On Tuesday, February 18, 2025, President Donald Trump announced his intention to impose a 25% tariff on imported automobiles, pharmaceuticals, and semiconductor chips. This move aims to bolster domestic manufacturing and address perceived trade imbalances. The President indicated that these tariffs could increase further throughout the year to encourage companies to relocate operations to the United States. Detailed information on the automotive tariffs is expected by April 2, following a comprehensive trade policy review.
Automobile Tariffs
President Trump has long criticized what he perceives as unfair treatment of U.S. automotive exports. For instance, the European Union imposes a 10% tariff on vehicle imports, significantly higher than the 2.5% duty the U.S. places on passenger cars. However, the U.S. maintains a 25% tariff on most imported pickup trucks, protecting a lucrative segment for domestic manufacturers like Ford and Chevrolet. The proposed 25% tariff on imported automobiles aims to promote fair competition and encourage automakers to boost their production in the United States.
Pharmaceutical and Semiconductor Tariffs
The proposed tariffs also target the pharmaceutical and semiconductor industries, with initial rates set at 25% or higher, potentially increasing over the year. President Trump did not specify an implementation date for these levies, stating he wants to provide companies time to establish U.S.-based production facilities. This approach aims to reduce dependency on foreign manufacturing and strengthen domestic supply chains in critical sectors.
Previous Tariff Actions
Since his inauguration in January 2025, President Trump has implemented a series of tariffs as part of his broader trade policy agenda. Notably, he imposed a 10% tariff on all imports from China and announced a 25% tariff on steel and aluminum imports, effective March 12. While measures targeting Mexico and Canada have been postponed, he has directed his team to develop reciprocal tariffs matching those imposed by all trading partners. These actions reflect the administration’s commitment to reshaping U.S. trade relationships and protecting domestic industries.
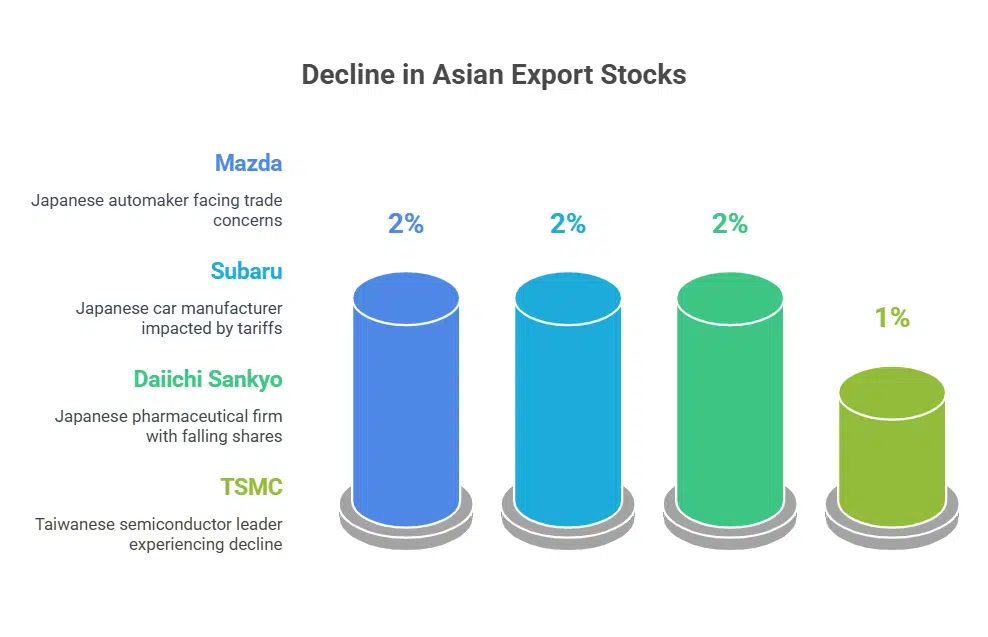
Global Market Reactions
The announcement of new tariffs has led to declines in major export stocks during Wednesday morning trading in Asia. In Japan, automakers Mazda and Subaru both saw shares fall by approximately 2%, as did pharmaceutical company Daiichi Sankyo. In Taiwan, semiconductor giant TSMC experienced a 1% drop. These market reactions underscore investor concerns about potential disruptions to global supply chains and the broader economic impact of escalating trade tensions.
International Responses and Potential Trade Negotiations
The European Union, which currently imposes a 10% tariff on vehicle imports, may seek negotiations to address the proposed U.S. tariffs. EU trade chief Maroš Šefčovič is expected to engage with U.S. economic advisers to discuss trade concerns and prevent a potential trade war. Additionally, President Trump has suggested that pharmaceutical and semiconductor companies will be given time to establish U.S. operations to avoid the new tariffs, indicating a willingness to work with industries to mitigate negative impacts.
Economic Implications
Economists warn that the proposed tariffs could lead to higher consumer prices and potential trade wars with key international partners. The tariffs are expected to increase production costs, which may be passed on to consumers in the form of higher prices for automobiles, pharmaceuticals, and electronic devices. Furthermore, retaliatory measures from affected countries could impact U.S. exports, leading to broader economic consequences. The administration argues that these measures are necessary to protect domestic industries and reduce trade deficits, but the long-term effects on the global economy remain uncertain.
In summary, President Trump’s announcement of new tariffs on imported automobiles, pharmaceuticals, and semiconductor chips represents a significant escalation in his administration’s trade policy. While intended to bolster domestic manufacturing and address trade imbalances, the move has prompted concerns about potential economic repercussions, both domestically and globally. As the situation develops, stakeholders across various industries will be closely monitoring the administration’s actions and their potential impacts on international trade relations.