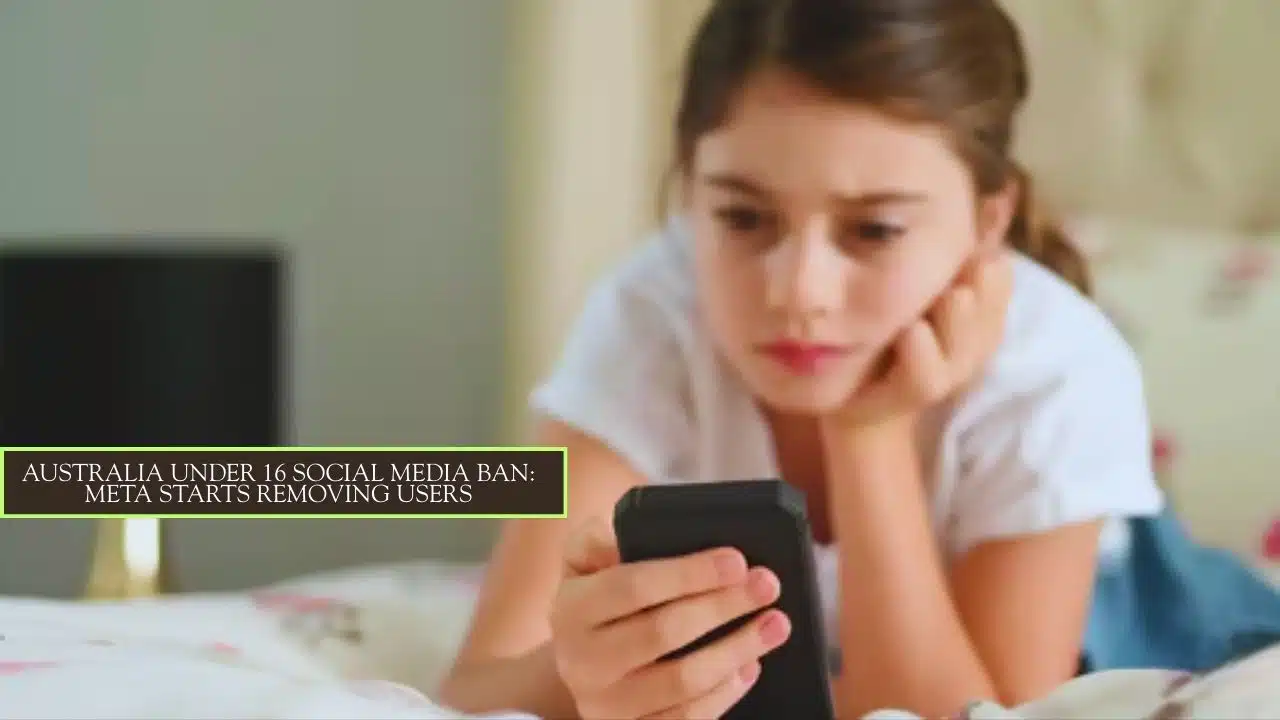
Meta has begun removing Australian users under the age of 16 from its platforms Instagram, Facebook, and Threads starting December 4, 2025. This move comes ahead of Australia’s new groundbreaking legislation that will ban children under 16 from holding social media accounts, which officially takes effect on December 10. Meta has estimated that about 350,000 Instagram accounts and 150,000 Facebook accounts belonging to under-16 users in Australia will be deactivated as part of this compliance effort. The company is providing users with the opportunity to download and save their content before any account removal takes place.
Furthermore, users who contest their age being incorrectly logged as under 16 can complete an age verification process via Meta’s partnership with Yoti, an age verification service that requires video selfies or government-issued identification to confirm age. Once a user reaches 16, they will be able to regain access to their accounts and content on these platforms.
Australia’s Social Media Ban and Legislation Overview
This law is a first of its kind globally and represents Australia’s resolve to protect children and teenagers from potential harms associated with social media use. The legislation, which takes effect December 10, requires social media platforms to take “reasonable steps” to prevent children under 16 from creating or maintaining accounts on their services. Failure to comply can result in severe penalties for platforms, including fines of up to A$49.5 million (approximately US$33 million). The law covers not only Meta’s platforms but also includes major players such as TikTok, YouTube, Snapchat, X (formerly Twitter), Reddit, Kick, Threads, and Twitch. The Australian eSafety Commissioner, an independent government agency responsible for online safety, is tasked with enforcing the ban.
On December 11, one day after the law’s commencement date, the Commissioner will issue notices to the affected platforms seeking detailed information about the accounts removed under the new legislation. These platforms are also required to provide monthly updates for six months following the initial notice to prove ongoing compliance with the ban.
How Platforms Are Responding to the Ban?
Meta’s early action in removing under-16 users ahead of the ban is part of its effort to comply and avoid significant penalties. At the same time, other platforms have also revealed their strategies to align with the new rules. YouTube, owned by Google, has announced that starting December 10, users identified as under 16 will be automatically signed out of their accounts. However, these users will still be able to watch videos on the platform without signing in. YouTube has publicly criticized the legislation as “rushed” and argued that it may make Australia’s children less safe online. The company points out that account holders have access to parental controls, which might no longer be available to children who are forced off their accounts. In response to these concerns, Australia’s Communications Minister Anika Wells dismissed YouTube’s warnings as “weird” and insisted that if YouTube acknowledges the existence of unsafe or inappropriate content on its platform for age-restricted users, it is incumbent upon YouTube, not the government, to fix those safety issues.
In addition to Meta and YouTube, other companies like Snapchat, X, TikTok, and Twitch are making preparations to comply with the ban, although specific details on their approaches vary. This marks a significant change for many young Australians who have grown up using social media as a regular and important part of their social interactions.
Government Rationale and Concerns Raised
The Australian government has been very vocal about the motivations behind the new social media law. Communications Minister Anika Wells referenced concerns about “predatory algorithms,” which were described by the inventor of the algorithmic features themselves as being akin to “behavioural cocaine.” The goal is to shield “Generation Alpha”—children born from 2010 onwards—from these manipulative content delivery systems that encourage excessive use and potential psychological harm. Wells openly acknowledged that it is unlikely that all children will stop using social media immediately on December 10. However, she emphasized that any company found to be still allowing under-16s to use their platforms post-deadline would be breaking the law and face significant consequences.
Despite these aims, the law has attracted criticism from various quarters. Privacy advocates have expressed concern about the mass data collection necessary to verify age online. Senator David Shoebridge highlighted the seriousness of the issue, warning that approximately 2.4 million young Australians could be locked out of social media accounts, which might have adverse impacts on their mental health and social development. There is also ongoing legal pushback such as the Digital Freedom Project seeking to obtain a High Court injunction to halt the legislation’s implementation. Critics argue that while protection of minors is crucial, the approach taken by the Australian government risks unintended consequences such as exclusion, privacy invasion, and disruption of social connections.
Meta’s Age Verification System and Recommendations
Meta has implemented a sophisticated age verification system known as Yoti, which is designed to balance privacy with compliance. This system allows users to verify their age through uploading government-issued identification, taking a video selfie, or even via social vouching mechanisms. The use of artificial intelligence helps detect fake IDs or attempts to circumvent the system by users who are actually underage. Meta argues that instead of placing the entire responsibility on social media platforms to verify the ages of users post-signup, app stores themselves should perform age verification at the point of app download. This, Meta claims, would create a more effective, uniform, and privacy-protecting approach that could reduce the burden on social media companies while enhancing protections for children across all apps.
Impact and Broader Implications
Australia’s decision to enforce a legal age limit of 16 for social media use sets a global precedent in digital regulation, stirring debate on how best to protect children online while respecting user rights and digital freedoms. It poses significant challenges for tech companies in balancing regulatory compliance, user safety, and privacy issues. The law forces platforms to rethink how they manage young users, parental controls, and content moderation. As the ban takes effect, the coming months will likely reveal the practical impacts on young users, platform policies, and broader social dynamics in Australia—and perhaps beyond as other countries consider similar laws.