In the digital era, your domain is more than just a website—it’s your online identity, brand, and reputation. Whether you manage a personal blog, an e-commerce store, or a large enterprise website, your domain is a central asset that must be protected from cyber threats. Unfortunately, as the digital world expands, so does the sophistication and volume of cyber attacks.
Cybercriminals are continually finding new ways to exploit vulnerabilities, targeting domains for everything from stealing sensitive data to damaging reputations. In 2023 alone, cybercrime was estimated to cost businesses globally over $8 trillion.
This staggering figure highlights the urgency of protecting your domain against potential breaches. Effective ways to protect your domain from cyber attacks are not just optional; they are critical to ensure your online assets remain safe.
This article will take you through comprehensive and effective strategies to protect your domain from cyber threats. By the end, you will be equipped with actionable insights and techniques to safeguard your domain and ensure your digital presence remains secure.
Why Your Domain is at Risk: Understanding the Threat Landscape?
Before diving into the strategies, it’s important to understand why your domain is a prime target for cybercriminals. Cyber attacks come in various forms, each with its own set of risks and consequences. Here are the most common threats to domains:
- Domain Hijacking: Cybercriminals target registrars with weak security to gain access to domains. Once in, they can transfer ownership of the domain to themselves, leaving the rightful owner locked out of their account.
- DDoS Attacks (Distributed Denial of Service): Attackers flood your server with an overwhelming amount of traffic, causing your website to crash or become inaccessible. This results in downtime and lost revenue.
- Phishing and Malware Injections: Cyber attackers often inject malicious code into your website, which can harvest personal information from visitors or spread malware to their devices.
- DNS Spoofing: This involves manipulating DNS records to redirect users to fraudulent websites, leading to stolen credentials, financial losses, or a tarnished reputation.
- Weak Passwords: Simple or reused passwords are often the easiest way for hackers to gain access to domain registrars or hosting accounts. Once inside, they can modify or delete your domain.
Understanding these risks will help you see the critical importance of implementing security measures to protect your domain from these growing threats.
Effective Ways to Protect Your Domain from Cyber Attacks
In this section, we will explore specific, effective ways to protect your domain from cyber attacks. These methods range from basic security practices to advanced solutions. Each method is explained in simple terms to ensure you can implement them easily, no matter your technical expertise.
1. Choose a Reliable Domain Registrar and Hosting Provider
The first step in domain protection is selecting a registrar and hosting provider that prioritizes security. A poor choice here can expose your domain to threats from the start.
Why it matters: If your registrar or hosting provider has weak security measures, your domain can easily be hijacked or compromised. Additionally, unreliable service providers may not offer the resources you need to defend against common cyber threats.
| Feature | What to Look for | Why It’s Important |
| Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) | Enables an additional layer of login security | Reduces the chances of unauthorized access |
| Automatic Security Updates | Automatically updates server and software security patches | Ensures vulnerabilities are patched in a timely manner |
| DDoS Protection | Mitigates DDoS attacks by filtering traffic | Prevents your site from going down during high traffic attacks |
| Free SSL Certificates | Secure your website with HTTPS encryption | Protects sensitive data from being intercepted |
Case Study: In 2020, the domain of the popular domain registrar GoDaddy was targeted in a cyber attack, resulting in a breach of over 28,000 customer accounts. This case highlights the importance of choosing a registrar that provides robust security features.
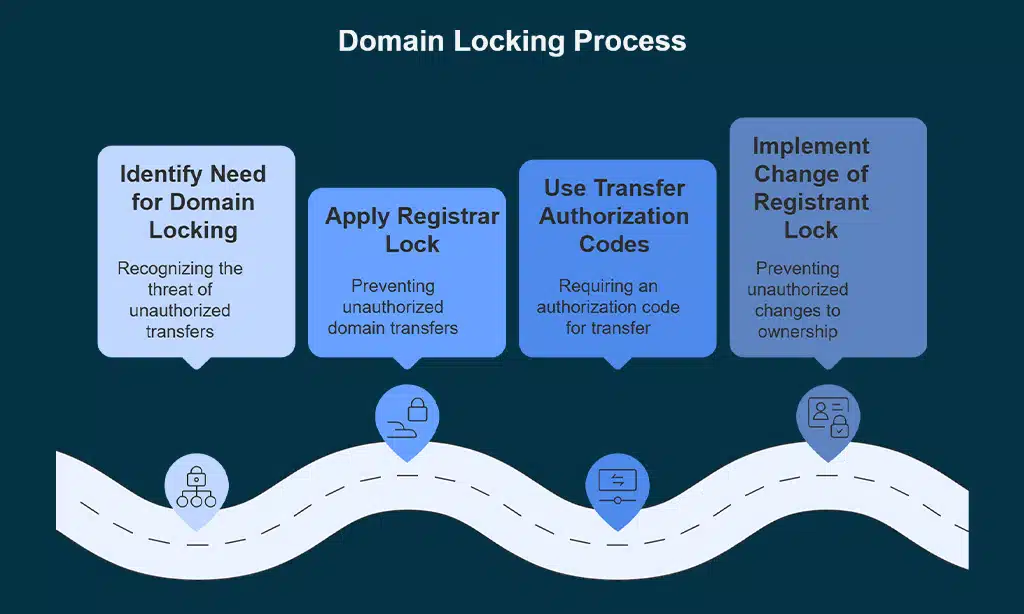
2. Enable Domain Locking
Domain locking is one of the simplest yet most effective ways to protect your domain from unauthorized transfers. When you lock your domain, it prevents any transfer requests without your approval.
Why it matters: Without domain locking, cybercriminals can take control of your domain and transfer it to another registrar without your consent. Locking the domain ensures that only authorized users can make changes to your domain registration.
| Action | What It Does | How to Implement |
| Registrar Lock | Prevents unauthorized domain transfers | Most registrars allow you to lock your domain from the account settings |
| Transfer Authorization Codes | Requires an authorization code for transferring your domain | Obtain and store these codes securely in case of a transfer |
| Change of Registrant Lock | Prevents unauthorized changes to ownership details | Apply this feature from your registrar’s management panel |
3. Utilize Strong and Unique Passwords
Cybercriminals frequently exploit weak passwords as the gateway to domain registrar and hosting accounts. A single weak password can allow attackers to take control of your domain.
Why it matters: Passwords are often the first line of defense. Using weak or reused passwords puts your domain at risk. A strong, unique password that’s difficult to guess or brute-force is essential for domain protection.
| Action | Best Practices for Strong Passwords |
| Length | Ensure your passwords are at least 12 characters long |
| Complexity | Use a mix of upper/lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols |
| Avoid Personal Information | Don’t use easily guessable information like names or birthdates |
| Unique Passwords | Never reuse passwords across different accounts |
Example: The 2014 Sony Pictures hack was partially due to weak passwords and poor password management. If Sony had enforced stronger password practices, it might have prevented hackers from accessing its sensitive internal systems.
4. Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
Two-factor authentication (2FA) adds an extra layer of security by requiring two forms of identification before granting access to an account. This is one of the most effective ways to protect against unauthorized access.
Why it matters: Even if a hacker manages to obtain your password, they will still need the second form of authentication, which is typically a one-time code sent to your phone or email.
| Action | What It Does | How to Implement |
| SMS-based 2FA | Sends a text message with a code | Enable it from your registrar’s or hosting provider’s account settings |
| Authenticator App | Generates time-sensitive codes on your phone | Use apps like Google Authenticator or Authy for increased security |
| Biometric 2FA | Uses facial recognition or fingerprints for authentication | Implement biometric authentication where supported for added convenience |
5. Regularly Update Your Software and Plugins
Outdated software and plugins can introduce security vulnerabilities that attackers can exploit. Regular updates help patch these vulnerabilities and secure your domain against attacks.
Why it matters: Hackers commonly target outdated versions of CMS (e.g., WordPress), plugins, and themes, which often contain known security flaws. Keeping everything up to date reduces the risk of exploitation.
| Action | What to Update | Why It’s Important |
| Content Management Systems (CMS) | Ensure your CMS is on the latest version | Reduces exposure to known security vulnerabilities |
| Plugins and Themes | Regularly update all plugins and themes | Protects against exploits that target outdated components |
| Server Software | Update web server software like Apache or Nginx | Ensures your server is not vulnerable to attacks |
6. Secure Your Website with SSL/TLS Certificates
An SSL/TLS certificate encrypts the data exchanged between your website and its visitors, ensuring sensitive information like credit card details and login credentials are secure.
Why it matters: Websites without SSL certificates are flagged as insecure by browsers, which could lead to loss of user trust. Additionally, SSL encryption helps protect data from man-in-the-middle attacks.
| Action | What It Does | How to Implement |
| SSL/TLS Encryption | Secures the data exchange between your site and visitors | Obtain an SSL certificate from your hosting provider or registrar |
| HSTS (HTTP Strict Transport Security) | Forces HTTPS connections | Enable HSTS in your website’s server configuration to enforce HTTPS |
7. Implement DNSSEC (Domain Name System Security Extensions)
DNSSEC is a protocol designed to protect DNS data from manipulation and fraud. By implementing DNSSEC, you can prevent attackers from hijacking your website’s DNS records.
Why it matters: DNS spoofing or cache poisoning attacks can redirect users to fraudulent websites, causing loss of data and credibility. DNSSEC ensures that the DNS data is authentic and unaltered.
| Action | What It Does | How to Implement |
| DNSSEC Protection | Adds an additional layer of security to DNS | Contact your domain registrar to enable DNSSEC for your domain |
8. Perform Regular Backups
Regular backups are essential for ensuring that you can recover your domain and website in the event of a breach, server failure, or accidental deletion.
Why it matters: Backups allow you to restore your domain and website to a previous, clean state, mitigating the damage caused by an attack.
| Action | What to Backup | Why It’s Important |
| Website Files | Backup all files, including media and code | Ensures that all your website content is recoverable |
| Databases | Backup all user and site-related databases | Protects valuable data, such as customer information or blog posts |
| Offsite Storage | Store backups in a secure location, such as cloud storage | Prevents backups from being compromised in case of a server breach |
9. Monitor Your Domain’s WHOIS Information
WHOIS records contain publicly available information about the ownership of a domain. Keeping this data up-to-date and protected can help prevent unauthorized access or fraudulent transfers.
Why it matters: Cybercriminals can exploit outdated or publicly visible WHOIS information to initiate attacks or impersonate domain owners.
| Action | What to Do | Why It’s Important |
| Enable WHOIS Privacy | Mask your personal information from public view | Prevents malicious actors from targeting you based on publicly available data |
| Regular WHOIS Monitoring | Ensure your WHOIS records are accurate and up to date | Allows you to spot any unauthorized changes to your domain ownership |
10. Educate Your Team and Stakeholders
While technology plays a significant role in domain security, human error is often the weakest link in cybersecurity. Training your team and other stakeholders about best security practices can go a long way in preventing attacks. In fact, according to a study by IBM, human error is responsible for 95% of all cybersecurity breaches.
Why it matters: Cybersecurity is not just the responsibility of IT teams or website administrators—it’s a shared responsibility. The more your team understands the risks and learns to recognize suspicious activities, the less likely they are to fall for phishing attacks, social engineering, or other cyber threats.
| Action | What It Does | Why It’s Important |
| Regular Security Training | Educates employees on phishing, password hygiene, and data protection | Reduces the risk of human errors like falling for phishing scams |
| Phishing Simulations | Conduct simulated phishing campaigns to test and educate employees | Raises awareness of real-world threats and improves response times |
| Incident Response Plan | Prepares staff to respond effectively to security breaches | Minimizes the impact of an attack and ensures a rapid recovery |
Case Study: In 2017, the Equifax breach, which compromised the personal information of 147 million people, was largely due to human error. An employee failed to apply a security patch to a vulnerable server, allowing hackers to exploit the flaw. This highlights how one oversight by an individual can lead to catastrophic results.
Tip: Develop a Security Awareness Program to ensure all employees are familiar with the company’s cybersecurity policies and practices. This will help your team stay alert to any potential threats.
Wrap Up: Stay Vigilant and Proactive
The digital landscape is constantly evolving, and so are the threats posed by cybercriminals. The increasing frequency and sophistication of cyber attacks make it imperative to have robust, comprehensive protection in place for your domain.
By applying the effective ways to protect your domain from cyber attacks outlined in this article, you can minimize the risk of attacks, safeguard your brand’s reputation, and protect the valuable data entrusted to you by users.
Remember, cybersecurity is a continuous process. It requires regular updates, monitoring, and improvements. The more proactive you are, the less likely it is that your domain will fall victim to cyber attacks.
In conclusion, protecting your domain requires both strategic and technical measures, combined with a keen understanding of the current threat landscape. By ensuring that your domain, website, and online assets are secure, you are not only protecting your business but also fostering trust with your audience, which is one of the most valuable assets of all.
By following these strategies, you not only secure your domain against attacks today but also create a solid foundation for a future free from the constant fear of cyber threats. Stay vigilant, stay informed, and always prioritize the security of your domain.
Visual Aids for Quick Reference:
| Comprehensive Security Checklist for Domains | Quick Summary |
| Domain Locking | Protects your domain from unauthorized transfers |
| 2FA (Two-Factor Authentication) | Adds a layer of security for login protection |
| Regular Software & Plugin Updates | Ensures you’re protected from known vulnerabilities |
| DNSSEC Implementation | Secures your DNS and protects against spoofing |
| SSL/TLS Certificates | Encrypts data exchanges and boosts trust with users |
| Password Management & Strength | Prevents unauthorized access through weak passwords |
| Employee Training | Helps mitigate the human factor in cyber threats |
| Backup Strategies | Ensures data restoration in case of a breach |
| WHOIS Privacy | Protects personal information and prevents targeting |
| Monitoring and Alerts | Keeps an eye on suspicious activities related to your domain |
Key Takeaway: A comprehensive security strategy combines prevention, detection, and response. By integrating these measures into your domain management practices, you can significantly reduce the likelihood of falling victim to cyber attacks. Stay proactive and continually evaluate and update your security systems to adapt to new threats.