In recent years, the global financial system has witnessed significant shifts challenging the long-standing dominance of the U.S. dollar. Notably, countries like Russia and China have intensified their bilateral trade using local currencies, such as the yuan and ruble, aiming to reduce dependence on the dollar.
Similarly, India has introduced a rupee settlement system to facilitate international transactions without involving the dollar.
De-dollarization diplomacy refers to the process by which countries reduce their reliance on the U.S. dollar for international trade and reserves.
This movement has profound implications for financial hegemony, as it challenges the traditional economic influence exerted by the United States. The increasing use of economic sanctions and the strategic role of systems like SWIFT have accelerated efforts toward a more multipolar financial world, diminishing U.S. dominance.
Historical Context: The Rise and Risks of Dollar Dominance
Explore the historical background of De-dollarization diplomacy. Find out the rise and risks of the dollar dominance by time.
From Bretton Woods to the Petrodollar
The Bretton Woods Agreement of 1944 established the U.S. dollar as the world’s primary reserve currency, pegged to gold. This system positioned the dollar at the center of international trade. In 1971, the “Nixon Shock” ended gold convertibility, transitioning the dollar to a fiat currency.
Subsequently, the petrodollar system emerged, with oil transactions predominantly conducted in dollars, further entrenching U.S. financial power.
The “Exorbitant Privilege” and Its Costs
The dollar’s dominance has afforded the U.S. several advantages, including low borrowing costs and significant global influence. However, this “exorbitant privilege” comes with risks.
The U.S. can export inflation through policies like quantitative easing, affecting global markets. Additionally, the world’s heavy reliance on dollar liquidity makes the global economy vulnerable to U.S. domestic financial policies.
Sanctions and SWIFT: Catalysts for De-Dollarization Diplomacy
What are the sanctions and SWIFT for the De-dollarization diplomacy? Explore here.
The Weaponization of the Dollar
The U.S. has increasingly used the dollar as a tool for economic sanctions. A notable example is the 2022 sanctions on Russia, which included freezing $600 billion in reserves and excluding Russian banks from the SWIFT system.
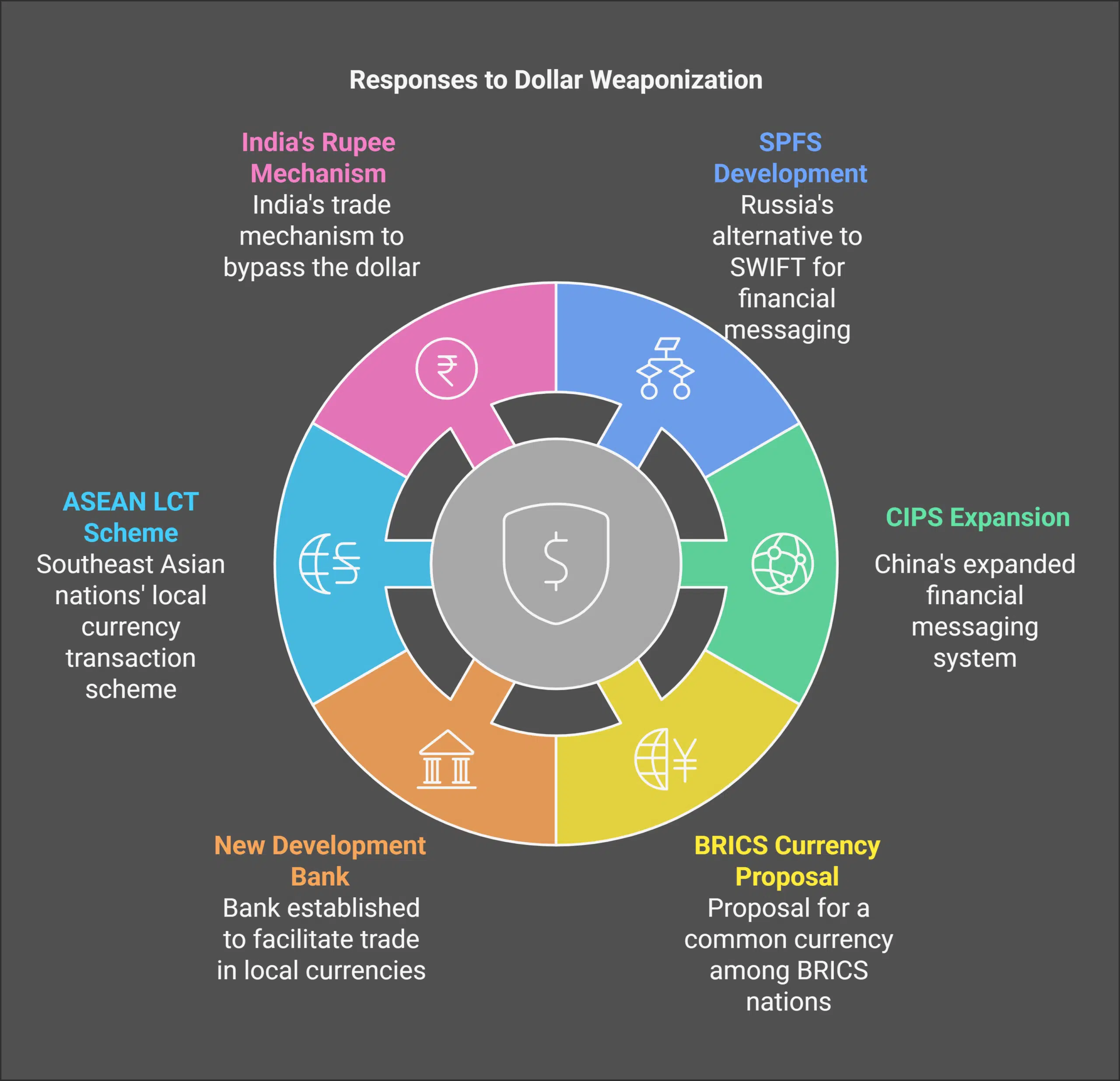
In response, Russia developed the System for Transfer of Financial Messages (SPFS), and China expanded its Cross-Border Interbank Payment System (CIPS) as alternatives to SWIFT.
Global Backlash and Strategic Responses
In reaction to these sanctions, international coalitions like BRICS (Brazil, Russia, India, China, South Africa) have initiated measures to reduce dollar dependence. Efforts include proposing a common currency and establishing the New Development Bank to facilitate trade in local currencies.
Additionally, ASEAN countries have implemented the Local Currency Transaction (LCT) scheme, and India has developed a rupee trade mechanism to bypass the dollar.
Case Studies: Regional Moves Toward Financial Independence
Here, you will get to know some case studies for the regional movements toward financial independence.
China’s Digital Yuan and Petro-Yuan Ambitions
China has been at the forefront of developing a digital yuan, aiming to facilitate international trade without relying on the dollar. The digital currency allows for direct transactions, reducing the need for intermediary banks. Furthermore, discussions have emerged about Saudi Arabia potentially accepting yuan for oil sales, signaling a shift towards a “petro-yuan” system.
Russia’s Ruble-Yuan Pivot and Sanctions Evasion
In response to Western sanctions, Russia has increased its use of the yuan in trade with China. Currently, ruble-yuan transactions account for approximately 70% of trade between the two nations. Additionally, Russia’s SPFS has been adopted by countries facing similar sanctions, providing an alternative to SWIFT.
India’s Rupee Internationalization Strategy
India has implemented measures to internationalize the rupee, including establishing Vostro accounts for 18 countries. This system enables these nations to hold rupees in local accounts, facilitating trade without the dollar. The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has been proactive in promoting the rupee for international transactions, aiming to reduce dependence on the dollar.
Challenges and Risks of De-Dollarization Diplomacy
Find out the challenges and the risks of the de-dollarization diplomacy in 2025.
Liquidity and Trust Deficits
While efforts to de-dollarize are gaining momentum, alternative currencies like the yuan and ruble lack the liquidity and global trust that the dollar enjoys. The depth of the U.S. financial markets and the widespread acceptance of the dollar make it challenging for other currencies to replace it in the short term.
Emerging economies also face currency volatility, which can deter international partners from adopting their currencies for trade.
U.S. Countermeasures and Economic Fallout
The U.S. has responded to de-dollarization efforts with potential countermeasures, including imposing secondary sanctions and trade tariffs. For instance, President Donald Trump has threatened 100% tariffs on BRICS nations if they attempt to create a new currency to replace the dollar. Such actions could lead to economic fragmentation, complicating global trade and increasing transaction costs.
The Future of Global Finance: Scenarios and Implications
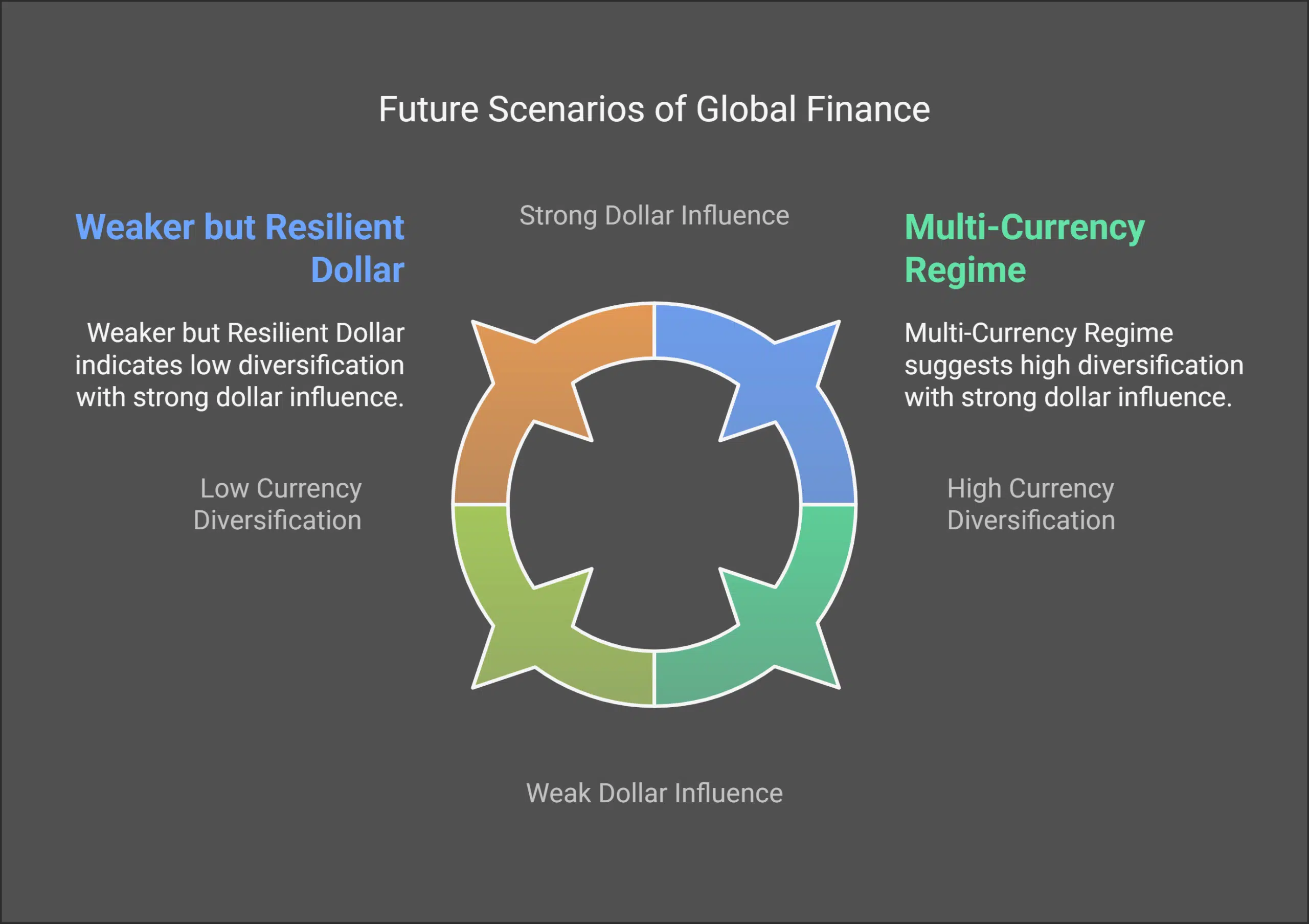
Scenario 1: A Multi-Currency Regime
In this scenario, regional blocs like BRICS and ASEAN adopt local currencies for trade, reducing reliance on the dollar. The rise of Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) could further facilitate cross-border payments, making transactions more efficient and less dependent on traditional banking systems. This shift could lead to a more balanced global financial system with multiple key currencies.
Scenario 2: A Weaker but Resilient Dollar
Despite de-dollarization efforts, the dollar may retain its dominance in commodities trading and as a safe-haven currency. However, its share in global reserves could gradually decline. As of 2024, the dollar’s share in global reserves has decreased to 47%, indicating a slow erosion of its dominance.
Nevertheless, the inherent strengths of the U.S. economy and the established trust in its financial institutions may ensure the dollar remains a central player in global finance.
Strategic Implications for Policymakers and Businesses
The evolving landscape of de-dollarization presents both challenges and opportunities for policymakers and businesses worldwide. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for strategic planning and risk management.
Navigating Geopolitical Realignments
For Policymakers:
- Diversification of Currency Reserves: As the global financial system becomes more multipolar, there’s a strategic advantage in diversifying foreign exchange reserves beyond the U.S. dollar. This approach can mitigate risks associated with dollar volatility and potential sanctions.
- Strengthening Regional Alliances: Engaging in regional trade agreements that utilize local currencies can reduce dependence on the dollar. For instance, the BRICS nations have explored mechanisms to facilitate trade in their respective currencies, enhancing economic resilience.
- Developing Alternative Payment Systems: Investing in or adopting alternative payment infrastructures, such as China’s CIPS or Russia’s SPFS, can provide countries with more autonomy in international transactions, reducing exposure to potential SWIFT-related sanctions.
For Businesses:
- Currency Risk Management: With the potential increase in the use of multiple currencies, businesses should implement robust currency risk management strategies. This includes utilizing hedging instruments to protect against exchange rate fluctuations.
- Supply Chain Diversification: Companies should assess their supply chains to identify vulnerabilities related to currency dependencies. Diversifying suppliers and markets can mitigate risks associated with currency volatility and geopolitical tensions.
- Adapting to Digital Currencies: The rise of central bank digital currencies (CBDCs) offers new avenues for transaction efficiency but also requires businesses to adapt their payment systems and ensure compliance with varying regulatory frameworks.
Recommendations for the U.S.
To maintain its financial hegemony amidst de-dollarization trends, the United States might consider the following strategies:
- Modernizing Financial Infrastructure: Investing in modern payment systems, such as developing a digital dollar, can enhance the efficiency and appeal of the U.S. currency in international markets. However, recent policy decisions, like the executive order banning the development of a digital dollar, may hinder progress in this area.
- Fostering International Collaboration: Building and maintaining strong economic partnerships can encourage continued use of the dollar in global trade. Diplomatic efforts should focus on reinforcing alliances and addressing the concerns of emerging economies.
- Prudent Use of Sanctions: While sanctions are a tool of foreign policy, overreliance can incentivize countries to seek alternatives to the dollar. A balanced approach that considers long-term geopolitical implications is advisable.
By proactively addressing the challenges and opportunities presented by de-dollarization, policymakers and businesses can better navigate the shifting tides of the global financial landscape.
Wrap Up: The Inevitability of Financial Multipolarity
The global financial landscape is undergoing a significant transformation as nations actively pursue de-dollarization strategies. This movement is driven by a desire to mitigate the risks associated with over-reliance on the U.S. dollar and to establish a more balanced and resilient international monetary system.
Recent initiatives, such as the BRICS nations exploring alternative payment systems and the increasing adoption of local currencies in bilateral trade agreements, underscore a collective shift towards financial multipolarity. These efforts aim to reduce the dominance of the dollar in global trade and finance, thereby diminishing the leverage of U.S. economic sanctions and influence.
However, the path to a multipolar financial system is fraught with challenges. Alternative currencies currently lack the liquidity, stability, and widespread acceptance that the dollar enjoys. Building the necessary financial infrastructure, fostering trust among international partners, and achieving policy coordination are complex endeavors that will require time and concerted effort.
For policymakers and businesses, this evolving landscape necessitates strategic foresight. Diversifying currency reserves, investing in alternative payment systems, and developing robust risk management frameworks will be crucial steps in adapting to a more decentralized financial environment.
In conclusion, while the U.S. dollar is likely to remain a central pillar of the global financial system in the near term, the momentum towards de-dollarization indicates an irreversible trend towards financial multipolarity.
Stakeholders across the spectrum must prepare for a future where multiple currencies play significant roles in international trade and finance, reflecting a more distributed and equitable economic order.