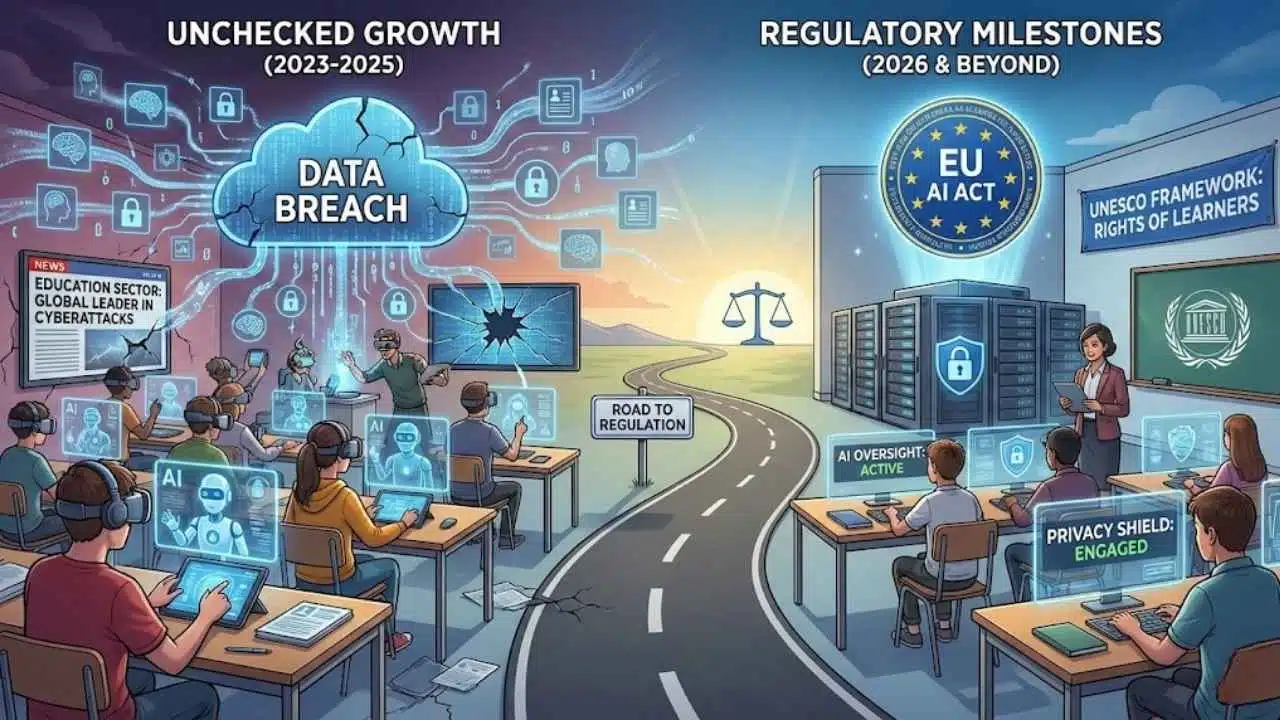
The “wild west” era of AI in the classroom is officially ending. As of early 2026, the full implementation of the EU AI Act and new UNESCO guidelines are forcing a collision between trillion-dollar EdTech innovations and the fundamental rights of students. We are no longer just asking “Can AI teach?”; we are legally mandating “Should AI watch?” This shift marks a critical turning point where global standards are finally catching up to algorithmic adoption, threatening to upend business models and reshape pedagogy worldwide.
Key Takeaways
The era of unregulated AI experimentation in schools is over. The new global standards represent a mature, albeit painful, realization that while we want our students to be smart, we also need them to be safe. The future of EdTech belongs to those who can innovate within the guardrails of privacy, not those who try to break them.
- Regulatory Tsunami: The EU AI Act’s full enforcement for “High-Risk” education systems begins August 2, 2026, forcing a massive compliance overhaul for grading and admission algorithms.
- The Security Crisis: In 2025, the education sector became the world’s most attacked industry, enduring 4,388 cyberattacks per week per organization, driving the urgent demand for these new privacy standards.
- Economic Divide: A “Compliance Gap” is emerging where wealthy schools access secure, sovereign AI clouds, while underfunded districts risk using non-compliant, predatory tools.
- Pedagogical Pivot: New laws like California’s SB 243 now mandate AI transparency, shifting the curriculum from “using AI” to “auditing AI.”
The Road to Regulation: How We Got Here
The integration of Artificial Intelligence into education was initially hailed as the “great equalizer,” promising personalized tutors for every child and automated grading to free up teachers. From 2023 to 2025, the market saw an explosion of Generative AI tools—from “empathetic” chatbots to predictive analytics platforms that claimed to forecast student failure before it happened.
However, this unchecked growth created a surveillance paradox. By late 2025, the education sector had become the global leader in data breaches, enduring an average of 4,388 cyberattacks per organization every week. High-profile disasters, such as the late 2024 breach of major student information systems and the 2025 ransomware attack on Chicago Public Schools, exposed the sensitive data—from medical records to behavioral logs—of millions of minors.
The tipping point arrived with two major regulatory milestones: the full enforcement of the EU AI Act in mid-2026, which classifies education as a “High-Risk” sector, and the release of UNESCO’s 2025 “Protecting the Rights of Learners” framework. These events have moved the conversation from theoretical ethics to hard compliance, forcing governments and corporations to draft the global standards we are analyzing today.
The Friction Between Code and Classroom
The “High-Risk” Designation and Compliance Shock
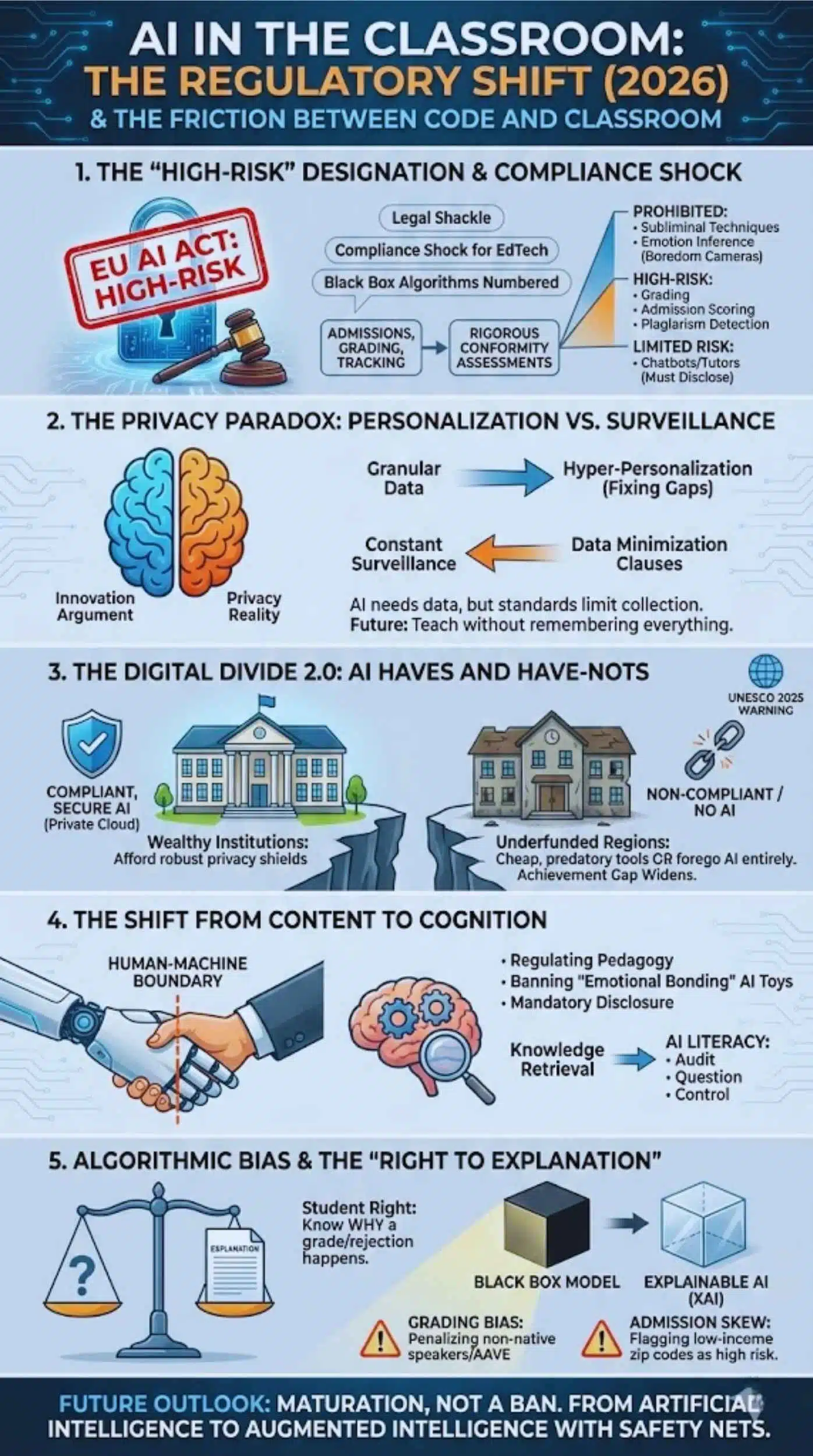
The defining feature of the new global standards is the classification of educational AI as “High-Risk.” This is not merely a label; it is a legal shackle. Under the EU AI Act and aligned global frameworks, any AI system used for admissions, grading, or tracking student progress must now undergo rigorous conformity assessments.
This has created a “compliance shock” for the EdTech industry. Startups that built their models on “move fast and break things” are finding that they cannot afford the transparency logs and human oversight mechanisms now required. The days of “black box” algorithms determining a student’s academic trajectory are legally numbered.
Key Regulation Breakdown
- Prohibited: AI that uses subliminal techniques or infers emotions (e.g., cameras tracking if a student looks “bored”).
- High-Risk: AI used for grading, admission scoring, or plagiarism detection.
- Limited Risk: Chatbots and tutors (must disclose they are machines).
The Privacy Paradox: Personalization vs. Surveillance
The central ethical conflict lies in the mechanism of AI itself. To function well, an AI tutor needs data—lots of it. It needs to know a student’s weak spots, their learning pace, and perhaps even their frustration levels.
- The Innovation Argument: Granular data allows for “hyper-personalization,” fixing learning gaps in real-time.
- The Privacy Reality: This requires constant surveillance. New standards are drafting “Data Minimization” clauses that strictly limit what can be collected. The analysis suggests a future where AI must learn to teach without remembering everything about the student—a technical hurdle many platforms are currently failing to clear.
The Digital Divide 2.0: AI Haves and Have-Nots
While regulations aim to protect students, analysts warn of an unintended consequence: the “Compliance Gap.” Wealthy institutions and nations will afford compliant, high-end AI systems with robust privacy shields (like Apple’s Private Cloud Compute).
Conversely, underfunded schools in developing regions may be left with two choices:
- Use cheap, non-compliant, and potentially predatory AI tools.
- Forego AI entirely, widening the educational achievement gap. UNESCO’s 2025 report explicitly highlights this risk, warning that privacy regulation must not become a luxury good that only the Global North can afford.
The Shift from Content to Cognition
The new standards are not just regulating software; they are implicitly regulating pedagogy. By banning AI toys that simulate “emotional bonding” (as seen in recent California legislation) and mandating that students be informed when they are interacting with an AI, regulators are enforcing a boundary between human and machine.
This pushes the educational focus away from “knowledge retrieval” (which AI does better) toward “AI Literacy”—teaching students how to audit, question, and control the very tools attempting to teach them.
Algorithmic Bias and the “Right to Explanation”
A critical component of the new draft standards is the “Right to Explanation.” If an AI assigns a grade or rejects an admission application, the student now has the right to know why. This challenges the dominant Deep Learning models, which are often opaque. We are witnessing a market pivot toward “Explainable AI” (XAI), where interpretability is valued over raw predictive power.
Documented Bias Cases (2024-2025)
- Grading Bias: AI essay graders penalizing non-native English speakers or students using African American Vernacular English (AAVE).
- Admission Skew: Predictive algorithms flagging low-income zip codes as “high dropout risk,” unfairly denying entry to advanced programs.
How Regulation is Reshaping the EdTech Market
The impact of these regulations creates a distinct split in the market. The following tables analyze the shifting landscape.
Winners vs. Losers in the Regulated Era (2026)
| Category | The Winners | The Losers | Why? |
| Corporate | Big Tech (Microsoft, Google, Apple) | Small EdTech Startups | Big Tech has the capital to build “sovereign clouds” and fund compliance teams. Startups effectively face a “regulatory moat.” |
| Institutions | Elite Private Schools & Universities | Public K-12 & Rural Schools | Wealthy schools can license compliant, “walled-garden” AI. Public schools rely on free/cheap tools that are now banned or restricted. |
| Technology | “Offline” & Edge AI (e.g., Lego) | Cloud-Only Chatbots | Tools that process data locally on the device (Edge AI) bypass many privacy restrictions compared to cloud-dependent models. |
| Pedagogy | Human-Centric/Hybrid Models | Fully Automated “Robot Tutors” | Regulations mandate “Human-in-the-Loop.” Systems designed to replace teachers face the harshest scrutiny. |
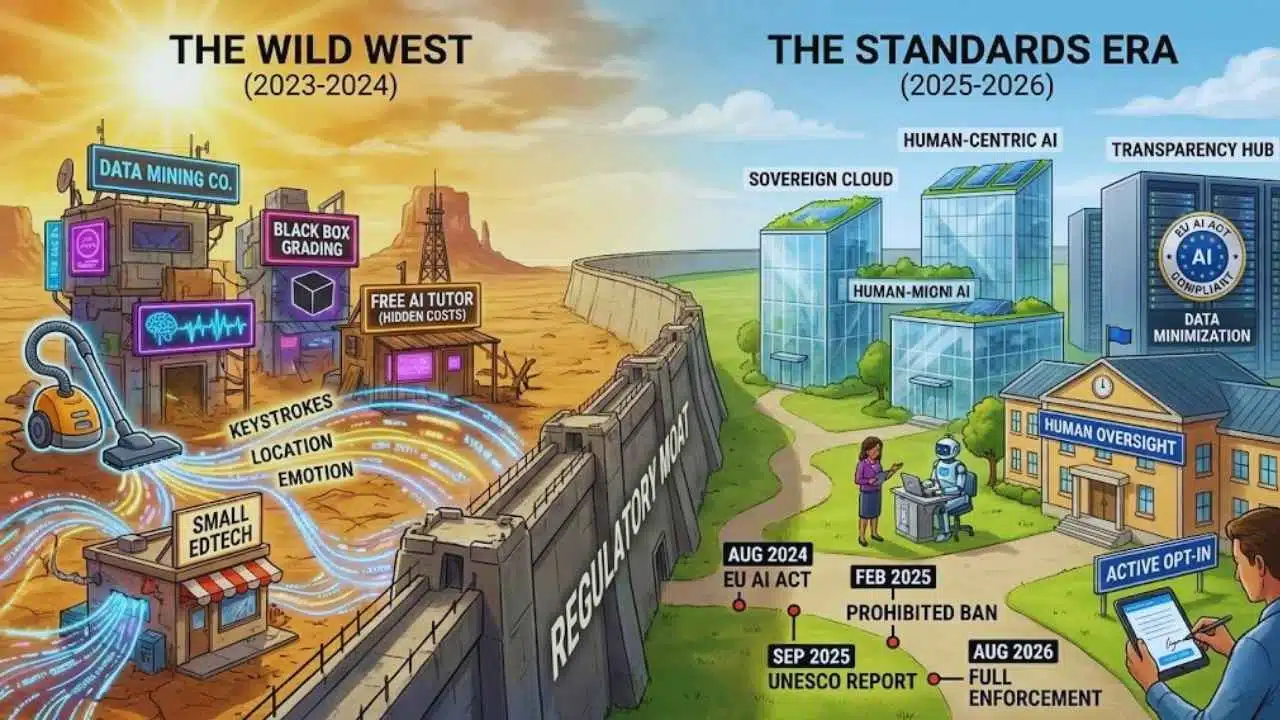
The Regulatory Shift – Before vs. After (2024-2026)
| Feature | The “Wild West” (2023-2024) | The “Standards Era” (2025-2026) |
| Data Collection | “Hoover everything” (Keystrokes, location, emotion). | Data Minimization: Collect only what is strictly necessary for the specific lesson. |
| Parental Consent | Buried in 50-page Terms of Service. | Active Opt-In: Explicit, granular consent required for AI profiling. |
| Grading | Automated “Black Box” scoring accepted. | Human Oversight: A human teacher must review and validate AI-generated high-stakes grades. |
| Transparency | Unknown if you are chatting with a bot. | Mandatory Disclosure: AI must identify itself as non-human immediately. |
Timeline of Key Regulatory Milestones
| Date | Event | Impact |
| Aug 2024 | EU AI Act Enters Force | The clock starts ticking for compliance; definitions of “High Risk” are solidified. |
| Feb 2025 | Prohibited Practices Ban | AI that uses “subliminal techniques” or “social scoring” in schools is banned in EU. |
| Sep 2025 | UNESCO “Rights of Learners” Report | Establishes the global “soft power” standard for human rights in AI education. |
| Jan 2026 | US State-Level Bans (e.g., CA) | Legislation targets “AI Toys” and surveillance, fragmenting the US market. |
| Aug 2026 | Full EU AI Act Application | Full enforcement of high-risk obligations; non-compliant EdTech faces fines up to 7% of global turnover. |
Expert Perspectives
To understand the nuance of this transition, we must look at the conflicting viewpoints shaping the debate.
- The Technocrat’s Warning: “By over-regulating, we are essentially freezing the curriculum in 2020,” argues a lead analyst from a Silicon Valley think tank. Their concern is that requiring “explainability” will force schools to use older, dumber AI models, denying students access to the cutting-edge reasoning capabilities of newer “black box” systems.
- The Human Rights Stance: “We are not impeding innovation; we are preventing experimentation on children,” counters a UNESCO ethics advisor. This perspective emphasizes that children, unlike adults, cannot meaningfully consent to data harvesting. They view the strict standards not as bureaucratic red tape, but as a digital child protection act.
- The Educator’s Reality: “I don’t need an AI to tell me a student is failing; I need resources to help them,” notes a representative from a Global Teachers Union. For educators, the focus on AI regulation is a distraction from the deeper issue: AI is often sold as a cheap alternative to hiring human teachers, a trend these standards aim to reverse by mandating human oversight.
Future Outlook: What Happens Next?
As we look toward late 2026 and 2027, the “News Analysis” suggests three key trajectories:
- The Rise of “Clean AI” Certifications: Just as we have “Organic” food labels, we will see “Fair Trade Data” or “Privacy Certified” stamps on EdTech products. Schools will procure software based on these trust signals rather than just features.
- Sovereign Education Models: Nations will stop relying on generic global LLMs (Large Language Models). We will see the rise of “National Education Models”—AI trained specifically on a country’s curriculum and cultural values, hosted on government servers to ensure data sovereignty.
- The Litigation Wave: The first major lawsuits under the new standards will likely occur in late 2026. These test cases—likely involving a student unfairly graded by an algorithm or a breach of biometric data—will set the judicial precedents that define the real-world limits of AI in the classroom.
Final Thoughts
The drafting of these standards is not a “ban” on AI, but a “maturation.” It forces a move from Artificial Intelligence to Augmented Intelligence—where the technology supports the human learner rather than mining them. For educators and policymakers, the task now is to ensure these rules create a safety net, not a ceiling, for the next generation of learners.