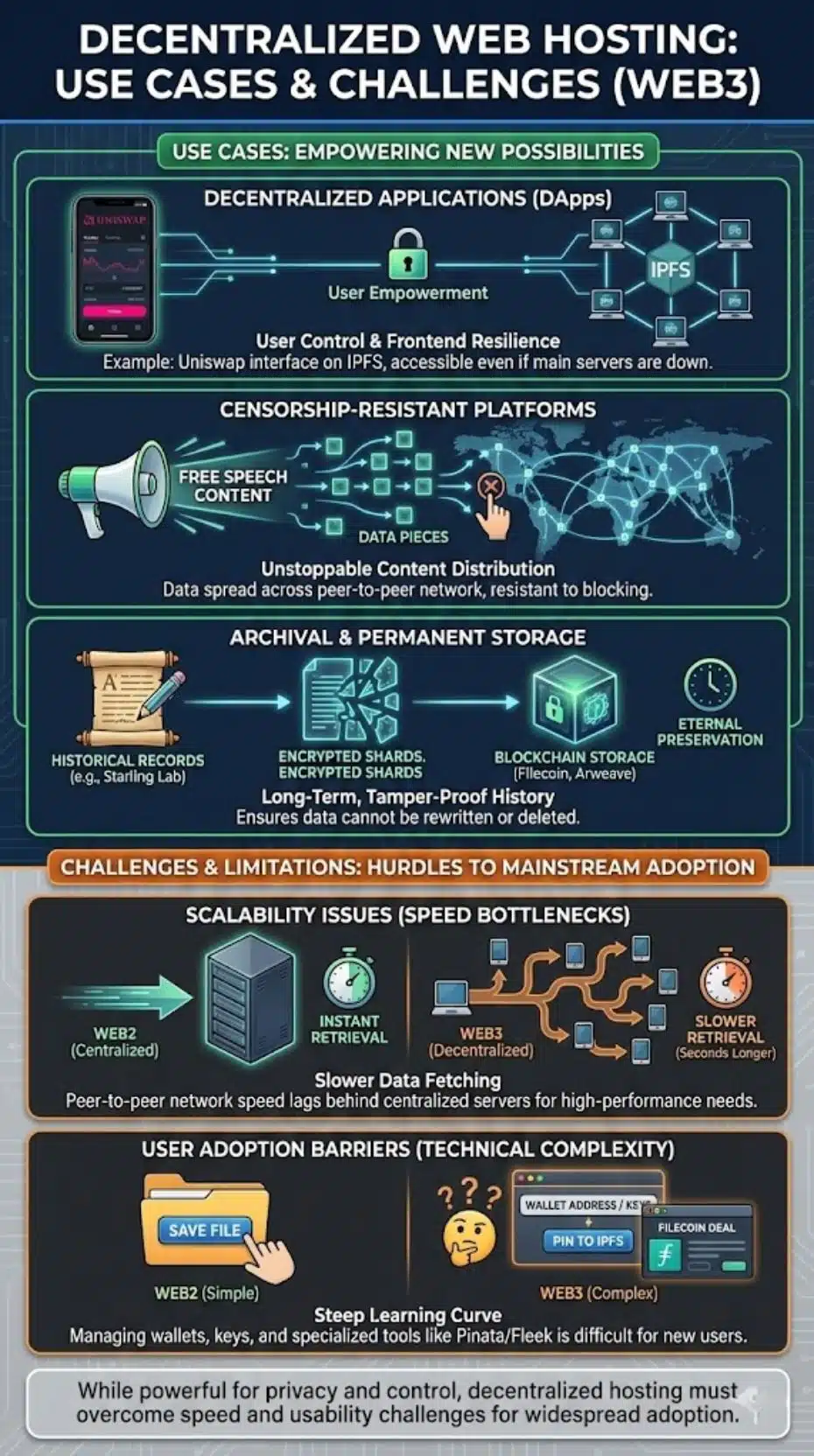
DApps use blockchain and peer-to-peer networks to run digital tools without one central authority. These apps bring user empowerment, letting people control their own data and privacy. Web3 technology makes this possible by storing information across many computers instead of in a single server.
A famous example is Uniswap. While it deals with billions of dollars in crypto trading, its frontend interface is frequently hosted on IPFS. This ensures that even if the company’s main servers were attacked, the trading interface would remain accessible to users worldwide via the decentralized network.
Censorship-resistant platforms
Censorship-resistant platforms use decentralized web hosting to keep content online, even if someone tries to take it down. Blockchain and peer-to-peer networks spread data over many computers instead of relying on a single server. This makes it almost impossible for any group or government to block information fully.
In 2024, people use these platforms when they want strong data protection or must speak out without fear of being silenced. Activists, journalists, and regular users share news through systems that protect free speech using smart contracts and cryptography. Data stays safe with encryption while blockchain records each action so nothing gets lost or changed in secret.
Archival and permanent storage solutions
Web3 uses decentralized networks like IPFS and Filecoin to store data for the long term. Files are broken into small pieces, spread across many peer-to-peer computers, and secured with blockchain technology. This approach helps keep files available even if some servers go offline or try to censor content.
The Starling Lab, a joint project by Stanford and USC, uses these protocols to preserve sensitive historical records, such as testimony from genocide survivors. By storing this data on decentralized networks (like Arweave and Filecoin), they ensure that history cannot be rewritten or deleted by bad actors in the future.
Challenges and Limitations of Decentralized Web Hosting
Decentralized web hosting faces some hurdles—curious how these impact Web3 privacy? While the technology is powerful, it isn’t perfect yet.
Scalability issues
Web3 networks run on peer-to-peer technology and blockchain, which can slow things down as more users join. As more data moves across the network, delays in loading websites or applications may occur. Traditional web hosting uses large data centers that handle many requests at once. Web3 spreads these requests across many devices instead, making it harder to grow quickly.
Retrieval speed is the biggest bottleneck. Fetching a file from a decentralized network can take seconds longer than fetching it from a localized Amazon server. While projects like “Saturn” (a Web3 Content Delivery Network) are improving this, the “instant” feel of Web2 is still superior for high-performance needs.
User adoption barriers
People find it hard to use decentralized web hosting. New users often struggle with blockchain, cryptography, and peer-to-peer networks. Many get confused by long wallet addresses or keys needed for digital identity and data ownership.
There is also the “right-click save” problem. In Web2, saving a file is easy. In Web3, pinning a file to IPFS or managing a Filecoin deal requires using tools like Pinata or Fleek. Until these tools become as simple as Dropbox, mainstream adoption will remain slow.
The Future of Decentralized Web Hosting
The future brings new tools and creative ways to keep your online life safer. The industry is rapidly solving the speed and cost issues that held it back in the early 2020s.
Innovations in blockchain scalability
Blockchain networks now use better methods to handle more users and data. Developers have added sharding, which splits big chains into smaller parts called shards. Each shard runs its own tasks at the same time, making things faster for everyone.
A major milestone was Ethereum’s Dencun Upgrade in March 2024. This update introduced “blobs” (EIP-4844), which drastically reduced the cost of storing data on Layer 2 networks. This makes it feasible to build complex, data-heavy applications on the blockchain without bankrupting the developers.
Growing adoption of Web3 technologies
More people are using Web3 technologies every day. These new tools use decentralization and blockchain to give users more power over their data. Instead of sharing private details with big companies, people keep control themselves. This shift means better privacy and stronger data protection for everyone.
Web3 also helps make content harder to censor since it spreads information across many computers worldwide. With this method, user empowerment grows, and digital identity becomes safer. Many developers now build Web3 platforms that focus on secure, peer-to-peer networks and smart contracts—pushing the internet into a new era where users have true ownership of their information.
Final thoughts
Decentralized web hosting with Web3 puts privacy, control, and security back into the hands of users. Instead of trusting one company with your data, you can share and store information across a network using tools like blockchain and IPFS. The shift from “renting” your digital space to “owning” it is more than just a trend; it’s a necessary evolution for privacy.
These methods are simple to use and help protect against hacking or censorship while making sure sites stay online longer. Watching these changes unfold shows just how much better our digital lives can get when we choose smart technology for true data ownership. Start exploring these new options today, because your privacy matters more than ever in the growing internet age.