Many shippers face high costs and delays on Brazil’s roads. Brazil has one of the worst road infrastructure ratings, and traffic laws are hard to follow. This post gives smart fixes, from delivery drones and digital transformation to warehouse automation and better fleet management.
Keep reading.
Key Takeaways
- The World Economic Forum ranks Brazil 102 of 140 for its 2.7 million km of roads, and 65% of freight moves by truck, driving up fuel and time costs.
- Diesel takes one-third of a truck’s budget, and fleet upkeep rose more than 20% in the last decade because of bad roads and local tax rules.
- The sector lacks 30% of its technicians, so the IBP trains 1,200 managers a year and e-learning tools help bridge the skills gap.
- Many carriers still lack GPS, route software, and real-time tracking, but AI tools and inspection drones cut idle time and speed deliveries.
- Public-private partnerships upgrade the Carajás rail line, dredge rivers, and add smart ports in São Paulo. They also build green hubs to cut shipping costs.
Infrastructure Limitations
Brazil has 2.7 million kilometers of roads but ranks 102 out of 140 for road quality in the World Economic Forum report. Ruts and potholes slow trucks and raise transport costs. Long trips over rough, scarred asphalt cost extra fuel.
Wide geography from Amazonas to the southeast region drains budgets fast. Lean maintenance leaves crumbling bridges at risk. Drivers dodge gaping holes like a real life video game.
Public transport systems in São Paulo suffer under stress. Rapid bus lanes still clog in traffic jams. Ports and air transport links lack sync so supply chains stall. The IBGE and central bank warn that sluggish land transport drags down brazil’s economy.
Firms feel the pinch in shipping costs and hold more inventory. Safety signs and seat belt checks remain scarce outside urban hubs.
Dependence on Road Transportation
More than 65% of Brazilian freight moves on highways. 18-wheelers pound the pavement from São Paulo to Manaus. Shippers jam loads onto crowded lanes. Trucks face rough road conditions and deep potholes.
Weak road infrastructure drags down supply chain management. The National Logistics Plan spares little for rail upgrades. The Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics warns that infrastructure investment lags behind demand.
Cargo owners lean heavily on highways. This heavy dependence trips up growth in the Brazilian market.
Big cities groan under traffic congestion. Big rigs mingle with cars and buses in gridlock. Traffic accidents spike on busy routes. The nation logs one of the highest road traffic fatality rates on the planet.
Police strain to enforce road safety amid a sea of vehicles. Intelligent transportation systems buck under sheer volume. Bus rapid transit lines often feel the pinch from freight snarls.
High accident counts drive up insurance costs. This tangled web saps profits and stalls economic recovery.
Rising Operational Costs
Recent years saw high fuel costs. Global oil prices, currency exchange rates, and local tax policies drive pump prices. Truckers spend a third of budgets on diesel. High diesel costs sting like a paper cut, hitting shipping across Brazil’s roads.
Fleets add GPS devices and connected sensors to cut waste. A cloud TMS plans routes around poor road conditions. Infrastructure investment lags behind demand on highways in South America.
Fleet upkeep rose more than 20 percent in the last decade. Rough terrain in the north region of Brazil forces early part swaps. Some logistic firms test drones and scanners to spot wear before breakdowns.
That tactic trims downtime, but locks in tech fees. Brazil’s formal economy pays extra for labour laws and environmental rules. Operations in the Brazilian market now rank among the costliest in a global logistics overview.
These costs now weigh on the country’s share of nominal GDP.
Shortage of Skilled Professionals
Companies across the Brazilian logistics sector face a significant shortage of skilled professionals, with over 30% of technician roles unfilled. A team without training runs like a truck without gas.
It hurts efficiency on highways and raises safety risks during transporting. Logistics firms cannot adopt new AI solutions or apply supply chain management methods without trained staff.
Government, labor unions, and private firms must invest in vocational training and capacity building to close this gap.
A simple e learning platform can boost learning, and a learning management system can track progress. The Brazilian economy relies on road infrastructure, and it falters when people lack skills.
A solid training program in information and communication technology can cut delays and lower the unemployment rate. Logistics leaders use on the job coaching, and the IBP sponsors workshops in São Paulo to train 1,200 managers each year.
Technology Gaps in Logistics
High costs block many carriers in the brazilian market from buying route optimization software and GPS tracking devices. Weak road infrastructure, paired with bad road conditions, raises operating risks and spoils data signals.
Federal austerity measures limit infrastructure investment. Carriers face gaps in infrastructure and underemployment in remote areas.
Real-time shipment tracking tools bring more transparency and boost productivity. Telematics and preventive maintenance spot engine issues early, cut expensive repairs. This approach fits SDGs 9 and industry innovation and infrastructure goals for economic growth.
Firms drop fuel waste and improve passenger safety. They meet environmental regulations and tight compliance rules. That adds value to globalization and exports.
Regulatory Complexities
Brazil requires permits from ANVISA and the labour ministry. Logistics players follow traffic laws, vehicle safety rules like seat belts, and environmental rules to protect the Amazon rainforest.
These complex regulations add time, inflate costs, and slow deliveries. ERP software helps track compliance, but it needs heavy setup. SISCOMEX import system can take weeks for customs clearance.
Firms in São Paulo and Rio Branco staff legal teams to handle labour laws and environmental norms. Brazil’s public debt limits infrastructure investment in ports and roads.
Rules carry hefty fines for non-compliance and risk reputational harm. Brazil’s economy can stall under this burden. Carriers worry about penalties and brand damage in the brazilian market.
Industry groups push for Port Community System upgrades at major ports. Private firms join cooperatives to cut bureaucratic steps. They train staff in labour rules, track vehicle conditions, and audit road transport records.
Digital platforms speed approvals and cut red tape.
Innovations in Infrastructure Development
New projects reshape Brazil’s infrastructure. They power trade and cut costs.
- Locomotive lines around Estrada de Ferro Carajás get new tracks and bridges. This infrastructure investment lifts load limits, speeds shipments across the Amazonian rainforest, seeds job creation and boosts Brazil’s economy.
- Waterway channels get dredged to expand barge routes. This shift eases overworked roads, cuts costs in the Brazilian market and smooths key economic activities.
- Major ports in the city of São Paulo and Brasília get smarter cranes and digital docks. Public-private partnerships drive these upgrades, trim loading times and slash fuel use.
- Key highways receive fresh asphalt and tighter safety regulations. New deals enforce labour laws for construction crews, cut distracted driving risks and boost long haul efficiency.
- Freight convoys gain GPS tracking and closed-circuit cameras. This security layer thwarts thieves, cuts robbery losses and pads the gross domestic product by keeping trucks on the road.
- Logistics firms plug route optimization software into their portal. This tool routes around snarls, trims journey duration and lowers fuel burn across the network.
- Facilities link road, rail and air transport under one roof. This multimodal hub nods to industry, innovation and infrastructure goals, speeds cargo shifts and cuts handling time.
- Inspection drones scan bridges and tunnels and send live feeds to a secure portal. They spot cracks fast, tackle infrastructure challenges and trim repair costs.
Adoption of Digital Logistics Platforms
Companies adopt remote tracking, route planning tools, and data analytics. These tools track trucks and ships in real time. They cut miles and fuel costs on poor road infrastructure.
Operations adjust on the fly, like a chess player reacting to an unexpected move. The state of São Paulo sees big gains. Road conditions in rural areas get fewer delays. Users feed data to dashboards and aid calls for infrastructure investment.
A management system controls stock levels. Warehouse staff scan barcodes and update counts with one click.
Real time shipment tracking shines light into dark corners of the supply chain. Dropoffs Platform shows each box on a live map. Small firms in the brazilian market slash late delivery rates.
Data flow spans trucks, trains, and air transport. Planners set new routes in minutes not hours. An alert pings via email when a hold-up hits. Managers spot a delay at a glance. They fix problems faster with clear insight.
Integration of Green and Sustainable Practices
Green shifts in logistics cut fuel bills. This move boosts Brazil’s economy.
- Fleet managers use IoT sensors to spot idle time, cutting wasted gas that can reach half gallon per hour.
- Preventive maintenance boosts gas mileage by 4 percent on average, per FuelEconomy.gov data.
- Hybrid and electric vehicles trim fuel spend, helping to mitigate rising fuel costs.
- Solar panels on warehouses power lights and charge automated machines, lowering grid bills.
- Satellite navigation steers clear of poor road conditions, slashing idle time and wear.
- Multimodal green hubs link roads, rails and waterways, easing infrastructure challenges.
- Public infrastructure investments add charging stations along highways, beefing up road infrastructure.
- Training drivers under updated labour laws spreads eco habits across the Brazilian market.
- Small jet operators in air transport test biofuels to cut carbon use.
Improvements in Multimodal Transportation Systems
Brazil ramps up infrastructure investment along railways, waterways, and port infrastructure. New tracks link São Paulo to Santos, easing strain on poor road infrastructure and bad road conditions.
The international monetary fund backs some projects to bolster Brazil’s economy. Air transport hubs also get upgrades to speed high-value goods. This mix drives growth in the brazilian market.
Transport Management System (TMS) platforms and Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) tools link truck, rail, and barge schedules. Cargo rolls onto a train after a short truck haul. Barges then float south along key rivers.
This cut delays tied to infrastructure challenges. Control tower software tracks each load. Freight moves faster, road reliance falls.
Use of Artificial Intelligence in Logistics Operations
AI spots weak spots in road infrastructure. This tech uses demand sensing and supervised learning. Predictive analytics cuts delays caused by poor road conditions. Drivers find fresh routes, dodging traffic jams.
Firms save time, fuel, money, on long hauls. Stock levels sync to shifts in the brazilian market. That helps reduce the deficit in supply chains.
Major carriers test robotics, drones in air transport. Workers load small parcels in record time. WMS links to vision software for swift picks. Systems track labour laws, log driver shifts.
A TMS feeds live updates to every manager. Spam in alerts drops, thanks to smart filtering. Such a mix lifts brazil’s economy in a tight economic environment. It feels like having a digital co-pilot on each route.
Advancements in Warehouse Automation
Carrier robots zip along aisles, lifting pallets. Conveyor lines shuttle crates to packing docks in seconds. Tracking tags scan each item and feed data to a Warehouse Management System.
Cloud platforms link scanners, lights, and robots in one digital web. This shift slashes errors and speeds up delivery.
Growth in automation drives infrastructure investment across Brazil. Companies in the brazilian market invest in updated storage racks and high bay lights. They align upgrades with labour laws and train staff to run apps on tablets.
Such moves cut errors and boost safety. Next steps may link shelves to drones flown by air transport for fast restock.
Implementation of Real-Time Tracking Solutions
Logistics teams in the Brazilian market add satellite positioning systems to each truck. They fit IoT sensors, too. Teams link them to route optimization software. This step cuts idle time and slashes fuel costs.
It boosts transparency and efficiency. Many outfits stream live video from road cameras at ports and hubs. They clamp down on theft and robbery risks with more surveillance. Dropoffs Logistics Management Platform ties all updates to one dashboard.
Managers watch every cargo move on cloud platforms, as if they had eyes in the sky. Alerts ping teams about delays on rough road infrastructure or blocked highways. They tweak schedules to skip trouble spots and meet labour laws on delivery hours.
The move sparks more infrastructure investment. It drives growth even under Brazil’s tough financial crises.
Encouraging Public-Private Partnerships
Public and private groups join forces to fix road infrastructure. They cut theft and speed up shipping.
- The government and transport firms fund rail track upgrades on major lines, tackling infrastructure challenges and lowering delays.
- Private firms invest in cargo lifts and storage sites at ports, boosting capacity and cutting cargo wait times.
- Partners install surveillance systems along road routes to fight theft and improve security.
- Private security squads patrol key hubs, so remote working staff can track loads safely.
- States slash permit times via joint committees, trimming red tape in labour laws and border checks.
- Firms and authorities co-build water terminals and channel locks, shifting cargo to waterways and cutting road wear.
- Corporations back training centers for quality education, tackling the vacancy of skilled staff.
- Alliances fund apps for real-time tracking along routes, so shippers in the brazilian market can follow loads on maps.
- Teams test drone trips for last-mile links to islands like madeira, proving air transport gains.
- Stakeholders raise funds for road repairs in high traffic zones, easing poor road conditions.
- Coalitions share cost on solar panels at warehouses, boosting green practice in storage sites.
- Cities and firms draw up safety drills and patrol plans to guard cargo, raising ethical business moves.
- Joint bodies publish annual reviews to measure gains in infrastructure investment and service speed.
- Public agencies and startups pilot smart systems in freight hubs, trimming idle hours in docks.
- Leaders secure private debt for track extensions, pushing longer routes to link remote areas.
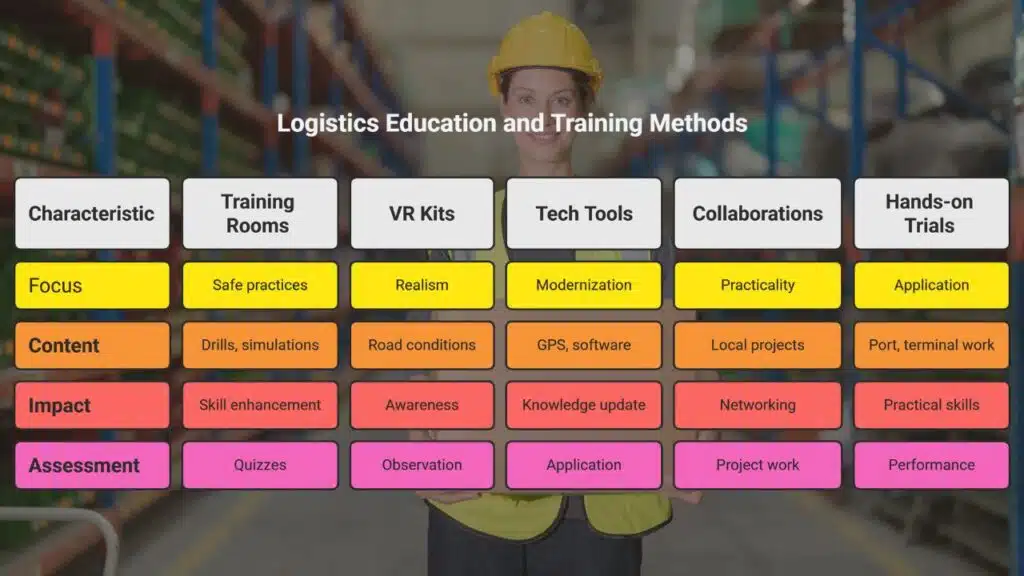
Boosting Education and Training for Logistics Professionals
Trainers must adapt to Brazil’s vast regions, use clear language. Over 69% of drivers admit to texting at the wheel, so courses stress distraction drills. Simulated sessions in training rooms let students practice safe turns, stops, hazard checks.
VR kits for vehicles mimic real road infrastructure, traffic, weather shifts. Learners see the impact of poor road conditions, drunk driving, phone distractions. Statistics show drunk driving causes about 25% of fatal crashes.
Tech tools like GPS tracking, warehouse system software, supply flow maps keep lessons fresh. Lean Logistics fits beneath these modules. Supply Chain Optimization comes next.
Collaborations with local firms link students to real projects. Instructors cover labour laws, cargo handling, network planning in the brazilian market. Workshops on air transport, customs rules, intellectual property rules ease trade steps.
Hands-on trials cut the gap from classroom to port, road terminal. Funding from infrastructure investment boosts labs. Cookies and short quizzes gauge knowledge spikes. Active sessions prevent yawns on long days.
Strengthening Compliance and Safety Standards
Brazil enforces road rules, safety standards, green laws, and labour laws. Audits eat time and budgets, and they stall infrastructure investment in the brazilian market. Poor road infrastructure deepens risks, and punishing surfaces test every tire.
Seat belt use stays low on highways; only half of backseat folks click belts, and eighty percent fasten up front.
Fleet operators install vehicle sensors and fleet tracking gear, they watch engine heat, tire health, and driver rest times. Preventive upkeep flags worn brakes early, stops bigger failures, and trims repair bills.
Logistics firms in air transport back this job, too; pilots run quick gear checks before each flight.
Takeaways
Logistics teams face hard roads, yet they find bright spots. New roads meet old trucks, so they test tracking systems and fuel monitoring tools. Smart platforms cut delays, like a magic wand for planners.
Artificial Intelligence helps spot storms in supply chain management. Warehouse Automation speeds orders, like clockwork. Blockchain locks in safe deals, and teams free more time. This scene hums with change, and the journey stays bright.
FAQs
1. What are the main road infrastructure challenges in Brazil?
The roads feel like a roller coaster ride. Bumps and cracks slow vehicles. Rough road conditions and tight lanes raise fuel costs and risk damage. Old bridges and worn out lanes cause sudden stops. It takes big infrastructure investment to smooth the ride.
2. How do labour laws affect day to day logistics?
Brazil has strict labour laws that cap work time and add costs. Rest rules for vehicle operators feel like a safety net, but they add more breaks. Shift plans need careful timing to avoid fines. Firms must adapt fast or face steep fees.
3. Why does infrastructure investment matter in logistics?
Fresh funds can fix roads and widen routes. It can build new hubs and boost tech use. Better networks speed transport, cut waste, and spark growth.
4. What smart moves help beat these hurdles?
Some companies use flying machines to skip rough paths. Others share warehouse space to cut rent bills. They train teams in safe driving. They track trips with data to dodge delays. These ideas do more than patch cracks, they change the game.