Have you looked at your fertilizer bill or labor costs lately and felt a knot in your stomach? You aren’t the only one. Between unpredictable weather swings and the struggle to find skilled hands during harvest, growing food in the United States feels harder than ever. We used to rely on bigger machines to solve these problems, but even those require constant attention, fuel, and maintenance.
That is where the new wave of AgTech innovations comes in. We are seeing a massive shift right now. Farms are moving past “smart” tools that just beep at you and into fully autonomous systems that actually do the work for you.
In this guide, I’m going to walk you through exactly how these robots and AI systems are changing American agriculture in 2026. I’ll show you the specific tools solving labor shortages today and how they might fit into your operation.
The Evolution from Smart Farming to Autonomous Systems
Farming has traded its old toolbox for smart computers and machines that act on their own. We are moving away from tools that just tell you something is wrong to machines that fix the problem while you sleep.
Defining Smart Farming
Think of smart farming as the “notification era” of agriculture. You likely already use some of this. It involves using sensors, drones, and data analytics to keep an eye on things.
For example, a soil moisture probe from a company like Arable might send an alert to your phone saying, “Field B is thirsty.” That is helpful, but you still have to go out there and turn on the water.
Farmers use AI in agriculture to sort through this data fast. It guides decisions on watering or spraying only where needed. This helps save money on water and chemicals while protecting the environment. With these AgTech innovations, each plant can get just what it needs to grow strong.
Exploring Autonomous Systems in Agriculture
Autonomous systems take that next big step. Instead of just sending you an alert, the machine handles the task itself. Picture tractors, drones, and harvesters working on their own using computer vision, sensors, and artificial intelligence.
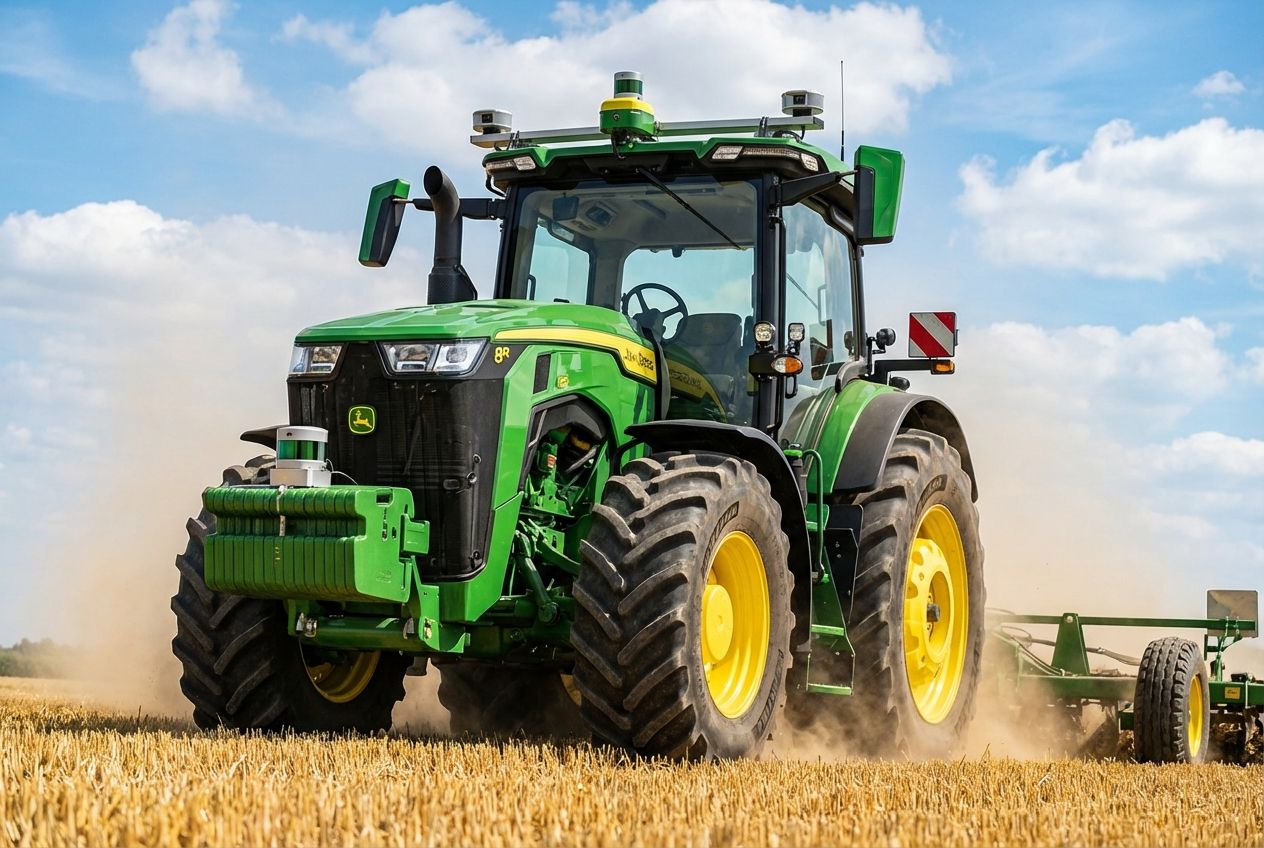
The John Deere 8R autonomous tractor is a prime example. It does not just steer itself; it uses six pairs of stereo cameras to “see” obstacles and stop if a rock or animal is in the way. You can control it entirely from a tablet while you work on something else.
Autonomous robots are not replacing farmers; they are becoming new helpers in the field that never call in sick.
These machines work differently from the old iron:
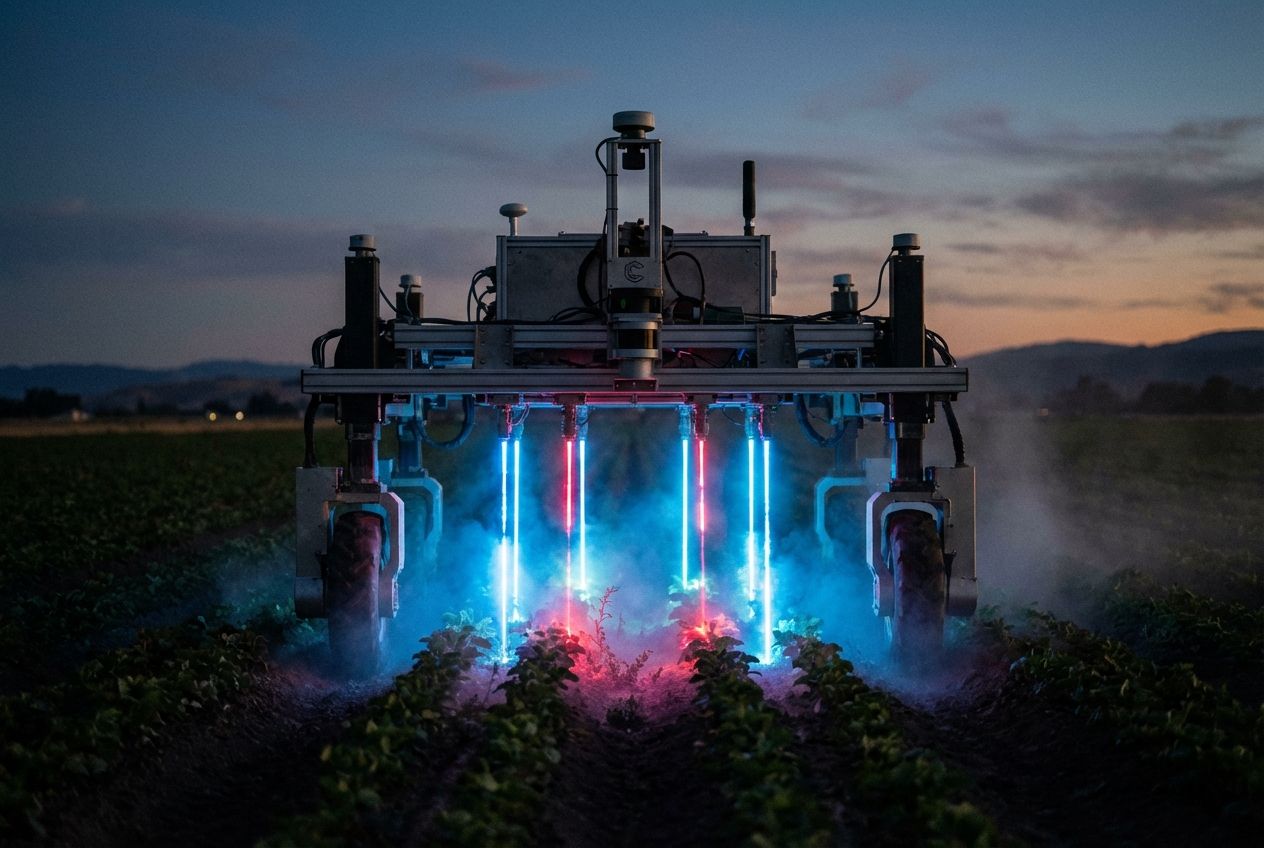
- They are precise: Robots like the Carbon Robotics LaserWeeder use thermal energy to zap weeds without disturbing the soil.
- They are relentless: Autonomous carts from Burro can follow pickers around all day, carrying heavy loads so your crew stays fresh.
- They are data-driven: Sensors scan soil health every day, so crops get only as much water as needed.
Farms of all sizes now use these technologies to save money while improving sustainability and food quality for everyone.
Main Factors Driving the Shift to Autonomous Systems
Why is everyone rushing to buy robots now? It usually comes down to three headaches: people, weather, and money.
Addressing Labor Shortages and Rising Costs
Finding good help is the number one challenge for most growers I talk to. In California, the minimum wage hit $16.90 per hour in 2026, and that is if you can even find workers. The H-2A visa program is expensive and complicated, leaving many farms short-handed during critical harvest windows.
Robots and autonomous machinery now do hard tasks like planting, weeding, picking fruit, or milking cows. These machines work all day without stopping for lunch breaks.
For instance, the Monarch MK-V electric tractor can run autonomous mowing patterns for hours. This frees up your tractor driver to manage other tasks. Similarly, automated weeding robots can replace a hand crew of 20 people, which changes your entire budget.
Responding to Climate Change and Sustainability Goals
Farmers feel the heat, both from the sun and stricter rules. The 2025 drought left nearly 60% of the Western U.S. in severe dry conditions. You cannot afford to waste water when allotments are cut.
New AgTech innovations step in here. Smart farming tools help track water use so every drop counts. Autonomous machinery plants seeds at just the right depth for healthier soil.
Robotics can cut down on fuel waste by running only when needed. Data analytics lets growers see how much fertilizer is really needed. Farms now shrink their carbon footprints while growing enough food for everyone.
“Farming isn’t just putting seeds into dirt anymore,” says Sam Carter, an Iowa grower. “Now we fight climate change one field at a time.”
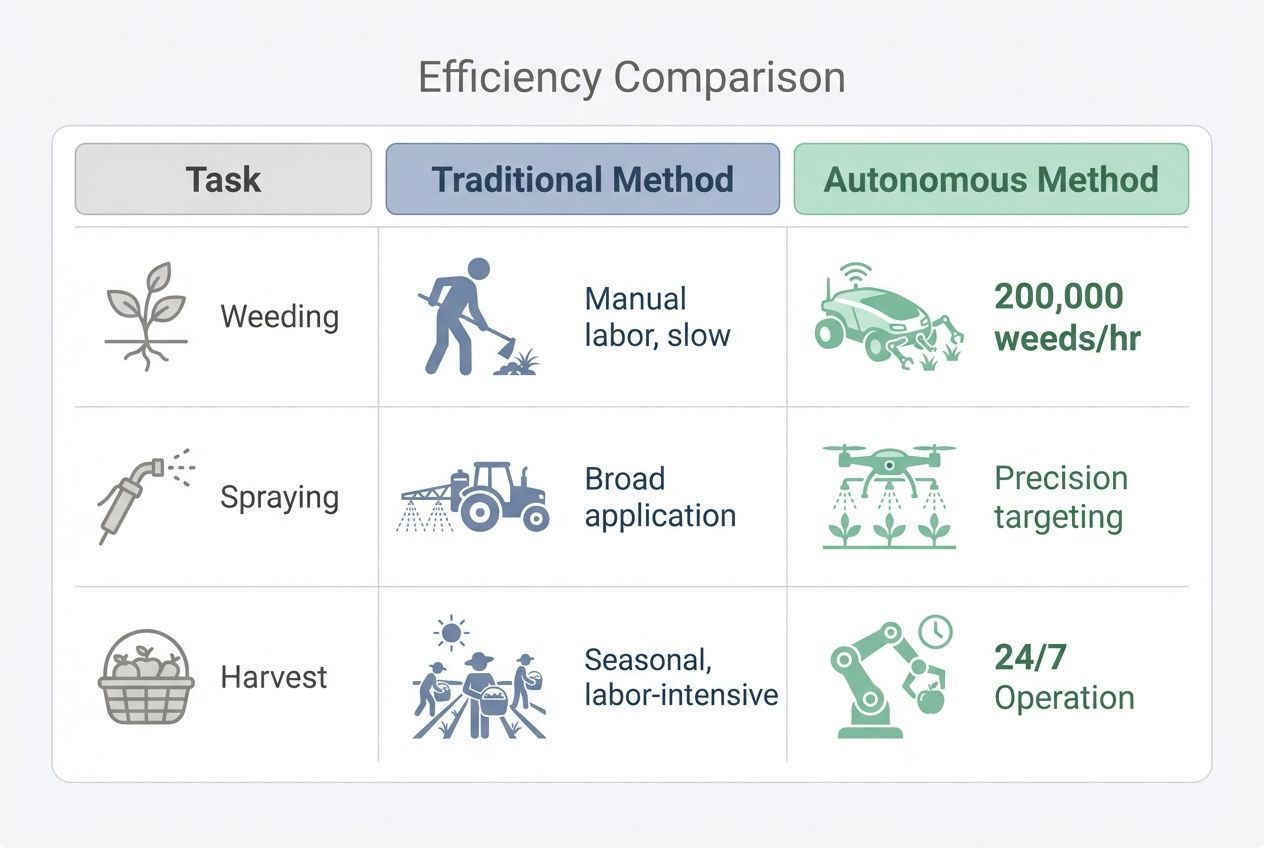
Enhancing Efficiency and Productivity in Agriculture
Efficiency isn’t just a buzzword; it is survival. Autonomous tractors and robots can plant, spray, and harvest crops without breaks or fatigue.
Consider the difference in efficiency:
| Task | Traditional Method | Autonomous Method |
|---|---|---|
| Weeding | Hand crews or blanket spraying | Laser weeders kill 200,000 weeds/hr with zero drift |
| Spraying | Treating the whole field | See & Spray systems treat only the specific weed |
| Harvest | Daytime only | Autonomous harvesters can run 24/7 to beat the rain |
Farms using these tools often see yield bumps of 10 to 20 percent. Precision agriculture puts fertilizer only where it is needed most. This shrinks costs while keeping plants healthy as a horse.
Technological Foundations of the Transition
Farms have started using smarter tools that can think and act on their own. These changes are shaking up how food gets grown, making old ways seem slow as a snail in rush hour.
AI and Machine Learning Applications in Agriculture
AI tracks plant health by spotting crop diseases early using pictures from field sensors and drones. Machine learning checks weather data, soil reports, and past harvests to help growers choose the best planting times.
A great example is Google’s Mineral project, which is now integrating into other platforms. It analyzes plant images to tell you exactly how a specific variety is performing in your specific soil. These tools can find weeds or pests before they spread.
Advanced AI models predict water needs for each part of a field. Farmers then use less water but grow more crops with smart irrigation systems guided by these insights. Companies like John Deere use machine vision in tractors for precise row planting.
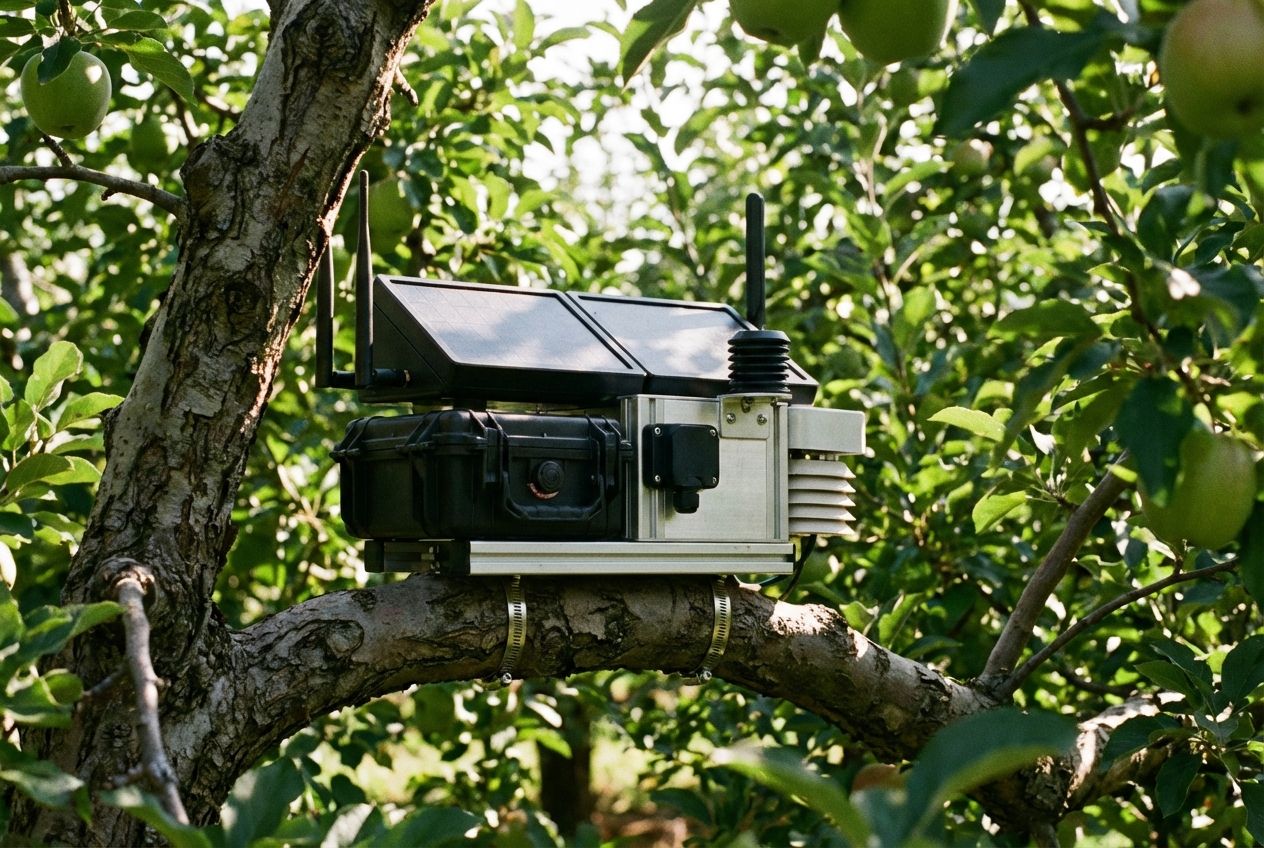
IoT Solutions for Real-Time Agricultural Monitoring
Sensors on the field track soil moisture, temperature, and plant health 24 hours a day. Farmers receive alerts if crops get too dry or need nutrients. Small weather stations collect data on rain and wind right in the middle of each farm.
Connected devices stream this information straight to phones or computers using IoT Internet of Things networks. Specific tools leading this charge include:
- Semios: Widely used in orchards to monitor pest pressure and climate automatically.
- Ranch Systems: Robust telemetry stations that handle everything from soil moisture to valve control.
Cows wear smart collars that report their activity and even location. Drones check for pests above tall corn rows while sensors in irrigation pipes catch leaks early.
Role of Robotics and Autonomous Machinery
Robotics takes on tough jobs in agriculture. Machines plant, weed, spray, and harvest fields day and night. Autonomous tractors steer themselves across acres with GPS and sensors.
In California’s lettuce fields, robotic thinners from companies like Blue River Technology use cameras to spot plants and decide which ones to keep. These machines cut labor costs fast; one robot may do the work of 20 people.
Drones scout for pests or dry spots from above while small ground robots check soil health at the root level. Data collected flows into farm computers for quick decision-making.
Utilization of Advanced Sensors and Drone Technology
Robotics gets the job done, but sensors and drones take farming to the next level. Small, smart sensors now live in fields across America. They track soil moisture and plant health every single day.
Drones fly high above crops like a flock of birds with sharp eyes. Models like the DJI Agras T50 are workhorses; they can map a field and then spray it with incredible precision. A drone can check 100 acres in less than an hour, work that once took people all day by foot or tractor.
With real-time imaging and AI analytics, farms quickly respond to threats before damage spreads further across their land. That means more food on our tables and less waste in each harvest season.
Breakthroughs in AgTech Innovations
Farm tech keeps outpacing itself, delivering surprises every season. Some changes spark big shifts in how fields work and what farmers can do with a simple click or swipe.
Development of Autonomous Tractors and Harvesting Machines
Autonomous tractors now steer fields with no human inside. John Deere, Case IH, and Kubota have released self-driving models since 2022. At CES 2025, John Deere unveiled the new autonomous 9RX tractor, designed for heavy-duty tillage without a driver in the cab.
These machines use AI, cameras, sensors, and GPS to plant seeds in straight lines or harvest ripe crops on their own. Some can work all night without stopping for breaks or food.
Self-propelled harvesters collect wheat or corn using lasers and computer vision to spot the best path through each row. Labor shortages pushed farms in California’s almond groves and Midwest cornfields to use these tools faster than before.
AI Enhancements in Precision AgTech: From Predictive to “Agentic”
AI in precision agriculture started by helping farmers predict crop problems. Today, it can do much more than guess the weather or spot a sick plant from drone images. Now, smart systems can act on their own, not just wait for people to tell them what to do.
We call these “Agentic” systems. For example, a platform connected to a Zimmatic pivot can notice a dry patch and turn on the irrigation nozzles for that specific sector automatically.
John Deere’s See & Spray system spots weeds and tells sprayers exactly where to work, saving chemicals and money while protecting the environment. With these advances, mistakes drop, and harvests get bigger with less waste.
Conversational Agronomy: The New Interface
AI has moved from making predictions to talking directly with farmers. Voice assistants now answer questions about soil, weather, and crop health. A farmer can ask a simple question on their phone and get real-time advice from an intelligent system backed by precision agriculture data.
Think of FBN’s “Norma”, an AI agriculture advisor. You can ask it, “What herbicide works best for waterhemp in my region?” and it gives you an answer based on millions of data points.
Much like texting a friend for quick help, these systems use natural conversation instead of complex dashboards. Farmers waste less time searching for information or calling experts. Conversational agronomy tools shorten the gap between high-tech insights and action in the field.
Advancements in Smart Irrigation and Water Management Systems
Smart irrigation systems use sensors, weather data, and IoT devices. These tools help farmers give crops the right amount of water at the right time. For example, drip irrigation guided by soil-moisture sensors can cut water waste by up to 50%.
Big companies like Netafim and Jain Irrigation lead this charge. Their latest systems, like the Jain Logic platform, combine satellite data with ground sensors to automate valves.
AI in agriculture now forecasts rain patterns so farmers can adjust watering schedules quickly. Satellites measure field moisture levels from space, while drones spot dry spots before plants wilt. Some systems even shut off valves or turn them on without human help if leaks or flooding are detected.
Applications of CRISPR and Other Biotechnological Innovations
CRISPR changes how farmers grow crops. This tool lets experts cut and fix genes in plants, making them stronger or more resistant to disease. In 2023, scientists used CRISPR to create tomatoes that last longer on shelves.
Recently, Pairwise released a new type of mustard green that removed the bitter wasabi flavor, making it tasty for salads. This kind of innovation opens up new markets for growers. Some corn now grows with less water because of gene edits, saving both time and resources.
New DNA tests find plant diseases early, helping farmers take action before crops get ruined. Gene-edited potatoes resist bruising during harvest, which means less food waste from field to store shelf.
Growth of Vertical Farming and Controlled Environment Agriculture
Vertical farming keeps crops safe indoors. Plants grow in stacked layers, using less land and water than outdoor farms. Some systems work all year, even in cities where there is little space or sunlight.
While pioneers like AeroFarms faced financial trouble in 2023, the industry has matured. Companies like Oishii are successfully selling premium strawberries grown in New Jersey warehouses, and Plenty is ramping up its massive indoor farm in Compton, California.
Controlled environment agriculture (CEA) uses smart tools like AI, IoT sensors, and automation to watch over every seedling. Robots plant seeds and pick leafy greens while computers manage light cycles or nutrients in the water. These tech-driven methods help save up to 90% more water compared to old-style field farming.
Advantages of Adopting Autonomous Agricultural Systems
Farms run smoother when machines handle the tough jobs. These tech upgrades spark fresh ideas and make big changes in how fields are cared for.
Reducing Labor Dependency in Agriculture
Autonomous machinery, like self-driving tractors and robotic harvesters, cuts the need for large teams in the field. Smart farming uses AI and sensors to track crops and soil, so one person can do work that once took many hands.
In California, for example, farms using robotics have seen labor costs drop as much as 30 percent since 2021. The Carbon Robotics LaserWeeder is a standout here; growers report it can reduce weeding labor bills by up to 40% annually.
Across rural areas with fewer people willing to take farm jobs, these AgTech innovations keep food production strong. Even small farms benefit; instead of hiring extra help during busy seasons, growers use machines that plant seeds or spray crops around the clock with little human oversight.
Boosting Resource Efficiency
AI in agriculture helps save seeds, water, and fertilizer. Tractors can drive themselves using GPS and sensors. These machines know how much to plant or spray with little waste.
Drones spot dry spots or bugs from above so farmers can act fast. IoT in farming gives real-time data on soil, weather, and crops. Precision agriculture cuts down waste by putting resources exactly where crops need them most. With smart tools working all day without rest, farms use less fuel but grow more food every season.
Improving Crop Yields and Quality
Autonomous machinery uses data and smart sensors to plant seeds at the best depth, spacing, and time. Farmers can spot pests before they spread using drones with cameras, which helps save more crops each season.
Machines that apply fertilizer or water only where it is needed help plants grow stronger and healthier. AI in agriculture studies plant growth patterns over many seasons, choosing crop varieties that deliver bigger harvests even during tough weather.
These high-tech systems adjust their actions as conditions change, giving each plant just what it needs for top results.
Mitigating Environmental Impact
Sensors track soil health, water levels, and chemical use. This helps farmers cut back on waste. Smart irrigation systems bring water right where crops need it most.
Using targeted spraying technology like Greeneye Technology, farmers can reduce herbicide usage by up to 78% because the machine only sprays the weeds, not the crop. This keeps rivers cleaner and soil safer for wildlife.
These advances push agriculture closer toward sustainability while protecting resources for future generations. Boosting resource efficiency leads directly to better crop yields and quality.
Obstacles and Limitations to Adoption
Farmers face roadblocks as they try to use new machines and tools. Some changes feel like trying to teach an old dog new tricks, but there’s plenty more ground to cover ahead.
Overcoming High Initial Investment Costs
The sticker price on these tools can be shocking. A fully autonomous tractor can cost upwards of $500,000. However, companies are finding ways to help.
John Deere now offers a retrofit kit for around $50,000 that can turn a standard tractor into an autonomous one. This makes it easier for growers to try autonomous machinery and AI in agriculture without spending a fortune upfront.
Pooling resources through co-ops spreads out costs. Neighbors can share the use of expensive tools like drones or advanced sensors. Bigger farms sometimes rent out their high-tech machines to smaller ones that need help during planting or harvest seasons.
Solving Technology Integration and Connectivity Challenges
Farmers often find that different machines or tools will not “talk” to each other. A tractor fitted with one sensor might not share data with a drone using another system. Mixing many pieces of AgTech can feel like putting together a puzzle missing half its parts.
Farms in rural areas also may have poor internet, making it tough for robots and smart monitors to work as planned. This is changing fast, though.
In 2024, John Deere partnered with Starlink to bring satellite internet to tractors in remote areas. This ensures that even if your field is miles from a cell tower, your autonomous machine stays connected.
Addressing Resistance to Change among Farmers
Solving technology integration and connectivity problems opens the door to new challenges. Many farmers hold tight to old ways, feeling safe with what they know. The average age of a U.S. farmer is 58 years old, and shifting from a manual steering wheel to an iPad controller is a big leap.
Autonomous machinery or AI in agriculture can seem strange, almost like science fiction. Change gets harder when money is tight. New robotics and IoT solutions cost more than an old tractor or shovel, and risk carries a weight on every farm.
Honest talks help build trust here; hands-on trials help too. Making tech fit local needs brings confidence, one step at a time, just like planting seeds row by row.
Projecting the Future of AgTech and Autonomous Systems
Tomorrow’s fields may run themselves, making food grow smarter and faster. Curious how science and money could shape your next meal? Keep reading.
Financial Innovations to Support Technology Adoption
Banks and tech firms offer new ways for farmers to get what they need. Leasing programs, low-interest loans, and shared machinery plans help spread costs over time. Some startups use blockchain or mobile apps so small farms can pool funds.
Companies like Bushel are modernizing how farmers get paid, offering digital wallets that make transactions instant. Agri-insurance covers the risk if a crop fails because of weather or bugs. Carbon credit sales give farms cash back for protecting the soil or planting trees, boosting sustainable agriculture goals.
Constructing Climate-Resilient Agricultural Strategies
Farmers must adapt to wild weather and rising heat. Using AI in agriculture can help people predict droughts or floods before they hit. With data from IoT sensors, crops get only the water and nutrients they need, wasting less during dry spells.
Drones spot stubborn weeds or patches where plants struggle after a heatwave. Robotics work through rain, sun, or cold snaps to keep harvests on schedule.
Vertical farming lets growers raise leafy greens indoors all year, safe from storms outside. Investing in smarter irrigation and strong seed genes helps every crop stand tall against changing seasons.
Forwarding AI and Data-Driven Agricultural Solutions
AI now reads drone images to spot pests and weeds faster than any scout. On some farms, machine learning checks soil health every hour using small sensors buried in the ground. These tools predict plant diseases long before leaves start curling or yellowing.
Row-bots, controlled by data, pick ripe fruit at dawn while dashboards update crop managers with real-time stats about moisture and yield. Data analytics lets growers track weather shifts each day so they plan harvests with less guesswork.
With these solutions, fields talk back through devices spread from fence post to field row, giving clearer answers so people can grow more food with fewer mistakes.
FinTech and The Business of Carbon
Money talks, even in farming. Financial tech tools are helping farmers turn carbon into cash.
Digital MRV (Measurement, Reporting, Verification)
Digital MRV tools help farmers track carbon, water, and soil data without piles of paperwork. These smart systems use sensors, drones, and AI to measure farm activities in real time.
Farms can upload this data straight to the cloud. This means quicker reporting for sustainability checks and easier proof for climate-smart agriculture credits. Companies find it simpler to meet rules and get rewards for eco-friendly farming.
Accurate measurement stops guesswork about emissions or soil health. A wheat farmer in Kansas uses digital MRV with IoT devices to log daily CO2 levels from his crops. Digital records also speed up audits by insurance firms and carbon market platforms like Indigo Ag or Nori, which want fast verification before paying out incentives.
Parametric Insurance
Just as Digital MRV gives fast, clear data for farms, parametric insurance makes covering risks in agriculture simpler and faster. This insurance pays out not by checking actual loss on the ground but by using set triggers, like rainfall levels or temperature measurements through IoT sensors.
Companies like Descartes Underwriting specialize in this. If a certain trigger is hit, such as less than 50 millimeters of rain during planting season, farmers get their payment, no need for slow claims or paperwork.
This saves time and helps with cash flow after disasters like droughts or floods. By cutting red tape and letting technology handle the details, smart farming shifts risk management into the digital age simply and affordably.
The Invisible War: Cybersecurity and RegTech
Hackers want farm data, so digital defenses must stand strong. Shovels and firewalls are both now essential on the modern farm.
The “Compliance Cliff”: EUDR & Traceability
Farms selling internationally face strict new rules from the European Union Deforestation Regulation, or EUDR. While originally set for 2024, the implementation has been delayed to December 30, 2026, for large companies. This gives US producers a little breathing room, but the deadline is real.
By that date, anyone selling crops like soybeans, cocoa, or beef in the EU must prove that their goods did not come from land cleared of forest after December 2020. That means farms need digital records showing where each crop grew and every step it took to reach store shelves.
This rule pushes AgTech companies to offer strong traceability tools. Digital ledgers, like IBM Food Trust, track a tomato from dirt to dinner plate using sensors and QR codes, making sure nothing gets lost along the way.
Traceability demands feed into smart farming systems built on AI, IoT devices, and real-time monitoring—building a bridge between regulations and next-generation agriculture tools.
Controlled Environment Agriculture (CEA) Correction
Controlled Environment Agriculture, or CEA, keeps plants safe from wind, pests, and wild weather. This approach uses sensors to monitor light, water use, and temperature every hour of the day.
Workers can adjust settings with a tap on a screen. In vertical farms like those in New Jersey or Singapore, crops grow year-round without soil using hydroponics. Lettuce grows in stacks under LED lights that mimic the sun but use less energy.
CEA helps farmers cut waste by nearly 90 percent compared to outdoor methods. Strawberry yields often double inside these controlled spaces since pollination happens perfectly each time, no bees required! Water use drops by almost 95 percent as systems recycle it again and again.
With fewer pesticides needed and shorter travel to stores, fresh food reaches tables faster while helping save resources for everyone’s future.
Final Thought: Cultivating Silicon and Soil
From smart sensors in the soil to tractors that steer themselves, farming tech is changing fast. These new tools make life easier, cut down on waste, and help crops grow better with less effort.
You might wonder how much one farm can change things, but each step matters for our future food supply. Thinking about your own farm or garden? Start small, try a sensor or simple robot, and see what it does for you.
If you want to know more, local AgTech groups and online guides offer handy tips you can use today. Growing both silicon chips and sturdy plants side by side is how we feed families now, and keep fields green for tomorrow.