The Chornobyl Nuclear Risk 2026 escalated to a critical level on January 20, as Russian missiles once again plunged the world’s most infamous nuclear site into darkness. Following a massive aerial bombardment of Ukraine’s energy backbone, the Chornobyl Nuclear Power Plant (ChNPP) lost its connection to the national grid, the second blackout in just over a week.
Although the reactors are decommissioned, the site is far from dormant; it requires constant electricity to cool over 20,000 spent fuel assemblies. With the grid severed, the plant was forced to rely on emergency diesel generators, leaving safety dependent on a finite fuel supply.
This analysis dissects the anatomy of these calculated strikes, exposing the thinning margins of Ukraine’s nuclear safety and the brutal reality of a weaponized winter.
The ‘Winter Siege’: A Dual Crisis
As the lights flickered and died in the Exclusion Zone, forcing safety systems onto emergency diesel generators, a parallel catastrophe unfolded in the capital. Kyiv, already battered by weeks of relentless assaults, entered a new phase of what locals are calling the “Winter Siege.” Over 5,600 high-rise buildings lost heating in sub-zero temperatures, leaving hundreds of thousands of civilians to face the biting frost in their own homes.
This dual crisis, nuclear brinkmanship at Chornobyl and a humanitarian freeze in Kyiv, marks a sinister evolution in the war’s tactics. While Russian officials dismiss the outages as minor technicalities and accuse the West of alarmism, the physics of nuclear safety tells a different story. With the New Safe Confinement structure already compromised by a drone strike in 2025, the margin for error at Chornobyl has vanished.
The January 20 Strike: Anatomy of the Attack
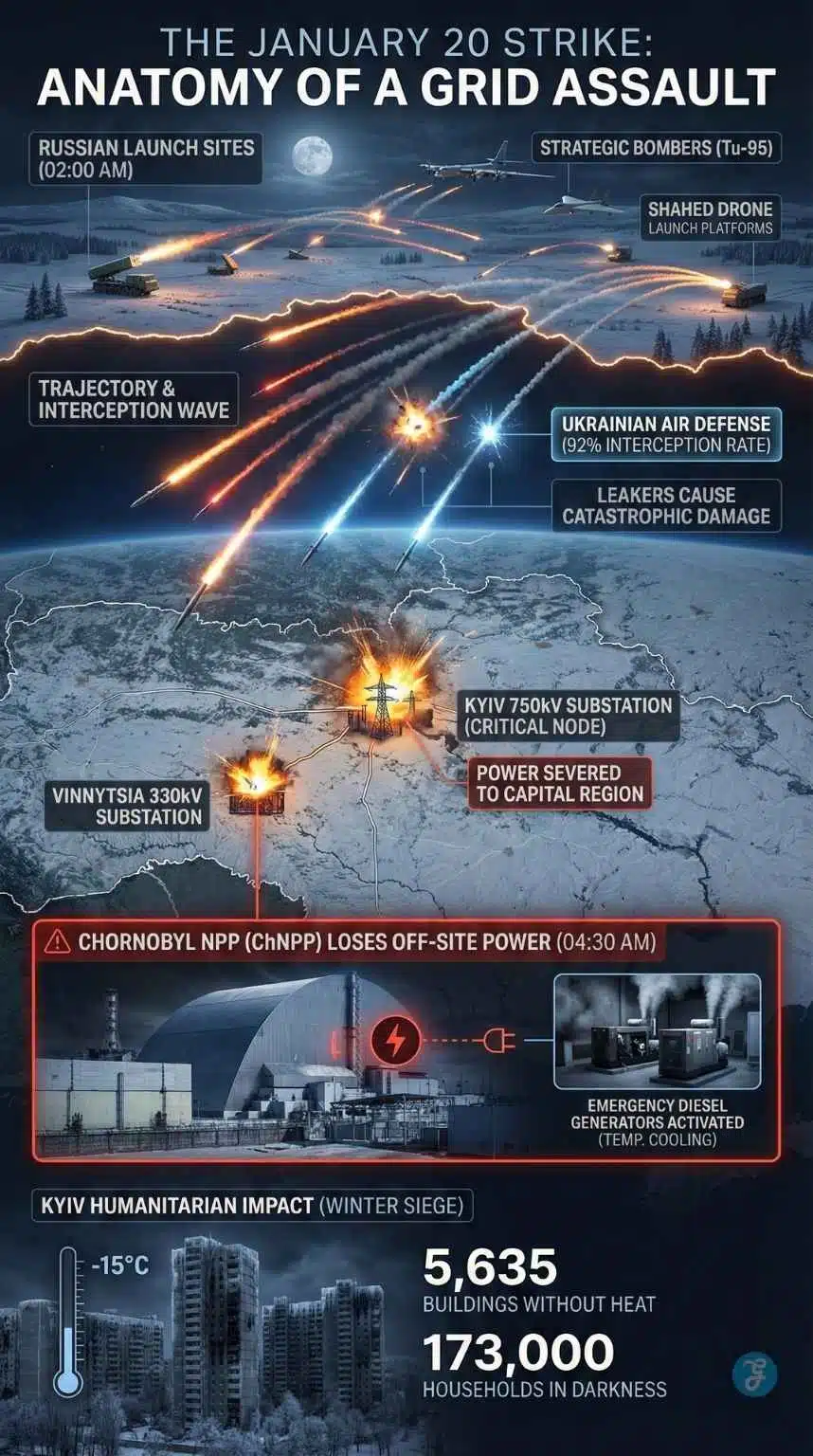
The assault began in the early hours of January 20, 2026, under the cover of a pitch-black winter night. Ukrainian air defense systems were alerted to the launch of strategic bombers from deep within Russian territory, followed by waves of Shahed loitering munitions launching from the north and south.
A Calculated Blitz on the Grid
Unlike general terror bombing, this attack was precise, technical, and devastatingly effective. The primary targets were not the power plants themselves, but the 750kV and 330kV high-voltage substations that form the “nervous system” of Ukraine’s energy grid. By severing these nodes, Russian forces aimed to fragment the unified energy system into isolated islands, making it impossible to balance loads or transmit power from generation sites to consumers.
Between 02:00 AM and 06:00 AM, multiple impacts were recorded across the Kyiv, Zhytomyr, and Vinnytsia regions. While Ukraine’s air defenses reported a high interception rate—shooting down nearly 92% of incoming threats—the “leakers” (missiles that bypassed defenses) and falling debris caused catastrophic damage to the designated substations.
Chornobyl Goes Dark
At approximately 04:30 AM, the control room at the Chornobyl Nuclear Power Plant received the critical alarm: “Loss of Off-Site Power.” The high-voltage lines supplying the plant had been severed by a strike on a regional substation.
- Immediate Consequence: The plant’s lights went out. The hum of the grid connection ceased.
- Emergency Protocol: Within seconds, the site’s emergency diesel generators roared to life. These massive engines are the last line of defense, designed to power the pumps that circulate water through the spent fuel pools. Without this circulation, the water would eventually heat up and boil off, exposing the fuel rods and releasing radioactive isotopes into the atmosphere.
- The Clock: While the generators functioned correctly, they represent a temporary fix. The site typically holds enough diesel fuel for 10 to 15 days of operation. Every hour on generator power is an hour closer to a potential failure point, mechanical breakdown, fuel shortage, or a subsequent strike on the fuel tanks themselves.
Power was eventually restored by Ukrenergo engineers by the evening of January 20, but the psychological and technical damage was done. The grid had proven fragile, and the reliability of external power, a fundamental requirement for nuclear safety, could no longer be guaranteed.
Deep Dive: The Compounding Nuclear Danger
To understand why a power outage at a decommissioned plant matters, one must look beyond the common misconception that “shut down” means “safe.” The Chornobyl Nuclear Risk 2026 narrative is driven by two critical factors: the physics of decay heat and the physical degradation of the site’s protective structures.
Why Decommissioned Fuel is Still Deadly
The Chornobyl reactors (Units 1, 2, and 3) are no longer generating electricity, but they are not empty. The site houses the Interim Spent Fuel Storage Facility (ISF-1) and the newer ISF-2, containing over 21,000 spent fuel assemblies.
Even years after removal from a reactor, nuclear fuel continues to generate significant heat through radioactive decay. This “decay heat” must be constantly removed.
- Active Cooling: The storage pools rely on electric pumps to circulate water.
- The Danger Zone: If power fails and generators die, the water stops moving. It begins to heat up. If the water boils away, the zirconium cladding on the fuel rods can oxidize, releasing explosive hydrogen gas and radioactive volatiles. This is the same mechanism that caused the Fukushima disaster, albeit on a different timeline and scale.
The Spectre of February 2025: A Compromised Shield
The risk of a radiological release is exponentially higher in 2026 than it was at the war’s start because the physical containment is damaged. We must revisit the critical incident of February 14, 2025.
On that date, a Russian Shahed drone struck the New Safe Confinement (NSC), the giant, gleaming arch that slid over the destroyed Reactor 4 in 2016. The strike was not a glancing blow; it breached the structure.
- The Damage: Specialists reported a hole exceeding 500 square feet, penetrating both the outer and inner cladding of the arch.
- The Consequence: The IAEA and Ukrainian State Nuclear Regulatory Inspectorate confirmed that the NSC had “lost its primary safety function.” The arch was designed to maintain a negative-pressure environment, ensuring that radioactive dust from the ruined reactor inside could not escape. With a gaping hole, that hermetic seal is broken.
The Cumulative Nightmare
Combine these two facts below:
- Broken Shield: The containment structure is leaking.
- Unstable Cooling: The cooling systems are relying on fragile diesel backups.
If a power failure leads to a fire or hydrogen explosion in the spent fuel pools, or if another missile disturbs the radioactive dust inside the sarcophagus, there is no longer a sealed dome to keep the fallout contained. The “defense in depth” strategy has been stripped away, layer by layer, until only luck and diesel fuel remain.
The Humanitarian Catastrophe: Kyiv’s ‘Winter Siege’
While Chornobyl represents a silent, invisible threat, the impact of the January 20 strikes on Kyiv was visceral, immediate, and freezing. The targeting of substations did not just cut power; it crippled the city’s district heating systems, which rely on electric pumps to push hot water through miles of pipes.
The Statistics of Cold
By the afternoon of January 20, Kyiv Mayor Vitali Klitschko confirmed the scale of the disaster: 5,635 high-rise residential buildings had lost heat.
- The Context: This outage occurred as ambient temperatures in the capital dropped to between -10°C and -15°C (14°F to 5°F).
- The “Yo-Yo” Effect: The psychological toll is immense. City officials noted that nearly 80% of these buildings had only just regained heating stability following the previous wave of attacks on January 9. The populace is trapped in a cycle of restoration and destruction, never allowing homes to retain thermal mass.
Infrastructure Collapse: Water and Power
The strikes created a cascading failure across municipal services:
- Electricity: 173,000 households in Kyiv City were plunged into darkness. For many, this meant no light, no internet, and no way to cook food (as many high-rises are purely electric).
- Water Crisis on the Left Bank: The Desnianskyi and Dniprovskyi districts experienced a critical drop in water pressure. Without electricity to drive the booster pumps, water could not reach the upper floors of apartment blocks. Residents were seen melting snow or queuing at communal wells, scenes reminiscent of the 1940s, not the 2020s.
Survival Mode
Kyiv has transformed into a fortress of survival. “Points of Invincibility”, tents equipped with generators, Starlink internet, and heaters, have become overcrowded hubs of life. Hospitals are operating on backup generators, prioritizing intensive care units and operating theaters while reducing lighting in corridors to save fuel. The city is functioning, but it is brittle. Every new air raid siren carries the threat of a total systemic collapse.
The Logistics of Repair: A Losing Race
The terror of the January 20 strikes lies not just in the immediate destruction, but in the timeline of recovery. While a missile takes minutes to destroy a high-voltage autotransformer, building a replacement takes six to twelve months.
According to data released by Ukraine’s Economy Ministry on January 20, the country has lost 8.5 GW of generating capacity since October 2025. The specific bottleneck is the 750kV equipment, massive, custom-built units that weigh hundreds of tons.
- The “Soviet” Problem: Ukraine’s grid relies on Soviet-standard specifications, which differ from European equipment. With domestic stocks exhausted, DTEK and Ukrenergo are scouring Africa and the Middle East for compatible second-hand units.
- The Cost: Economy Minister Oleksii Sobolev stated in Davos that urgent needs have hit $1 billion. The destruction is outpacing the funding; while repairs are attempted 24/7, the sheer deficit of hardware means many substations are being patched with “cannibalized” parts rather than fully restored.
- The Vulnerability: Until these massive transformers are replaced, the grid remains in a fragile “emergency mode,” unable to reroute power effectively if another line fails.
Voices from the Zero Line
Statistics about gigawatts often obscure the human reality. On the ground in Kyiv, the “Winter Siege” is measured in layers of blankets and the fading hope of the elderly.
Raisa Derhachova, an 89-year-old resident of Kyiv’s Desnianskyi district, described the terrifying familiarity of the cold to reporters on January 16:
“We survived World War II, and now this terrible war is upon us. Of course, it is hard to survive this… this terrifying cold. I play the piano sometimes just to keep my fingers moving.”
In the Obolon district, Zinaida Hlyha, 76, has resorted to heating water on a camping gas stove to fill bottles, which she places in her bed to survive the -15°C nights. Her stoicism reflects a hardening national mood:
“It is hard, but if you imagine what our guys in the trenches are going through now, you have to endure. What can you do? This is war.”
Meanwhile, UNICEF representatives reported seeing families “stuffing soft toys into windows” to block drafts, a desperate insulation tactic as glass remains shattered in thousands of homes.
The Hidden Front: Toxic Air and Mental Scars
Beyond the cold, the blackouts are creating invisible health crises that will outlast the winter.
- The Smog of Survival: With the centralized grid failing, Kyiv has turned into a city of diesel engines. Thousands of generators running simultaneously have degraded air quality, pushing PM2.5 levels into the “Unhealthy” range in dense residential blocks. Residents walking near “Points of Invincibility” report choking fumes, a localized environmental disaster that risks spiking respiratory illnesses among children and the elderly.
- The “Constant Backdrop” of Trauma: Mental health professionals warn that the population has moved beyond acute stress into chronic exhaustion. A report by Malteser International in mid-January noted a rise in “sleep disorders and self-reproach” among civilians.
The Psychological Shift: “Stress is no longer an acute reaction to an explosion,” one psychologist noted. “It is the constant backdrop of life.” The uncertainty of whether the light will turn on, or if the radiator will ever get warm again erodes the psychological resilience necessary to withstand the war.
The Russian Narrative: Denial and ‘Normalization’
Despite the clear correlation between the missile strikes and the power loss at nuclear sites, the Kremlin has maintained a narrative of aggressive denial. This strategy appears designed to “normalize” nuclear risk, to make the international community numb to these events so that they no longer trigger diplomatic escalations.
“Alarmism” and “Dramatization”
The primary voice of this narrative is Mikhail Ulyanov, the Russian Permanent Representative to International Organizations in Vienna. Following the January 20 blackout, Ulyanov publicly criticized the IAEA and Western nations.
- The Quote: He dismissed the concerns as an attempt to “create the impression” of a disaster, labeling the reaction as “dramatization” of what he termed “minor power outages.”
- The Logic: The Russian argument relies on a legalistic technicality. They claim they are striking “dual-use energy infrastructure,” not the nuclear plants themselves. They argue that since a missile did not hit the reactor dome, nuclear safety conventions have not been violated.
Gaslighting on a Global Scale
This rhetoric ignores the fundamental reality of nuclear engineering: a nuclear plant is part of the grid. You cannot destroy the grid surrounding a nuclear plant without endangering the plant itself. By severing the power lines, Russia is effectively pulling the plug on the life-support systems of the reactors.
- Strategic Goal: By repeatedly causing these “near-miss” events and then dismissing them when no explosion occurs, Russia is raising the threshold for what the world considers an “emergency.” It is a form of desensitization warfare. If Chornobyl loses power five times and nothing happens, the world stops watching the sixth time, which might be the time the generators fail.
International Response and Geopolitics
The international reaction to the Chornobyl Nuclear Risk 2026 incident reflects a growing sense of impotence and frustration among global watchdogs.
The IAEA’s Dilemma
IAEA Director General Rafael Grossi issued a sharp statement, confirming that “several electrical substations vital for nuclear safety were impacted.” However, the IAEA finds itself in a bind. It has inspectors on the ground at all Ukrainian NPPs, but its mandate is monitoring, not enforcement. Grossi can report the danger, but he cannot stop the missiles. The agency’s calls for a “safety zone” around the plants have been effectively ignored by Moscow, which views the energy grid as a legitimate military target regardless of what it powers.
The “Red Line” Debate
Western allies, including the US and EU, have condemned the strikes. UN Human Rights Chief Volker Türk labeled them “cruel” and a potential breach of international humanitarian law. Yet, there is a palpable hesitation to define these grid attacks as a “nuclear red line.”
- The Fear: Declaring that an attack on a grid connected to a nuclear plant is equivalent to a nuclear attack could trigger Article 5 or require direct NATO intervention, a step Western powers are desperate to avoid.
- The Result: Russia exploits this gray zone. They strike the substation next to the plant, causing the same functional damage as a direct hit, but without crossing the diplomatic threshold of attacking the reactor.
The Energy War Strategy
Geopolitically, these strikes are part of a broader attrition strategy for 2026. With the front lines largely static, Russia is targeting Ukraine’s economic viability. By making the major cities uninhabitable during winter and forcing the industrial base to shut down due to power rationing, the Kremlin hopes to trigger a wave of refugees and internal social unrest that will force Kyiv to the negotiating table on unfavorable terms.
Future Outlook: The Grid vs. The Atom
As we look toward the remainder of the winter, two scenarios emerge for Ukraine’s nuclear and energy security.
Scenario A: Resilience and Islanding
Ukraine’s energy engineers are performing miracles daily. The strategy of “islanding”, isolating nuclear plants from the main grid to power local regions independently, is being refined. If Ukraine can acquire more air defense systems (specifically Patriot and IRIS-T batteries) to protect the key 750kV nodes, they may be able to limp through the winter with rolling blackouts but no nuclear accidents.
Scenario B: The Total Blackout
The nightmare scenario involves a synchronized strike that severs the 750kV backbone completely, causing a “system split.” In this scenario, all operating nuclear plants (Rivne, Khmelnytskyi, South Ukraine) would trip offline simultaneously because there is no grid to accept their electricity. This would leave the entire country running on diesel generators. If this outage lasts longer than a week, exceeding the fuel reserves of the hospitals and nuclear sites, the humanitarian crisis becomes a catastrophe, and the nuclear risk becomes a probability.
Final Thought: Running on Borrowed Time
The January 20 strikes on Chornobyl serve as a stark warning: the safety of Europe’s nuclear heritage is currently hanging by a thread of copper wire. The “Winter Siege” of Kyiv is not just about cold homes; it is about the systematic dismantling of the safety margins that keep the atom in check. Russia has placed a bet that it can destroy the grid without breaking the nuclear plants, but with every missile, the odds of a tragic miscalculation shorten.