Learning online can be hard for disabled students. Many platforms are not easy to use or lack proper tools, like screen readers or closed captions. This makes it unfair and limits access to education.
Accessibility-First Platforms For Disabled Learners fix this problem. These platforms make sure everyone can learn, no matter their needs. They follow web accessibility guidelines and include helpful features.
In this blog, you will find five of the best platforms designed with accessibility in mind. Each platform has unique tools to help learners succeed.
Keep reading to discover solutions that truly work!
Defining Accessibility-First in Learning Environments
Accessibility-first means designing learning spaces for everyone, including those with disabilities. It ensures students with low vision, hearing impairments, or learning disabilities can access digital resources easily.
Features like screen readers and alt text help users interact with content. Closed captions support the hard-of-hearing. Tools that follow WCAG make platforms compliant and inclusive.
This approach prioritizes equal opportunities in education through accessible design and assistive technologies.
The Critical Role of Accessibility in Educational Platforms
Accessibility ensures equal learning chances for disabled students. Platforms that follow the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) help create fair spaces online. For example, screen readers assist visually impaired students in understanding online materials.
Closed captions and transcriptions make video lessons accessible to deaf learners. These tools break barriers and provide vital support for all users, including those with disabilities.
Accessible technologies improve ease of use for everyone, not just disabled individuals. Features like keyboard navigation enable smoother interaction without a mouse—benefiting people with motor challenges or temporary injuries.
According to Section 508 of the Rehabilitation Act of 1973, public systems must ensure digital accessibility compliance, promoting inclusion nationwide. Designers can also reduce obstacles by adding alt tags to images and ensuring proper form field labeling on websites used in schools or colleges.
Web accessibility empowers every learner by removing boundaries tied to disabilities.
Key Features of Accessibility-First Learning Platforms
Accessibility-first platforms focus on assistive tools, clear designs, and flexible settings to support all users—explore their features for a smoother learning experience.
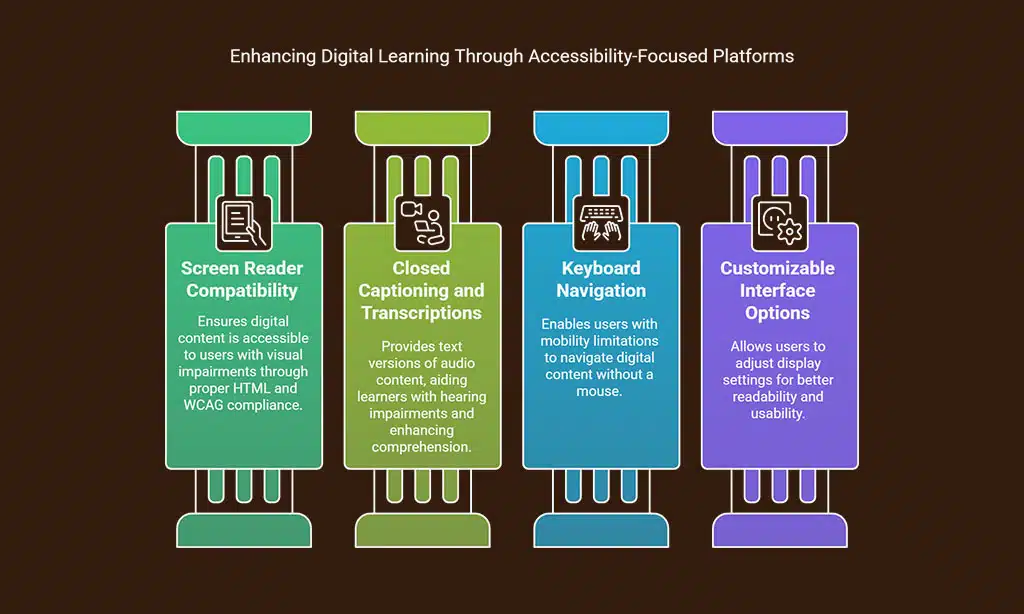
Ensuring Screen Reader Compatibility
Screen readers help people with visual impairments access digital content. Platforms must structure content for these tools to work effectively. Proper use of HTML tags, alt attributes for images, and header tags ensures clear navigation.
Websites should follow WCAG guidelines to meet accessibility standards.
Web designers must avoid using decorative images without alt text. They should also label form fields correctly for better understanding by assistive technologies. Accessible web design empowers all users and improves educational access for disabled learners.
Implementing Closed Captioning and Transcriptions
Closed captioning helps students with hearing impairments understand content. It shows spoken words as text on the screen. Transcriptions turn audio or video into readable documents.
Both tools follow web accessibility guidelines like WCAG 2.1.
These features aid learners with visual or learning disabilities too. Text-to-speech (TTS) can read transcriptions aloud for better understanding. Tools such as iOS and macOS support captions natively, making digital accessibility easier for users across platforms.
Equal access to information is a right, not a privilege.
Supporting Keyboard Navigation
Keyboard navigation helps users with limited mobility. It ensures they can move through digital content without a mouse. Platforms must support the “Tab” key to access links, buttons, and form fields.
The “Enter” or “Spacebar” keys activate features, improving usability for assistive technology tools.
Accessible websites follow WCAG standards for keyboard navigation. These guidelines ensure visuals don’t block actions for people with disabilities. Testing on browsers like Internet Explorer and systems like macOS ensures accessibility compliance is met across different devices.
Providing Customizable Interface Options
Customizable interfaces help disabled learners access content easily. These features adjust font size, screen contrast, and colors for better readability. Users with visual impairments benefit from these changes.
Form fields on accessible websites become simpler to use by adjusting stylesheets or cascading style sheets (CSS).
Platforms that meet WCAG guidelines allow users to modify settings based on their needs. Assistive technologies like virtual keyboards or mouse wheel support can also integrate smoothly with these options.
This creates an inclusive learning environment following accessibility-first principles.
Top 5 Accessibility-First Platforms for Disabled Learners
Accessible learning tools make education easier for everyone. These platforms focus on features like screen readers and keyboard shortcuts to support all users.
Exploring Moodle’s Accessibility Tools
Moodle offers tools that support accessibility compliance. It works well with screen readers and assistive technologies. This ensures students with visual impairments can access course materials easily.
Form fields in Moodle follow the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG). This helps make input areas accessible for all users.
Keyboard navigation is fully supported. Users can move through courses without a mouse, using only keys like Tab or Ctrl key. Decorative images have clear labels or are hidden from screen readers to avoid confusion.
With these features, Moodle creates inclusive designs for all learners online.
Utilizing Blackboard Ally for Enhanced Access
Blackboard Ally helps ensure accessibility compliance in online courses. It checks digital content against WCAG standards and highlights issues for improvement. This tool supports assistive technologies like screen readers and customizable interfaces, making learning materials more inclusive.
It provides alternative formats such as audio files or HTML versions of documents. Blackboard Ally also works with form fields and decorative images to enhance accessibility. Its feedback helps instructional designers create accessible websites for all learners, including those with visual impairments or learning disabilities.
Benefits of Canvas Accessibility Tools
Canvas offers tools that make learning easier for disabled students. It supports screen readers to help visually impaired users read course content. Closed captions and video transcriptions ensure access to videos for those with hearing impairments.
Keyboard navigation is available, so users can move through the platform without a mouse. Customizable settings allow learners to adjust text size, colors, or contrast based on their needs.
These features meet WCAG standards and promote inclusive design in education.
Accessibility Innovations in Microsoft Tools
Microsoft offers tools to support disabled learners. Features like screen readers ensure content is accessible for people with visual impairments. Their Narrator tool provides text-to-speech assistance, making navigation easier.
The customizable interface lets users adjust font size and colors based on their needs.
Keyboard navigation is another key feature. It allows users to move through Windows without a mouse. Closed captions are available in apps like PowerPoint and Teams, ensuring better communication during lessons or meetings.
These tools align with WCAG guidelines, promoting inclusive design for education spaces.
Coursera’s Commitment to Accessibility
Coursera builds accessible technologies to help learners with disabilities. The platform follows WCAG standards to ensure web accessibility and inclusive design. It supports screen readers, closed captions, and customizable tools for a better experience.
These features assist users with visual impairments or learning disabilities.
Courses on Coursera include transcriptions and keyboard navigation options. This helps students easily interact with content. Assistive tools empower all learners by making access equal for everyone.
Takeaways
Accessible learning platforms make education fair for everyone. They provide tools like screen readers, captions, and keyboard-friendly layouts. These features are easy to use and improve learning for all students.
Platforms like Moodle, Blackboard, and Canvas show how technology can open doors. Ask yourself—are your tools helping all learners? Start using these resources today to build a better future for disabled learners! Everyone deserves equal access to learn and grow.
FAQs
1. What does accessibility-first mean in digital platforms?
Accessibility-first means designing websites, apps, and tools to ensure they are usable for everyone, including people with disabilities. It follows guidelines like WCAG to improve web accessibility.
2. How do screen readers help disabled learners?
Screen readers read text aloud from accessible websites or mobile applications, helping users with visual impairments navigate content easily.
3. Why is keyboard navigation important for accessibility?
Keyboard navigation allows users who cannot use a mouse to move through form fields or menus using only their keyboard, making platforms more inclusive.
4. What role does the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) play?
WCAG sets rules for creating accessible technologies by focusing on features like readable text, descriptive images, and proper HTML5 coding practices.
5. How can inclusive design benefit disabled learners?
Inclusive design ensures that assistive technologies work seamlessly across operating systems like Mac OS or Windows 2000 while meeting standards set by the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA).
6. Why should developers test platforms with real users?
User testing helps identify issues in areas like privacy settings or decorative images that might not meet accessibility compliance under laws such as the Civil Rights Act of 1964.