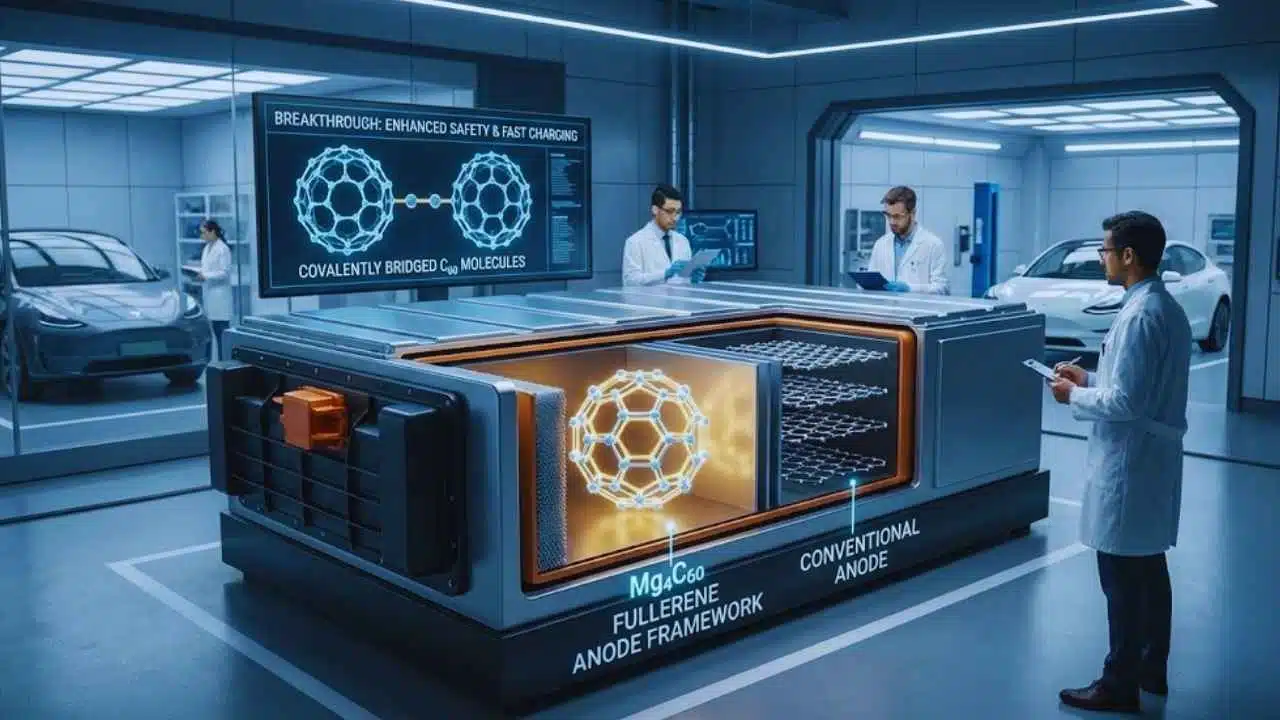
Tohoku University researchers say they have stabilized fullerene-based anodes for lithium-ion cells using a covalently bridged framework called Mg4C60, a step that could support safer fast-charging EV batteries.
What happened, and why it matters
Lithium-ion batteries used in most electric vehicles still depend on graphite anodes. Graphite is reliable and affordable, but it can struggle during aggressive fast charging. One widely discussed failure pathway is lithium plating, where lithium deposits on the anode surface instead of inserting into it—raising degradation risks and, in worst cases, safety concerns.
Researchers have long explored carbon alternatives. Fullerenes (C60)—soccer-ball-shaped carbon molecules—have attractive electrochemical behavior, but a major barrier has been instability in typical battery electrolytes, which can lead to loss of active material and structural breakdown over cycling.
A team led by Distinguished Professor Hao Li at the WPI-Advanced Institute for Materials Research (AIMR), Tohoku University (Japan) reports a new way to address that stability problem: tie fullerene molecules together with covalent bridges so the structure doesn’t collapse during battery operation.
The core breakthrough: a “covalently bridged” fullerene framework
The compound reported by the Tohoku-led team is Mg4C60, described as a layered, polymeric fullerene framework in which magnesium helps drive covalent connections between C60 units. The university says this redesign prevents the “structural collapse” that has historically limited fullerene anodes and helps avoid active-material loss.
The paper, “Covalent Bridges Enabling Layered C60 as an Exceptionally Stable Anode in Lithium-Ion Batteries,” was published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society on December 11, 2025 (DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c17338). Tohoku’s public announcement is dated December 24, 2025.
How it works (in plain language)
Many fullerene solids are held together mainly by weaker intermolecular forces. In battery conditions, that can make them more vulnerable to changing structure or dissolving into electrolyte.
In Mg4C60, the researchers report that magnesium promotes “intercage” covalent connections—stronger bonds between neighboring fullerene molecules—turning what would behave more like a molecular solid into a more robust framework.
In its press release, Tohoku describes the result as a way for “carbon to store lithium in a completely different and much more stable way,” positioning it as a potential blueprint for safer, fast-charging designs.
Why graphite struggles with very fast charging
Fast charging is not just a “bigger power plug” problem. Inside a battery, lithium ions must move through electrolyte, cross interfaces, and insert into the anode material quickly and uniformly. When the anode can’t keep up—because transport and reaction rates hit limits—lithium can deposit as metal on the surface (plating), which can accelerate aging and create uneven growth that raises safety risks.
Graphite’s theoretical capacity is commonly cited around 372 mAh/g, which is also why researchers chase higher-capacity materials—though many alternatives bring their own stability and safety challenges.
What the Mg4C60 result changes for fullerene anodes
Fullerene-based electrode concepts have shown promise for years, including because C60 can undergo rich redox chemistry. Reviews have summarized multiple fullerene battery approaches across lithium and beyond, but stability and compatibility issues have been recurring obstacles.
Tohoku’s claim is that covalent bridging directly targets that Achilles’ heel—helping the anode maintain its internal structure instead of degrading or losing material into electrolyte.
What’s still unknown (and what to watch next)
The university says the next steps include:
- applying the covalent-bridging strategy to a broader range of fullerene and carbon frameworks, and
- working with industry partners on scalability and integration into practical cell formats.
For EV relevance, the biggest watch items typically include:
- performance at high charge rates (how fast it can charge without damage),
- cycle life under realistic duty cycles,
- electrode loading and manufacturability,
- compatibility with commercial electrolytes and safety testing,
- and full-cell validation (not just half-cells).
Separate but related: magnetic control of lithium in anode reactions
In another recent battery-anode development, a POSTECH (South Korea) team reported a “magneto-conversion” strategy using an external magnetic field with ferromagnetic manganese ferrite in conversion-type anodes.
In the peer-reviewed Energy & Environmental Science paper (DOI: 10.1039/D5EE02644J), the journal listing reports a reversible capacity of 1400 mAh/g and Coulombic efficiency over 99% after 300 cycles, along with evidence aimed at dendrite-free lithium behavior in their hybrid approach.
This is a different path from Mg4C60, but it underscores the same industry pressure point: raising capacity and enabling faster charging without creating instability or safety hazards.
Key timeline
| Item | Organization | Date |
| JACS paper published: “Covalent Bridges Enabling Layered C60…” (Mg4C60) | Tohoku University / collaborators | Dec 11, 2025 |
| Public announcement/press release on Mg4C60 | Tohoku University (AIMR) | Dec 24, 2025 |
| Energy & Environmental Science paper first published online (magneto-conversion) | POSTECH team | Oct 8, 2025 |
Quick comparison: what these anode ideas are trying to fix
| Approach | What it replaces/changes | Claimed benefit focus | Key caveat to monitor |
| Graphite (today’s standard) | Baseline anode in most Li-ion EVs | Mature, scalable, stable | Fast charging can raise lithium plating risk |
| Mg4C60 covalently bridged fullerene | Fullerene anode redesigned with covalent bridges | Structural stability of fullerene anodes; safer fast-charging potential | Needs scale-up + practical cell validation |
| Magneto-conversion (manganese ferrite + magnetic field) | Conversion-type hybrid behavior + magnetic control | High capacity and dendrite suppression; reported 1400 mAh/g, >99% CE after 300 cycles | System complexity (field application, engineering integration) |
Why this is a notable EV-battery story now
Automakers and cell makers want batteries that can charge faster without compromising life or safety. Most improvements come from multiple levers at once—materials, electrolytes, charging protocols, and thermal control. That’s why an anode material that can better resist degradation during fast charging can be meaningful, even before it reaches commercial readiness.
Tohoku’s Mg4C60 report is notable because it targets a long-standing limitation specific to fullerene anodes—framework instability—with a design principle (covalent bridging) that the team says could extend to other carbon frameworks.
What comes next
Mg4C60 is not a commercial EV-battery part yet. But it adds a credible, chemistry-first strategy for improving carbon-anode stability beyond graphite, backed by a high-profile peer-reviewed publication and a clear plan to test scalability and practical formats with industry partners.
If follow-on studies show consistent fast-charge performance at practical electrode thicknesses—without lithium plating, rapid capacity fade, or electrolyte-driven failure—covalently bridged fullerene frameworks could become a serious contender in the broader race for safer, faster-charging EV batteries.