Listen to the Podcast:
Industry 4.0 and Smart Factory are two terms that have gained a lot of attention in recent years, particularly in the manufacturing industry. They represent the convergence of digital technologies and traditional manufacturing processes, and they have the potential to transform the way we design, produce, and deliver products.
The term Industry 4.0 was first coined in 2011 by the German government as part of a plan to promote the digitization of manufacturing processes. It builds on previous industrial revolutions, which saw the introduction of steam power, electricity, and computers into manufacturing processes. Industry 4.0 represents the fourth industrial revolution, characterized by the integration of physical and digital systems.
Smart Factory, on the other hand, refers to a manufacturing environment that is fully connected and optimized through the use of digital technologies. It is an advanced manufacturing facility that utilizes Real-Time Manufacturing Analytics Software to improve productivity, efficiency, and flexibility.
The Significance of Industry 4.0 and Smart Factory
The significance of Industry 4.0 and Smart Factory lies in their ability to enable manufacturers to optimize their production processes, improve product quality, and reduce costs. By leveraging technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), and cloud computing, manufacturers can gain real-time insights into their operations, enabling them to make faster and more informed decisions.
The evolution of Industry 4.0 and Smart Factory has been driven by the rapid advancement of digital technologies and the increasing demand for more efficient and sustainable production processes. As the manufacturing industry evolves, it is becoming clear that companies able to embrace these new technologies and processes will be best positioned to thrive in the years ahead.
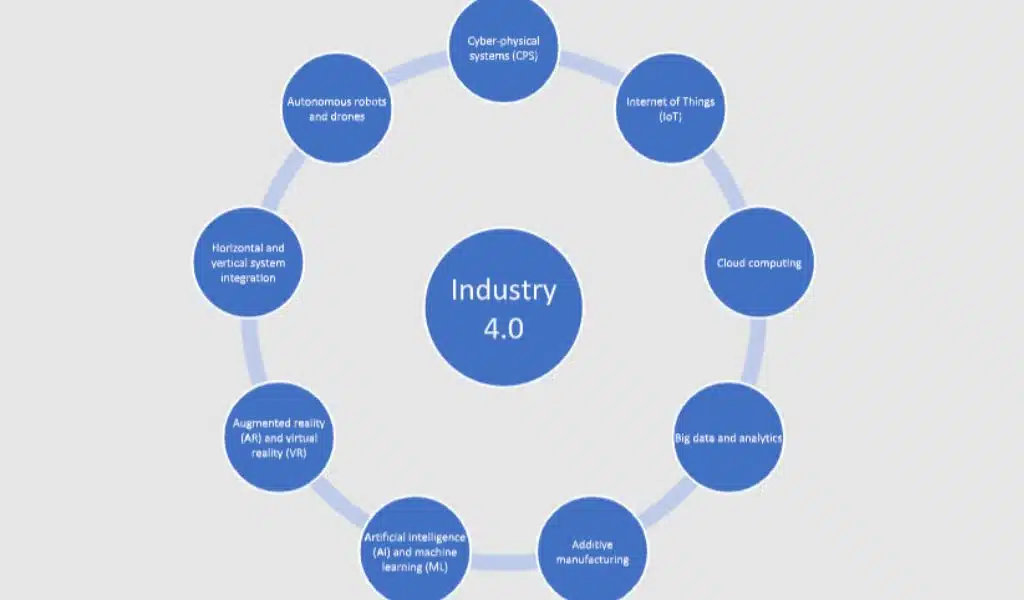
Nine Key Components of the Industry 4.0 Revolution
Implementing these components offers a range of benefits, including improved production efficiency, reduced downtime, increased flexibility, and better decision-making. By using these technologies and processes, manufacturers can optimize their operations and stay competitive in a rapidly changing marketplace.
A Smart Factory is a production facility that uses digital technologies to optimize production processes and supply chain operations. It is a system that combines the latest technologies, such as AI/ML, IoT, Data & Analytics with traditional manufacturing processes to create a flexible, adaptable, and responsive production environment.
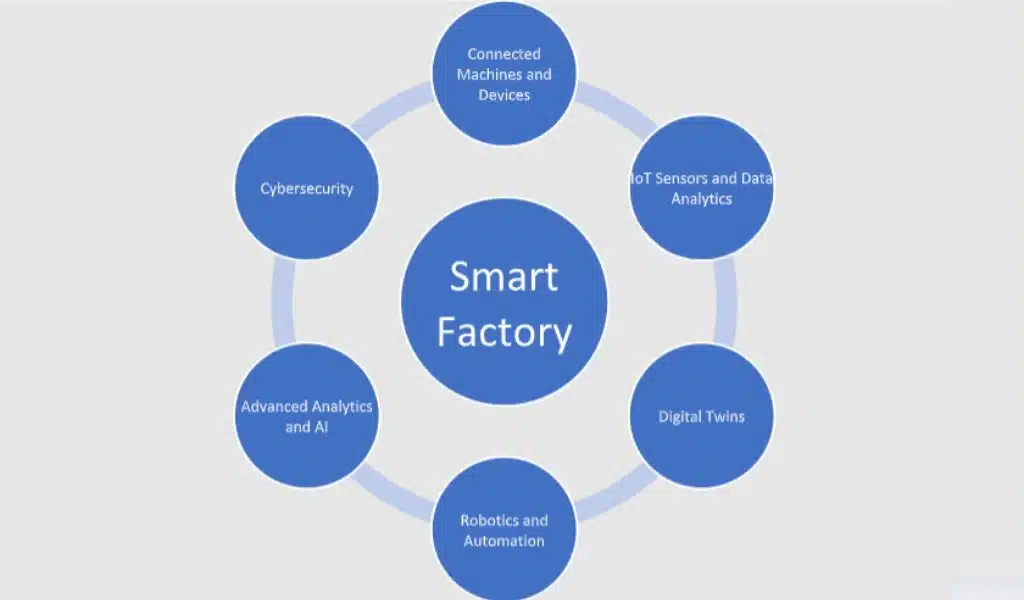
Key Components of a Smart Factory
The benefits of implementing a Smart Factory include increased efficiency, reduced downtime, better quality control, improved safety, and reduced costs. By using these advanced technologies and processes, manufacturers can optimize their operations and improve their bottom line.
Key Technologies are Driving the Adoption of Industry 4.0 and Smart Factory:
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI and ML technologies are used to analyze data and make predictions based on that data. In a manufacturing environment, these technologies can be used to optimize production schedules, reduce downtime, and improve quality control.
Cloud Computing and Data Analytics: Cloud computing enables manufacturers to access data and applications from anywhere at any time. Data analytics allows manufacturers to analyze enormous amounts of data and gain insights that can improve production efficiency and reduce costs.
Internet of Things (IoT): IoT refers to the network of physical devices, vehicles, and other objects that are embedded with sensors, software, and network connectivity. In a manufacturing environment, IoT devices can be used to monitor equipment performance, track inventory, and optimize production processes.
Future Prospects of Industry 4.0 and Smart Factory
The future prospects for Industry 4.0 and Smart Factory are bright. The global Industry 4.0 market size to grow from USD 130.90 billion in 2022 to USD 377.30 billion by 2029, growing at CAGR of 16.3%.
The market for Smart Factory technologies is also expected to grow rapidly, Smart Factory Market Size to Hit USD 138 Billion By 2030 Growing at a 5.23% CAGR – Report by Market Research Future (MRFR)
The adoption of these is expected to transform the manufacturing industry in the coming years. By integrating digital technologies into production processes and supply chain operations, manufacturers can optimize efficiency, reduce costs, and improve product quality. Some of the key trends that are likely to shape the future of Industry 4.0 and Smart Factory include:
Increased Automation: Automation is likely to play a key role in the future of manufacturing. Autonomous robots and drones are expected to become more prevalent in manufacturing environments, taking over repetitive tasks, and improving efficiency.
Digital Twins: Digital twins are virtual replicas of physical systems that can be used to simulate and optimize production processes. This technology is expected to become more prevalent in manufacturing environments, allowing manufacturers to test and optimize production processes before implementing them in the real world.
Increased Connectivity: The trend towards increased connectivity is likely to continue in the coming years, as manufacturers seek to integrate their operations with the broader supply chain. This will require increased collaboration between manufacturers, suppliers, and customers.
Edge Computing: Edge computing refers to the processing of data at the edge of the network, closer to where the data is generated. This technology is likely to become more prevalent in manufacturing environments, allowing manufacturers to process data in real-time and make faster, more informed decisions.
In addition to these trends, there are several other factors that are likely to shape the future of Industry 4.0 and Smart Factory. For example, sustainability is becoming an increasingly important consideration for manufacturers, as consumers and governments alike demand more sustainable production processes. As a result, we are likely to see an increase in the adoption of technologies that enable more sustainable production, such as renewable energy and circular economy models.
Another key factor that is likely to shape the future of Industry 4.0 and Smart Factory is the continued advancement of AI and machine learning technologies. These technologies are already being used to optimize production processes and improve product quality, but they are expected to become even more sophisticated in the coming years. This will enable manufacturers to gain even deeper insights into their operations and make even more informed decisions.
In conclusion, Industry 4.0 and Smart Factory are set to transform the manufacturing industry in the coming years. By implementing these modern technologies and processes, manufacturers can improve efficiency, increase productivity, and reduce costs. The key to success in this new era of manufacturing will be a willingness to embrace change and a commitment to continuous improvement. As the manufacturing industry continues to evolve, it will be those companies that are able to adapt and innovate that will thrive in the years ahead.