Ever struggled with delays in getting products from factories to stores? Slow supply chains can hurt businesses and frustrate customers. Knowing the best-performing countries helps companies plan better.
Norway tops the list for supply chain efficiency, thanks to strong logistics and risk management. Other leaders like Germany and Japan use technology and smart strategies to keep goods moving fast.
This blog reveals the 10 Countries With The Most Efficient Supply Chains and why they succeed. Read on to learn their secrets.
Key Takeaways
- Norway tops the list for supply chain efficiency. It excels in logistics and risk management. The country’s strong infrastructure keeps goods moving fast.
- Germany ranks high due to its advanced transport networks and tech. It scores well on the FM Global Resilience Index (2023). Automation and free trade deals boost exports like automotive parts and electronics.
- Switzerland uses blockchain and ERP systems to cut risks. It came second in the 2015 FM Global Resilience Index. Its stable economy helps global brands avoid disruptions.
- The Netherlands relies on ports like Rotterdam for trade success. Automated warehouses and intermodal transport keep shipping smooth. Low import duties and FTAs help businesses grow easily here too!
- Japan leads with robotics, IoT, AI tools—ranked highly by FM Global Resilience data as well! Companies like Toyota show how automation speeds up production lines while cutting costs significantly each year since starting these methods decades ago now already passed us all by quickly enough without notice until recently perhaps?
Germany: Excellence in Logistics and Infrastructure
Germany leads in supply chain efficiency thanks to top-notch logistics and infrastructure. Strong transport networks, like highways and railways, keep goods moving fast. The country scores high on the FM Global Resilience Index for reliable supply chains.
Its inventory turnover rates are impressive, cutting costs while keeping shelves stocked.
Key industries like automotive parts and electronics manufacturing thrive here. Warehousing is smooth with advanced systems such as automated guided vehicles and warehouse management tools.
Free trade agreements boost global connections, making exports easy. Germany’s approach blends tech, skilled workers, and strong governance for unmatched results in supply chain management.
Switzerland: Stability and Advanced Supply Chain Systems
Switzerland ranks high for supply chain efficiency, thanks to strong infrastructure and logistics. It came second in the 2015 FM Global Resilience Index. The country excels in economic stability, making it a reliable hub for global supply chains.
Businesses benefit from its advanced systems like ERP and inventory management tools. Risk management is top-notch, reducing disruptions from natural hazards or political shifts.
The Swiss keep their supply chains smooth with automation and blockchain technology. Sustainable practices drive their textile and consumer electronics sectors. Free trade zones and agreements boost international shipping.
Their workforce stays skilled despite challenges like an aging population. Data analytics helps companies track freight without delays. This precision makes Switzerland a leader in lean manufacturing and security for global brands.
Netherlands: A Strategic Logistics Hub in Europe
The Netherlands packs a punch in global logistics. Its ports, like Rotterdam, handle massive cargo volumes, making it Europe’s top gateway for trade. The country’s advanced infrastructure, including highways and rail networks, keeps goods moving fast.
Automated systems and warehouse management boost efficiency. The Dutch lead in intermodal transport, connecting ships, trucks, and trains seamlessly. Free trade agreements (FTAs) and low import duties help businesses thrive.
Policymakers focus on energy transition and sustainability, keeping supply chains future-proof. The Netherlands proves small size doesn’t limit big impact in global trade.
Key industries like electronics manufacturing and consumer goods benefit from this setup. The FM Global Resilience Index ranks the country highly for supply chain strength. With smart tech and strategic planning, the Netherlands stays ahead of the game.
Japan: Technological Innovation and Supply Chain Resilience
Japan leads in supply chain resilience with cutting-edge tech. The country uses robotics, IoT, and AI to streamline manufacturing and logistics. Big companies like Toyota automate production lines for efficiency.
This keeps costs low and quality high.
The FM Global Resilience Index ranks Japan among the top for strong supply chains. Its factories produce electronics, automotive parts, and consumer goods with precision. Advanced warehouse management systems track inventory in real time.
By 2030, robots will work alongside human managers more widely. This blend of innovation and tradition keeps Japan’s economy stable amid global challenges.
United States: Integration of Technology and Productivity
The United States excels in blending cutting-edge tech with top-tier productivity. Companies like ShipBob use automation to speed up fulfillment, offering real-time tracking and smart inventory management.
This gives brands the power to match giants like Amazon by slashing delivery times. For example, Our Place saved $1.5 million in freight costs while getting orders to customers in just 2.5 days.
The country’s focus on enterprise resource planning and electronic data interchange keeps supply chains agile, even under pressure from labor shortages or inflation risks tied to policies like the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA).
American manufacturers innovate relentlessly, especially in electronics and automotive sectors where tools like AGVs and conveyors streamline production. Third-party logistics providers, such as C.H.
Robinson, help businesses scale up without drowning in purchase orders or invoices. Strategic sourcing boosts efficiency for everything from consumer goods to copper mines, though challenges like counterfeit products persist.
With ecommerce booming, firms automate processes while tackling aging workforce issues head-on—proving tech isn’t just a fix but a foundation for lasting growth.
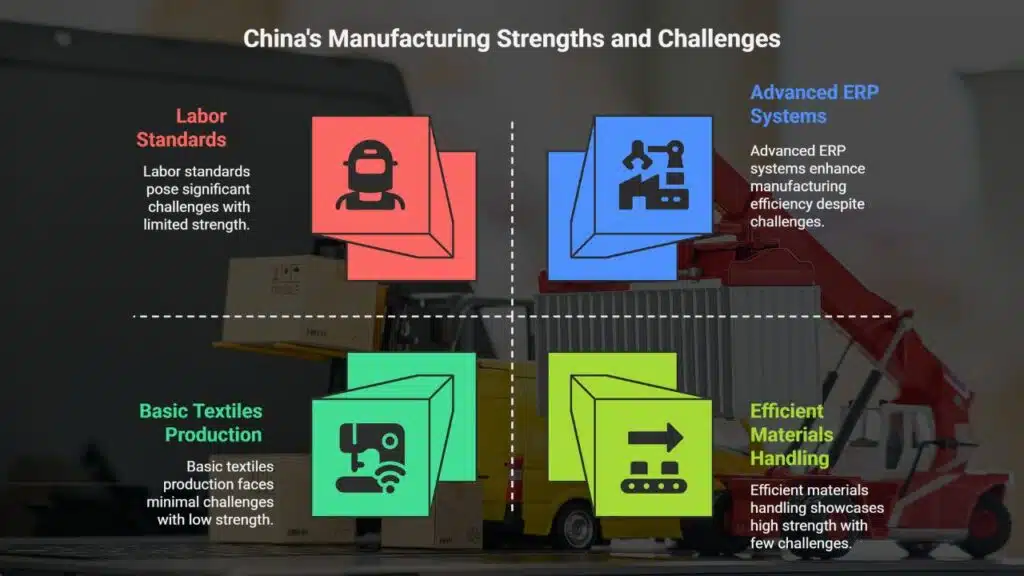
China: Scale and Global Manufacturing Powerhouse
China dominates global manufacturing with unmatched scale. Its supply chains produce everything from electronics to textiles, feeding demand worldwide.
Factories here rely on advanced ERP systems and automation. Programs like “Made in China 2025” boost tech innovation, especially in electric vehicles and consumer goods.
The Belt and Road Initiative expands trade routes, speeding up deliveries. Ports handle millions of containers, linking China to ASEAN countries and beyond. Companies like Lenovo and Samsung thrive thanks to efficient materials handling.
Yet challenges exist, like labor standards and environmental concerns. Despite this, China remains a key player in footwear production, ready-made garments, and electronics manufacturing.
The FM Global Resilience Index ranks it strong in supply chain resilience, proving its adaptability.
Third-party logistics firms streamline operations, while WMS tools keep warehouses running smoothly. From Shein’s fast fashion to Huawei’s telecom gear, China’s supply chain power is hard to beat.
Singapore: World-Class Port and Trade Efficiency
Singapore thrives as a global supply chain leader. Its port handles over 37 million shipping containers yearly, making it one of the busiest in the world.
The country’s seamless trade efficiency stems from smart logistics and strong foreign investment. Automated systems like electronic data interchange (EDI) streamline customs clearance, cutting delays.
Partnerships with third-party logistics providers ensure fast deliveries for consumer goods and electronics manufacturing exports. Singapore’s resilience shines through its strict safety regulations and economic stability, keeping disruptions low even during crises.
Companies use ShipBob-like technology here to track inventory in real-time, slashing costs while boosting speed. With world-class infrastructure and discounted shipping rates, Singapore helps businesses compete globally—no wonder it ranks high on the FM Global Resilience Index year after year.
South Korea: Advanced Technology and Export Expertise
South Korea stands tall as a global leader in supply chain efficiency. Its strength lies in cutting-edge tech and a strong export economy. The country dominates electronics manufacturing, producing top-tier consumer electronics like smartphones and semiconductors.
Big names like Samsung and LG drive innovation, using AI and robotics to streamline production. These tools cut costs and boost productivity, keeping South Korea ahead. The nation’s ports, like Busan, handle massive trade volumes with precision.
Third-party logistics firms play a key role, ensuring smooth movement of goods worldwide.
The garment industry and footwear production also thrive here, thanks to skilled labor and smart automation. South Korea’s supply chain resilience shines during disruptions, adapting quickly to shifts in global demand.
Businesses leverage IoT and big data for real-time tracking, reducing delays. The government supports exporters with policies that encourage growth. From automotive parts to ready-made garments, South Korea’s supply chain is a well-oiled machine.
Its success comes from blending tech, skilled workers, and smart business strategy.
Takeaways
Efficient supply chains keep the world moving. Countries like Germany and Japan lead with strong logistics, while Singapore and the Netherlands shine as trade hubs. Tech-driven nations such as South Korea and the U.S. boost productivity through automation.
No system is perfect, but these ten countries set the bar high. Whether it’s shipping coffee or electronics, their networks deliver—fast and smart.
FAQs
1. Which countries have the most efficient supply chains?
Countries with strong supply chain resilience include those leading in electronics manufacturing, automotive parts, and consumer goods. They often rely on third-party logistics and automation to stay ahead.
2. How do supply chains handle consumer electronics and textiles?
Efficient supply chains, like those in footwear production and ready-made garments (RMG), use automation to speed up processes. This helps meet demand while keeping costs low.
3. Why is supply chain resilience important for economic stability?
A strong global supply chain prevents delays in goods like coffee or automotive parts. It also helps businesses adapt to sudden changes, like shifts in consumer demand.
4. Can small businesses benefit from efficient supply chains?
Yes. Even small firms can use consultants or LTL shipping to improve their supply chain. Automation helps them compete with bigger players in industries like textiles manufacturing.
5. What challenges do supply chains face today?
Environmental concerns and labor issues, like those in the Rust Belt or Vietnamese factories, can disrupt production. Companies must balance speed, cost, and sustainability.