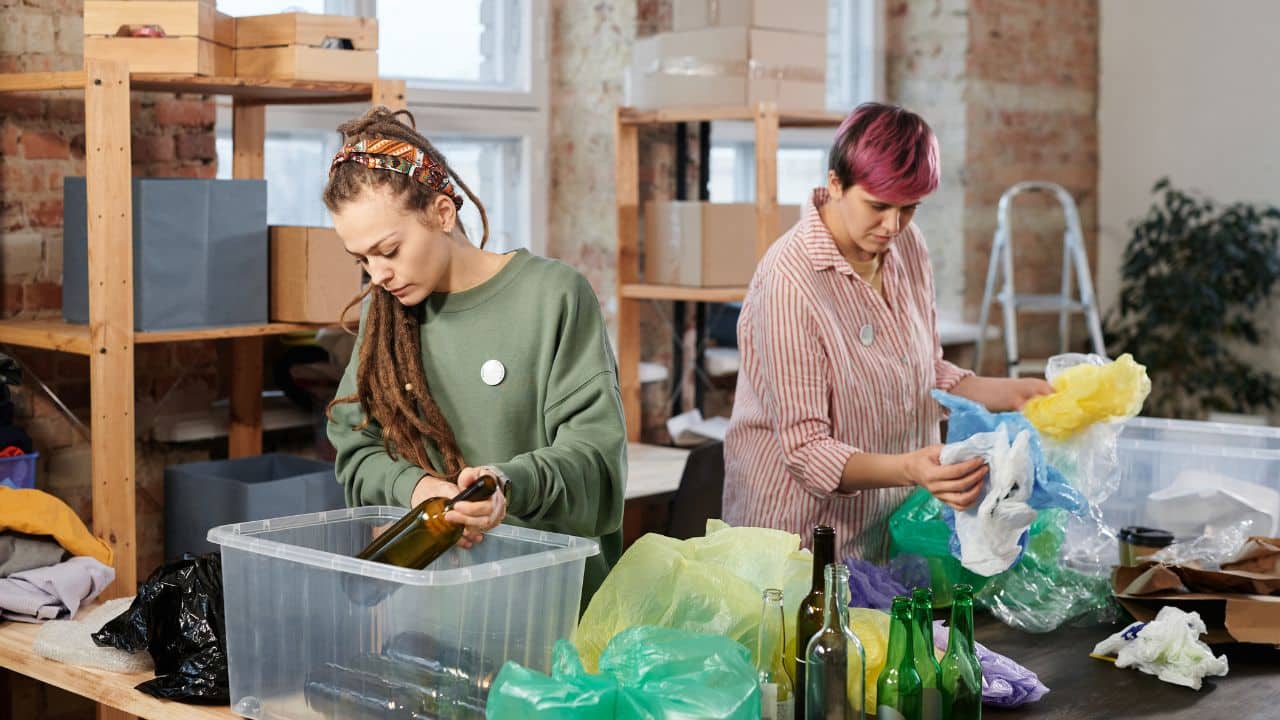
What is sustainable waste management? It refers to practices and strategies aimed at reducing, reusing, recycling, and responsibly disposing of waste materials to minimize environmental impact and conserve resources.
This approach focuses on treating waste as a valuable resource rather than a problem to be eliminated, aligning with the principles of a circular economy.
The Importance of Sustainable Waste Management
In today’s world, where environmental concerns are paramount, sustainable waste management has become a critical issue. The global municipal solid waste generation reached 2.01 billion tonnes in 2016 and is expected to increase by 70% to 3.40 billion tonnes by 2050.
This staggering growth in waste production poses significant challenges to our environment, public health, and economic systems.
Sustainable waste management offers a solution to these challenges by:
- Reducing environmental pollution
- Conserving natural resources
- Minimizing greenhouse gas emissions
- Creating economic opportunities
- Improving public health and sanitation
Key Components of Sustainable Waste Management
Waste Reduction
The most effective strategy in sustainable waste management is preventing waste generation in the first place. This involves:
- Minimizing packaging
- Choosing reusable products
- Avoiding single-use items
- Implementing efficient production processes
Reuse and Repurpose
Encouraging the reuse of products and materials extends their lifecycle and reduces the need for new resources. This can include:
- Donating usable items
- Repairing instead of replacing
- Finding creative ways to repurpose materials
Recycling
Recycling plays a crucial role in sustainable waste management by converting waste materials into new products. This process:
- Conserves natural resources
- Reduces energy consumption
- Decreases greenhouse gas emissions
According to the EPA, recycling and composting of municipal solid waste in the United States saved over 193 million metric tons of carbon dioxide equivalent in 2018.
Composting
Organic waste, such as food scraps and yard trimmings, can be composted to create nutrient-rich soil conditioners. This practice:
- Diverts waste from landfills
- Reduces methane emissions
- Improves soil health
Energy Recovery
Some waste materials can be converted into usable energy through processes like:
- Waste-to-energy incineration
- Anaerobic digestion
- Landfill gas capture
These technologies help reduce reliance on fossil fuels and lower greenhouse gas emissions.
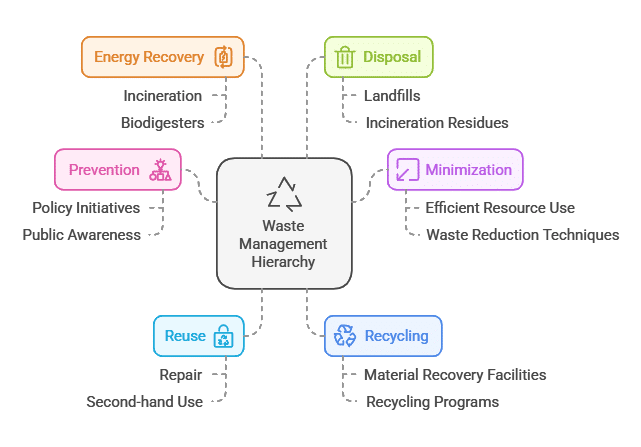
The Waste Management Hierarchy
The waste management hierarchy is a framework that prioritizes waste management strategies based on their environmental impact. From most preferred to least preferred, the hierarchy includes:
- Prevention
- Minimization
- Reuse
- Recycling
- Energy recovery
- Disposal
This hierarchy serves as a guide for policymakers and waste management professionals to make informed decisions that prioritize sustainable solutions.
Challenges in Implementing Sustainable Waste Management
Despite its benefits, implementing sustainable waste management faces several challenges:
Infrastructure and Technology
Many regions lack the necessary infrastructure and technology for efficient waste collection, sorting, and processing. Developing countries, in particular, struggle with inadequate waste management systems.
Financial Constraints
Implementing sustainable waste management practices often requires significant upfront investments in infrastructure, technology, and education. This can be challenging for municipalities with limited budgets.
Public Awareness and Participation
Successful waste management relies heavily on public participation. Lack of awareness and engagement can hinder the effectiveness of recycling and waste reduction programs.
Policy and Regulation
Inconsistent or weak regulations can impede the implementation of sustainable waste management practices. Effective policies and enforcement mechanisms are crucial for success.
Sustainable Waste Management Practices Around the World
Several cities and countries have implemented innovative sustainable waste management practices:
| City/Country | Practice | Impact |
| San Francisco, USA | Zero Waste Program | Achieved 80% waste diversion, highest in North America |
| Sweden | Waste-to-Energy | Converts 99% of household waste to energy or recycled materials |
| South Korea | Pay-as-you-throw system | Reduced food waste by 30% in its first year |
| Germany | Extended Producer Responsibility | Achieved a 67% recycling rate for packaging waste |
The Role of Technology in Sustainable Waste Management
Advancements in technology are playing an increasingly important role in improving waste management practices:
Smart Waste Collection
IoT-enabled sensors in waste bins can optimize collection routes, reducing fuel consumption and emissions.
Artificial Intelligence in Recycling
AI-powered sorting systems can improve the efficiency and accuracy of recycling processes.
Blockchain for Waste Tracking
Blockchain technology can enhance transparency and traceability in waste management supply chains.
Waste-to-Energy Technologies
Advanced thermal treatment and biological processes are improving the efficiency of energy recovery from waste.
Economic Benefits of Sustainable Waste Management
Sustainable waste management not only benefits the environment but also offers significant economic opportunities:
- Job creation in recycling and waste management sectors
- Resource recovery and cost savings for industries
- Development of new markets for recycled materials
- Reduced costs associated with environmental remediation
A study by the Global Waste Management Outlook 2024 suggests that adopting a circular economy model in waste management could lead to a net gain of USD 108.5 billion per year by 2050.
The Future of Sustainable Waste Management
As we move towards a more sustainable future, several trends are shaping the waste management landscape:
Circular Economy
The concept of a circular economy, where waste is minimized and resources are kept in use for as long as possible, is gaining traction globally.
Zero Waste Initiatives
More cities and businesses are adopting zero waste goals, aiming to divert all waste from landfills and incinerators.
Extended Producer Responsibility
Policies that make manufacturers responsible for the entire lifecycle of their products, including disposal, are becoming more common.
Sustainable Packaging
There is a growing focus on developing eco-friendly packaging materials and reducing packaging waste.
Takeaways
sustainable waste management is a critical component of our efforts to build a more environmentally friendly and resource-efficient world. By adopting practices that prioritize waste reduction, reuse, recycling, and responsible disposal, we can significantly reduce our environmental impact and move towards a more sustainable future.
What is sustainable waste management? It’s a comprehensive approach that not only addresses the immediate challenges of waste disposal but also contributes to long-term environmental sustainability and economic growth.