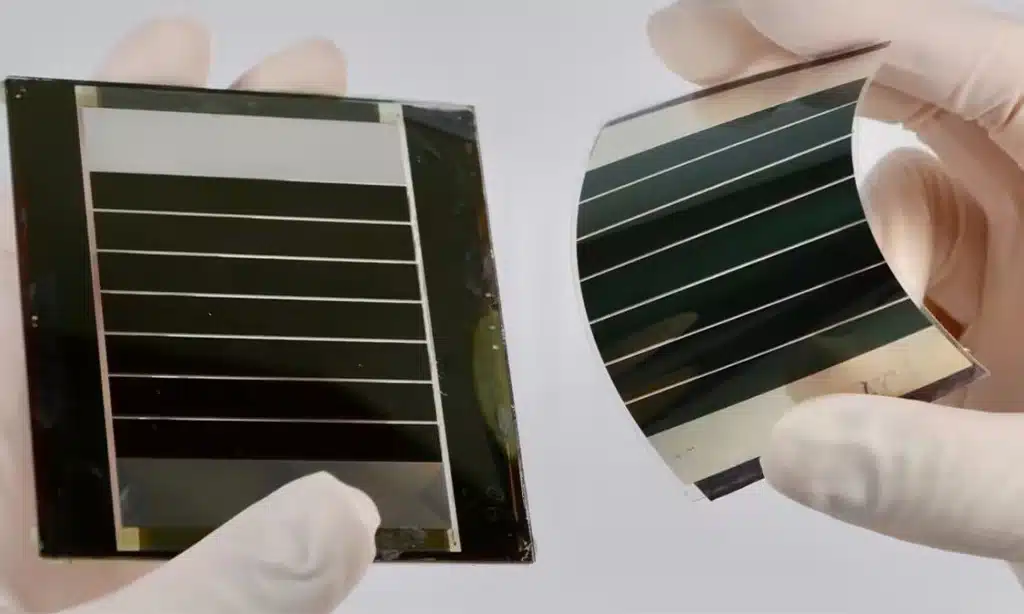
Perovskite solar technology has been called the next big leap in clean energy for more than a decade. The excitement is not just hype. Perovskite devices have reached jaw-dropping efficiency levels in laboratories, and they can be made using faster, potentially cheaper manufacturing methods than conventional silicon.
The real question is whether perovskite solar cells commercial ready is finally a fair statement for everyday buyers, utility-scale developers, and manufacturers. In this evergreen guide, you will learn what perovskites are, why they matter, what still holds them back, and what “commercial readiness” realistically means right now.
What Are Perovskite Solar Cells?
Perovskite solar cells are photovoltaic devices that use a class of materials known as perovskites as the light-absorbing layer. The word “perovskite” refers to a crystal structure, not a single chemical. In practice, most solar perovskites are made from hybrid organic-inorganic compounds that can be tuned for excellent light absorption.
Unlike traditional silicon solar cells, which rely on thick wafers of purified silicon, perovskite cells can use very thin active layers. These layers can be deposited using techniques that resemble printing or coating, which is one reason perovskites are often linked to lower production costs.
There are several common formats you will see discussed:
- Single-junction perovskite cells, which use one perovskite absorber layer
- Perovskite-silicon tandem cells, which stack perovskite on top of silicon
- Flexible perovskite cells, designed for lightweight and bendable applications
- Semi-transparent perovskite cells, aimed at windows and building surfaces
The variety matters because “commercial ready” can mean different things depending on the application. A flexible charger for indoor light has different durability needs than a rooftop panel expected to last for decades.
How Perovskite Solar Cells Work
All solar cells do the same basic job: convert sunlight into electrical energy. Perovskite solar cells do this using a thin absorber that captures photons and turns them into mobile charges.
When sunlight hits the perovskite layer, the material absorbs light very efficiently and generates pairs of negative and positive charges. These charges need to be separated and guided into an external circuit. That is where supporting layers come in.
A typical perovskite cell includes:
- A perovskite absorber layer that captures light
- An electron transport layer that moves electrons toward one electrode
- A hole transport layer that moves positive charges toward the other electrode
- Electrodes that collect the charges and deliver usable electricity
Perovskites can achieve high efficiencies partly because they absorb a broad range of the solar spectrum with minimal material thickness. This thinness is also a double-edged sword, because thin layers can be more vulnerable to moisture, heat, and manufacturing defects if they are not engineered and encapsulated correctly.
Efficiency Breakthroughs That Changed the Industry
Perovskites are famous for their rapid efficiency rise. In a relatively short time, lab devices moved from modest performance to competing with mainstream silicon. This speed is unusual in solar technology, which typically improves gradually.
Even more important than single-junction performance is the rise of tandem cells. A tandem design stacks a perovskite layer over a silicon cell. The two layers absorb different parts of the spectrum, allowing the combined device to harvest more energy from the same sunlight.
Efficiency is a strong signal of potential. It tells you the technology can compete on output per square meter, which is crucial for rooftops, buildings, and land-constrained solar farms.
But efficiency is not the finish line. Commercial solar is not a lab contest. The market rewards technologies that can deliver consistent output for years, handle real weather, pass certifications, and be financed at scale. That is why perovskite commercialization is less about record numbers and more about reliability, repeatability, and bankability.
Key Advantages Of Perovskite Solar Cells
Perovskites have several advantages that keep them at the center of solar innovation. Many of these advantages are not incremental. They can change where and how solar power is deployed.
Lower Manufacturing Cost Potential
Silicon panels require energy-intensive steps such as high-temperature processing and wafer slicing. Perovskite layers can, in principle, be deposited at lower temperatures and with less material waste. If manufacturers can scale production with high yield, the cost structure could be highly competitive.
Lightweight And Flexible Form Factors
Perovskite devices can be made on lightweight substrates, enabling flexible or semi-flexible modules. This can open new markets where traditional glass-and-aluminum panels are too heavy or too rigid.
Strong Performance In Challenging Light
Perovskites can be engineered to perform well in low-light conditions and under indoor illumination. This is promising for small devices, sensors, and the growing ecosystem of connected electronics.
Tandem Upgrades For The Existing Solar Industry
Perovskite-on-silicon tandem modules can build on today’s silicon manufacturing base. Instead of replacing the solar industry, perovskites can enhance it by boosting efficiency beyond what silicon can achieve alone.
These advantages explain why so many research teams, startups, and large manufacturers have invested heavily. They also explain why the phrase perovskite solar cells commercial ready keeps coming back into the conversation.
The Biggest Barriers To Commercial Readiness
Perovskites can be brilliant in the lab and still fail commercially. Solar panels live outdoors. They face heat, cold, humidity, UV exposure, wind, dust, and mechanical stress. A commercially ready solar technology must survive these stresses while delivering predictable performance over time.
Stability And Degradation
The most cited barrier is long-term stability. Many perovskite materials degrade when exposed to moisture or oxygen. Heat and strong illumination can accelerate changes in the material structure, leading to lower output.
In real-world terms, this means a module might start strong and then lose performance faster than buyers or financiers are willing to accept.
Sensitivity To Moisture, Heat, And UV
Perovskite layers can be sensitive to:
- Humidity and water vapor penetration
- Thermal cycling, such as hot days and cool nights
- UV exposure, depending on device architecture and materials
- Chemical reactions at interfaces between layers
Encapsulation helps, but the encapsulation itself must be durable, scalable, and cost-effective. A perfect lab seal is not the same as a manufacturable seal that survives 20 years on a roof.
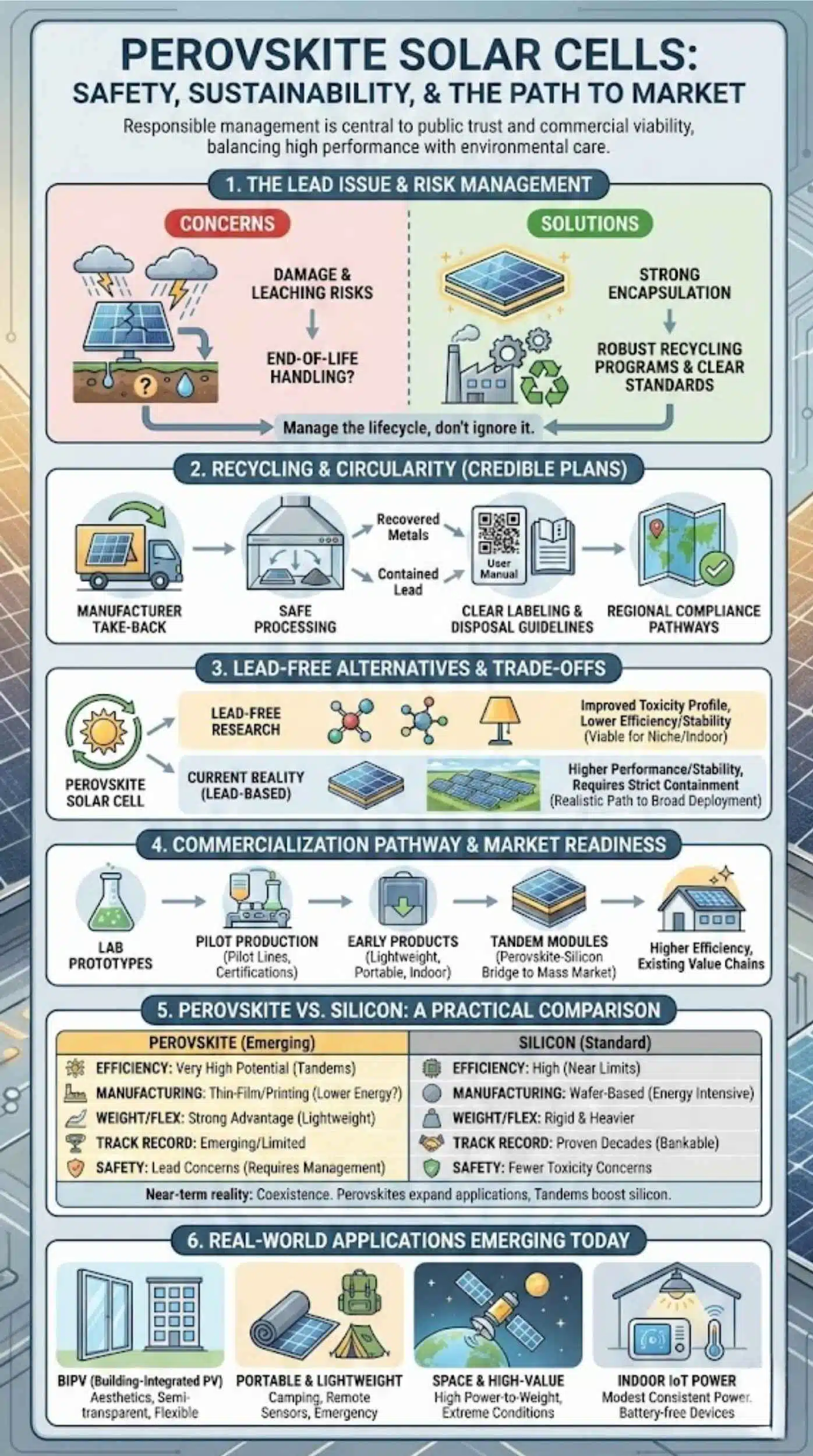
Lead Content And Regulatory Pressure
Many high-performing perovskite formulations include lead. This creates a major perception and policy challenge, even if the amount of lead is small and sealed within a module.
Regulators, installers, and consumers want clarity on safety during normal use, during storms or fires, and at end-of-life disposal or recycling.
Manufacturing Consistency And Yield
Commercial solar requires massive scale. Manufacturers need high yield, consistent film quality, and minimal defects. Perovskite layers can be sensitive to small changes in deposition conditions, solvents, and ambient environment.
A technology is not commercial ready if it only works when produced slowly under tightly controlled lab conditions. True readiness requires stable production lines that can deliver millions of consistent units.
Recent Breakthroughs Solving Stability And Durability
The story of perovskite progress is not just about efficiency. The most meaningful advances for commercialization are happening in stability engineering, materials tuning, and encapsulation design.
Better Encapsulation Approaches
Encapsulation is evolving from “seal it and hope” to system-level engineering. Modern approaches focus on:
- Multi-layer barrier films that slow moisture and oxygen ingress
- Improved edge seals, where degradation often begins
- UV-resistant encapsulants that remain stable outdoors
- Integration methods that protect both the cell and electrical interconnects
Encapsulation is also being designed with manufacturability in mind, because a solution that cannot scale is not a solution.
Materials Engineering And Additives
Researchers and manufacturers have improved stability by modifying the perovskite composition and adding stabilizing ingredients. These changes can reduce defect density and slow degradation pathways.
Another important trend is interface engineering. Many failures begin at the boundaries between layers, where chemical reactions or ion movement can occur. Stabilizing these interfaces can dramatically improve lifetime.
From Lab Stability To Real-World Exposure
Commercial readiness depends on field-relevant testing, not just short lab demonstrations. The industry is moving toward:
- Longer stress tests under heat and humidity
- Outdoor exposure trials across different climates
- Performance monitoring over seasons rather than weeks
- Failure analysis that leads to redesign, not just better reporting
This is also where tandem designs matter. A perovskite layer that is stable enough for tandem integration can ride on mature silicon module packaging and testing traditions, which may accelerate market acceptance.
Are Perovskite Solar Cells Safe And Sustainable?
Safety and sustainability are not afterthoughts in solar. They are central to public trust and policy support.
Understanding The Lead Issue
The lead debate is nuanced. Many perovskite devices use lead-based compounds because they deliver high performance and better stability than many lead-free alternatives today.
Key concerns include:
- What happens if a module is damaged during a storm
- Whether lead can leach into soil or water
- How panels are handled at end-of-life
- Whether recycling infrastructure exists and is enforced
A practical commercialization path involves strong encapsulation, robust recycling programs, and clear standards that address worst-case scenarios, not just normal operation.
Recycling And End-Of-Life Planning
A technology can be commercially successful and still fail socially if end-of-life issues are ignored. For perovskites, credible plans include:
- Take-back programs from manufacturers
- Recycling processes that recover metals and safely handle lead
- Clear labeling and disposal guidelines for installers and owners
- Compliance pathways that match regional environmental laws
Lead-Free Perovskites And Alternatives
Lead-free perovskite research continues, but it often trades efficiency and stability for improved toxicity profiles. Over time, lead-free options may become viable for certain use cases, especially in indoor devices or niche markets.
For now, the realistic path to broad deployment is not “pretend lead does not exist.” It is “control it, contain it, and manage the lifecycle responsibly.”
Current Commercialization Efforts And Market Players
If you want to judge whether perovskites are commercially ready, watch what companies do, not just what press releases say. Commercial readiness shows up in pilot lines, product warranties, certifications, and repeat orders.
Pilot Production And Early Products
Many commercialization efforts follow a predictable route:
- Build lab-scale prototypes
- Move to pilot-scale manufacturing
- Produce early modules for limited deployments
- Validate performance under real conditions
- Expand capacity once yield and durability stabilize
Some of the earliest products are likely to appear in markets where lightweight, portability, or indoor performance matters more than 25-year lifetimes.
Tandem Modules As The Bridge To Mass Market
Perovskite-silicon tandem modules have a strong commercialization logic. They can deliver higher efficiency while fitting into many existing solar value chains.
If tandem modules can prove long-term stability and manufacturable yield, they may become the primary way perovskites enter mainstream rooftops and utility solar.
Perovskite Vs Silicon Solar Cells
Silicon remains the industry standard for good reasons. It is proven, it lasts, and it has massive supply chains. Perovskites need to compete not only on performance but on trust.
Here is a practical comparison for decision-making.
| Factor | Perovskite Solar Cells | Silicon Solar Cells |
| Efficiency Potential | Very high, especially in tandems | High, but nearer mature limits |
| Manufacturing Path | Thin-film coating and printing potential | Wafer-based, energy-intensive |
| Weight And Flexibility | Strong advantage in lightweight designs | Generally rigid and heavier |
| Long-Term Field Track Record | Still emerging | Proven over decades |
| Bankability Today | Limited, improving | Strong and widely accepted |
| Safety Concerns | Lead in many formulations | Fewer toxicity concerns |
Perovskites can win on efficiency and form factor. Silicon wins on durability history and financing confidence. The likely near-term reality is coexistence, where perovskites expand what solar can do and tandems push efficiency beyond the silicon ceiling.
Real-World Applications Emerging Today
Commercial readiness is not one single threshold. It depends on use case.
Building-Integrated Photovoltaics
Perovskites can be made semi-transparent and tuned for aesthetics. That makes them interesting for windows, façades, and architectural features where traditional panels are awkward.
BIPV also values higher efficiency per surface area and flexible formats. It is a natural early market if durability targets can be met.
Portable And Lightweight Solar
Lightweight perovskite modules can serve:
- Camping and emergency chargers
- Remote sensors and temporary installations
- Devices that cannot carry heavy glass modules
These products may accept shorter warranties than rooftops, making them a plausible early commercialization segment.
Space And High-Value Specialized Uses
Space applications value high power-to-weight ratios. If stability under radiation and thermal extremes can be proven, perovskites may find roles in satellites and aerospace systems where costs can be justified.
Indoor Power For IoT
Many IoT sensors and small electronics need modest, consistent power indoors. Perovskites can be tuned for indoor spectra, potentially enabling battery-free or battery-assisted devices in offices, factories, and smart buildings.
These segments matter because they allow manufacturers to build experience, scale production, and improve reliability before going head-to-head with conventional rooftop panels.
Regulatory, Certification, And Bankability Challenges
Even if a panel works technically, it still must pass the commercial gatekeepers.
Certification And Testing Requirements
Solar modules typically need standardized testing for safety and performance. These tests are designed around outdoor durability and long-term reliability expectations.
Perovskite modules must demonstrate:
- Electrical safety under real operating conditions
- Resistance to heat, humidity, and thermal cycling
- Mechanical durability and encapsulation integrity
- Predictable performance degradation behavior
Passing tests is not enough. The industry also wants consistency across production batches, which ties back to manufacturing yield and quality control.
What Bankability Really Means
Bankability is the ability to secure financing based on trusted performance, warranties, and supplier stability. For utility solar, this is often the deciding factor.
Bankability usually depends on:
- Long-term field data, ideally across climates
- Strong product warranties backed by credible balance sheets
- Clear failure rates and degradation curves
- Insurance and risk models that can price the technology
This is why perovskite adoption may start in smaller deployments and niche markets. Over time, as data accumulates, financing becomes easier.
When Will Perovskite Solar Cells Be Fully Commercial?
This is the hardest question because “commercial” is not binary. It is a spectrum, and different markets move at different speeds.
Short-Term Adoption Scenarios
In the near term, perovskites are most likely to expand in:
- Indoor and low-light devices
- Lightweight and portable modules
- Limited deployments with performance monitoring
- Tandem modules in controlled rollout programs
These are settings where the value proposition is strong and risk tolerance is higher.
Medium-Term Mass Production Outlook
For mass-market rooftops and utility farms, the key milestones are:
- Consistent manufacturing yield at scale
- Proven multi-year outdoor stability
- Widely recognized certification and quality standards
- Bankability supported by insurers and lenders
If these are met, the phrase perovskite solar cells commercial ready will move from a headline to a purchasing reality.
What Could Accelerate Or Delay The Timeline
Acceleration tends to come from:
- Reliable tandem modules that leverage existing silicon packaging
- Strong partnerships with established solar manufacturers
- Standardized testing frameworks tailored to perovskites
- Clear end-of-life and recycling infrastructure
Delays tend to come from:
- Unresolved degradation pathways under real climates
- Quality control challenges in high-throughput manufacturing
- Regulatory friction around lead and disposal
- Lack of financing confidence without long-term data
What This Means For The Future Of Solar Energy
Perovskites are not just “another panel option.” They represent a new design space for solar.
If perovskites reach mature commercialization, the biggest impacts may include:
- Higher efficiency modules that reduce land and roof area needs
- New solar surfaces, including windows and lightweight structures
- Lower manufacturing energy requirements, depending on final processes
- Faster innovation cycles due to material tunability
Perovskite tandems could also help solar scale faster by making every square meter of installed solar more productive. That matters in crowded urban areas and in regions where grid expansion and land access are limiting factors.
Are Perovskite Solar Cells Finally Ready?
So, are perovskites ready today in the way silicon is ready. Not yet. Silicon has decades of field performance, mature global supply chains, and financing structures that perovskites are still building.
But it is no longer accurate to treat perovskites as a distant science project. Across pilot lines, tandem development, and early applications, the industry is actively converting breakthroughs into products. In several segments, the core question is no longer whether perovskites work. It is whether durability, manufacturing yield, and bankability can mature fast enough to support scale.
The most evergreen answer is this: perovskite solar cells commercial ready is becoming true in stages. For niche and controlled applications, readiness is arriving first. For mainstream rooftops and utility-scale deployments, readiness will hinge on multi-year outdoor reliability data, standardized certifications, and proven manufacturing consistency.