e Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act was introduced. to protect patient data and confidential information, associates and covered entities must follow these rules established by HIPAA.
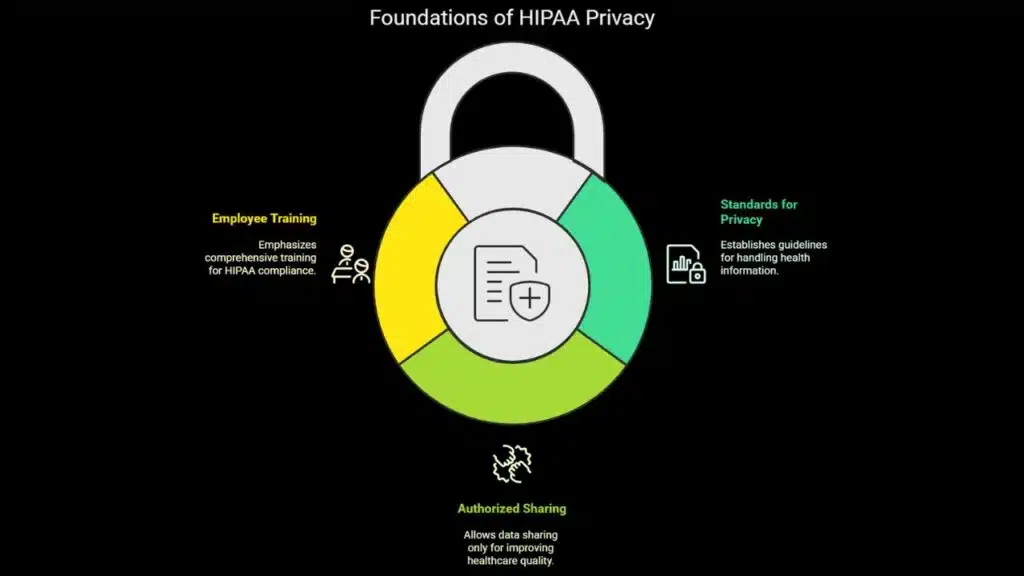
Without following the said rules, healthcare businesses can get HIPAA compliance. Lack of understanding of basic rules and regulations can be a serious issue. HIPAA training is an essential aspect of protecting patients’ data. Even for a patient, knowing the summary of the HIPAA Privacy Rule is important.
The HIPAA Privacy Rule is one of the important rules introduced by HIPAA. The privacy rule established a few important national practices and SOPs for handling and protecting individuals’ medical records.
Key Points of the HIPAA Privacy Rule
Understanding any complicated document and its important points can be difficult for many readers. Even the majority of employees from healthcare businesses don’t understand the true spirit of the act.
Not only doctors but also other stakeholders should comply with the national standards. Students, volunteers, and other members of the medical profession should familiarize themselves with the HIPAA Privacy Rule.
What is the HIPAA Privacy Rule?
This rule has been around for quite some time, and it was known as the Standards for Privacy of Individually Identifiable Health Information. In 2000, the U.S. Department of Human Services introduced the HIPAA Privacy Rule.
The HIPAA Privacy Rule sets important standards for protecting patients’ health information. Only the authorized sharing of patient data is allowed to improve the quality of health service delivery.
Understanding the summary of the Privacy Rule is not sufficient for employees, but this guide can give a clear idea about the goals that HIPAA aims to achieve. Make sure your team members and employees have more than the minimum HIPAA training.
What is PHI?
Personal Health Information (PHI) is a patient’s record collected and handled by any covered entity. It can include all records related to present and past medical conditions. This information will also include all financial matters related to the medical services offered to the individual.
PHI also relates to any medical records that can help others identify the patient’s real identity. Social security numbers, addresses, names, dates of birth, images, and other similar credentials are PHI. This record can be in printed, oral, or electronic form.
Who Must Comply with HIPAA Privacy Rules?
Covered entities must comply with the HIPAA Privacy Rule, and they include a wide range of businesses and service providers. Common CEs related to HIPAA include health plans, healthcare providers, and healthcare clearinghouses.
Any organization or company that pays for or processes patients’ medical bills must follow and understand the Privacy Rule. Services that process nonstandard medical records of patients process the given data for other projects. They are also part of the covered entities.
Rights of Patients
HIPAA not only sets standards for healthcare providers but also gives basic rights to patients. Consumers of the medical business or patients of any healthcare provider are entitled to these patient rights, including:
- Right to access PHI.
- Right to request changes in their PHI.
- Right to an accounting of disclosures.
- Right to have their PHI restricted against sharing with other providers.
- Right to receive confidential communications.
Certain cases and conditions allow covered entities to share and transfer PHI without the patient’s authorization. Treatment, healthcare operations, and financial matters are a few examples of cases where healthcare providers can disclose patients’ data.
What HIPAA Privacy Rule Aims to Achieve?
This rule focuses on protecting patients’ personal health information but also allows medical employees to use and disclose PHI without violating standard rules. HIPAA also ensures a safe environment for patients to access and request changes to their PHI.
Healthcare businesses are permitted to use and disclose PHI only in certain cases. Violation of these rules or failure to comply with national standards of data protection can get your business in trouble with authorities and the U.S. Department of Health.
Minimum Necessary Standard
If any other entity or business requests a patient’s data for any purpose other than treatment and payments, employees must make efforts to share the minimum data only.
Employees can share minimum data only to honor other healthcare businesses’ requests for information. The shared data should not help unauthorized individuals identify the patient.
Administrative Requirements
Compliance with the HIPAA Privacy Rule is not possible without reasonable efforts by the employer and the employees. Here are a few important administrative requirements for a healthcare business with HIPAA compliance. Here are a few important requirements that business administration must fulfill:
- Have a dedicated privacy official at the workplace.
- Train team members and workforce with essential HIPAA training.
- Implement different safeguards to protect the data and information of patients.
- Handle complaints of patients via a procedure.
- If any data breach happens, ensure safe practices to minimize the risk.
Enforcement of HIPAA Privacy Rule
These are some of the important points that patients and healthcare professionals should understand regarding patient data and information. The HHS Office for Civil Rights is responsible for enforcing and implementing the HIPAA Privacy Rule.
This is not just a rule on the paper; violation of any rule in HIPAA can result in fines and serious penalties from the authorities. A business may face criminal or civil penalties for not complying with the HIPAA Privacy Rule.
Final Words
The HIPAA Privacy Rule provides a complete framework for healthcare professionals to protect PHI. There is also room for reasonable sharing of the patient’s data for treatment and payment purposes only. It is very important for patients and medical professionals to understand the importance of advanced HIPAA training.
Trust is an important factor in the smooth delivery of health services. Patients are more likely to share sensitive and important data with doctors, and the accuracy of the data provided by patients helps with higher patient satisfaction.