Web developers face a real headache today. Data privacy laws keep changing, and each one brings new rules to follow. One mistake can cost your company millions in fines. GDPR violations alone have led to over $4.5 billion in penalties since 2018.
Here’s the thing: 85% of Americans think companies collect too much personal data. They worry about how businesses use their information. This means developers must build trust through proper data protection.
Your users want to feel safe when they visit your website.
This guide breaks down seven key privacy regulations that affect web development. You’ll learn what each law requires and how to stay compliant. We’ll cover GDPR, CCPA, COPPA, and four other important rules.
Each section gives you practical steps to protect user data and avoid costly mistakes.
Ready to master data privacy laws?
Key Takeaways
- GDPR violations have cost companies over $4.5 billion since 2018, making compliance essential for any developer handling EU citizens’ data.
- CCPA grants California residents powerful rights including data deletion, opt-out from sales, and access to their personal information within 12 months.
- COPPA requires verifiable parental consent before collecting any personal data from children under 13 years old through websites or apps.
- HIPAA demands strict security measures like encryption, multi-factor authentication, and audit trails to protect sensitive patient health information in applications.
- Privacy by design helps developers build user trust while avoiding costly fines across multiple international data protection regulations.
General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) Overview
GDPR stands as Europe’s toughest data privacy law, and it packs a serious punch for web developers who handle personal data. This regulation doesn’t just apply to European companies – it reaches across the globe to catch any business that processes EU citizens’ information, making compliance a must-have skill for modern developers.
What are the key principles of GDPR?
The General Data Protection Regulation builds on seven core principles that shape how companies handle personal data. These principles work like a roadmap, guiding developers through the complex world of data protection and privacy rights.
- Lawfulness, fairness, and transparency means companies must have valid legal reasons for collecting personal data and tell people clearly how their information gets used.
- Purpose limitation requires using data only for the specific reasons you told people about when you first collected it from them.
- Data minimization demands collecting only the personal information you actually need for your stated purpose, nothing more and nothing less.
- Accuracy mandates keeping all personal data correct and up to date throughout the entire data lifecycle.
- Storage limitation requires deleting personal information once you no longer need it for your original purpose or legal requirements.
- Integrity and confidentiality means protecting personal data from unauthorized access, loss, or damage through proper security measures and access controls.
- Accountability forces organizations to prove their gdpr compliance through proper documentation, privacy policies, and data protection measures.
How can developers ensure GDPR compliance?
GDPR compliance protects user data and builds consumer trust. Web developers must follow specific steps to meet these strict privacy requirements.
- Document consent requirements for every data collection action and maintain clear records of user permissions. Create systems that track when users give consent and what they agreed to.
- Provide a clear privacy policy with Data Protection Officer contact information for complete transparency. Users need easy access to understand how their personal data gets processed.
- Implement data minimization practices by collecting only necessary information for your service or function. Avoid gathering extra personal data that doesn’t serve a specific business purpose.
- Enable mechanisms for users to easily update or correct their personal information, supporting the accuracy principle. Build user dashboards where people can modify their data anytime.
- Delete or anonymize data promptly when it’s no longer needed, following storage limitation rules. Set up automated systems to remove old information based on data retention policies.
- Implement technical safeguards like data encryption and multi-factor authentication to prevent unauthorized access. Train staff on privacy by design principles and information security best practices.
- Maintain records of processing activities and conduct Data Protection Impact Assessments for high-risk projects. Appoint Data Protection Officers when your organization meets GDPR requirements.
- Verify that third-party vendors and partners also follow GDPR standards before sharing any sensitive information. Check their privacy policies and data protection measures regularly.
California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) Overview
California’s privacy law gives residents powerful rights over their personal data. This regulation forces developers to rethink how they collect, store, and share user information on their websites.
What rights does CCPA grant to California residents?
The California Consumer Privacy Act gives residents powerful control over their personal data. Companies must respect these consumer rights and respond to requests quickly.
- Right to Know What Data Companies Collect – California residents can ask businesses what personal information they gather, use, share, or sell. Companies must tell consumers exactly what data they collect at the point of collection.
- Right to Delete Personal Information – Consumers can request that businesses delete their personal data from company systems. Organizations must respond to these deletion requests promptly and remove the information completely.
- Right to Opt Out of Data Sales – People can stop companies from selling or sharing their personal information with third parties. Businesses must provide clear opt-out links and honor these requests immediately.
- Right to Access Personal Data – Residents can request copies of all personal information a company has collected about them. This includes data from the past 12 months and details about how it was used.
- Right to Correct Inaccurate Information – The California Privacy Rights Act extends CCPA to include correction rights for collected personal data. Consumers can fix wrong information in company databases.
- Right to Limit Sensitive Data Use – CPRA introduces the right to limit how businesses use and share sensitive personal information. This covers health data, financial details, and other private information.
- Right to Clear Privacy Policies – Organizations must provide consumers with accessible privacy policies that explain data practices. These policies must be easy to find and understand.
- Right to Equal Service – Companies cannot discriminate against consumers who exercise their privacy rights. Businesses must provide the same quality of service regardless of data requests.
- Right to Data Minimization – CPRA extends rights to include data minimization for all collected personal information. Companies can only gather data they actually need for business purposes.
How does CCPA affect web development?
CCPA forces web developers to build new features into their websites and apps. Notice at collection banners must be integrated into every site that collects California residents’ data.
Developers need to create opt-out interfaces that let users stop the sale of their personal information. These interfaces can’t be buried deep in settings menus, they must be easy to find and use.
Code changes go much deeper than just adding banners. Data minimization should be enforced at the code and database level, meaning developers can only collect what they actually need.
All user data must be retrievable, correctable, or deletable upon request. This means building systems that can quickly find and modify specific user records. Developers should audit third-party scripts and APIs to make sure they don’t violate CCPA rules.
Privacy automation tools like OneTrust can streamline compliance, but developers still need to maintain detailed records of all data processing activities.
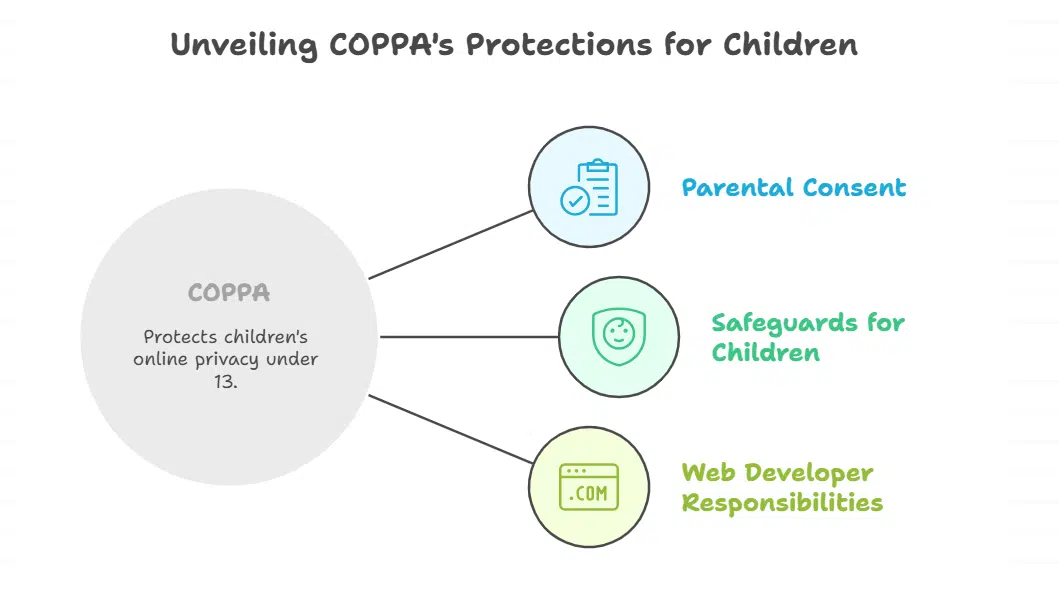
Children’s Online Privacy Protection Act (COPPA) Overview
COPPA protects children under 13 from having their personal data collected online without parental consent. Web developers must build special safeguards into their applications when they know kids might use their sites.
What are the rules for collecting data from children under 13?
Collecting personal information from children under 13 requires strict rules under the Children’s Online Privacy Protection Act. Web developers must follow specific steps to protect young users and avoid hefty penalties from the FTC.
- Parental consent is required before collecting any personal information from children under 13 years old through your website or app.
- Post a clear privacy policy that describes exactly what data you collect from children, how you use it, and who you share it with.
- Send direct notice to parents explaining your information collection practices, including what data you gather and how you plan to use their child’s details.
- Give parents the right to review their child’s personal data, delete it completely, or refuse any future collection of information.
- Keep children’s data only as long as needed to fulfill the original purpose, then delete it promptly to maintain data minimization standards.
- Put reasonable security procedures in place to protect the confidentiality and integrity of all children’s personal information you store.
- Limit data sharing with third parties to very strict conditions, as most sharing of children’s information violates privacy safeguards.
- Face substantial financial penalties if you violate these rules, since the FTC actively enforces COPPA compliance across digital platforms.
How can web applications comply with COPPA?
Web applications must follow strict rules when collecting data from children under 13. COPPA compliance protects kids and keeps your business safe from hefty fines.
- Set up verifiable parental consent mechanisms before collecting any data from users under 13 years old, using methods like credit card verification or signed consent forms.
- Create child-specific privacy notices that explain data collection in simple language and display them prominently on web pages where kids might visit.
- Limit data collection to only what your service absolutely needs to function, avoiding unnecessary personal information that could put children at risk.
- Build parent access tools that let moms and dads view their child’s information and request deletion whenever they want it removed.
- Audit your data storage practices regularly to delete children’s data when you no longer need it for your service operations.
- Use technical safeguards like data encryption and restricted access controls to protect any children’s information you store on your servers.
- Check that all third-party services, plugins, and tools you use meet COPPA requirements before adding them to your web application.
- Train your development team and staff on COPPA rules so everyone knows how to handle children’s data safely and legally.
- Monitor user registration processes to identify potential underage users and trigger parental consent workflows before data collection begins.
- Document your COPPA compliance procedures and keep records of parental consent to prove you follow the law during audits.
Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act (PIPEDA) Overview
Canada’s Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act governs how organizations collect, use, and share personal data across the country. This privacy law affects web developers who build applications that process Canadian users’ information, making compliance a critical part of software development.
What is Canada’s PIPEDA data privacy law?
Canada’s Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act stands as the country’s main data privacy law. PIPEDA governs how private sector organizations collect, use, and disclose personal information across Canada.
This law applies to commercial activities in all provinces, except those with substantially similar provincial laws. The legislation creates a framework that balances business needs with individual privacy rights.
PIPEDA enshrines ten core principles that guide data protection practices. These principles include accountability, consent, limiting collection, and safeguarding personal data. Organizations must inform individuals about the purposes for which their information is collected, used, or disclosed.
Data must only be collected for purposes that a reasonable person would consider appropriate. The law requires companies to implement security safeguards proportional to the sensitivity of the data they handle.
Individuals gain the right to access and request corrections to their personal information under this legislation. PIPEDA also includes mandatory data breach notification requirements for organizations that experience security incidents.
What responsibilities do developers have under PIPEDA?
Canada’s Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act puts specific duties on developers who handle personal data. Web developers must follow strict rules to protect user privacy and maintain consumer trust.
- Limit data collection to necessary information only – Developers must practice data minimization by collecting only personal data required for their application’s stated purpose, avoiding excessive information gathering that violates purpose limitation principles.
- Build robust consent management systems – Create clear mechanisms that allow users to give informed consent before any data collection or processing activities begin, making consent easy to withdraw at any time.
- Implement strong data security measures – Use encryption, access controls, and multi-factor authentication to protect personal data from data breaches and maintain integrity and confidentiality throughout the data lifecycle.
- Create user access and update features – Build functionality that lets users view, correct, and update their personal information stored in your application, supporting their fundamental data rights under privacy law.
- Develop clear privacy policies – Write accessible privacy notices that explain data collection practices, storage limitation periods, and user rights in plain language that average consumers can understand.
- Set up breach detection and notification systems – Install monitoring tools that can quickly identify security incidents and notify affected users promptly when data breaches occur, as required by law.
- Establish data retention policies – Create automated systems that delete personal data when it’s no longer needed, following storage limitation principles and reducing privacy risks over time.
- Conduct regular security audits – Review code, data flows, and privacy safeguards regularly to identify vulnerabilities and maintain compliance with evolving data protection principles and cybersecurity standards.
- Work with legal and compliance teams – Collaborate closely with privacy experts to stay current with PIPEDA changes and implement privacy by design principles throughout your development process.
Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) Overview
HIPAA protects health information when patients visit doctors, hospitals, and other medical providers. Web developers who build healthcare applications must follow strict rules to keep patient records safe and private.
How to protect health information in web applications?
Health information needs special protection in web applications. Patient records contain sensitive data that hackers love to target.
- Collect only the patient data you need for your healthcare service. Data minimization keeps you safe from privacy risks and reduces storage costs.
- Set up role-based access controls for your team members. Only doctors and nurses who treat specific patients should see their health records.
- Encrypt all patient data when it moves between servers and when it sits in storage. Data encryption protects against unauthorized access even if someone breaks into your system.
- Create audit trails that track who views or changes patient records. These logs help you spot suspicious activity and prove compliance during inspections.
- Update your privacy policies and consent forms regularly to match current rules. Patients must know how you use their health data before they share it.
- Answer patient requests quickly when they want to see, change, or delete their health information. Data rights give patients control over their personal medical details.
- Check that all third-party tools and plugins meet compliance standards before you install them. One weak link can expose your entire patient database.
- Store patient data only on secure servers or cloud services that specialize in healthcare. Regular hosting companies lack the privacy safeguards that medical data requires.
- Use multi-factor authentication for all accounts that can access patient records. Passwords alone won’t stop determined attackers from stealing health information.
What security measures support HIPAA compliance?
HIPAA compliance demands strict security measures to protect health information. Web developers must implement multiple layers of protection to safeguard patient data.
- Apply multi-factor authentication for all PHI access – Strong authentication prevents unauthorized users from accessing sensitive health records, even if passwords get compromised.
- Use end-to-end encryption for health data transmissions – Encrypt all data moving between systems to protect patient information during transfer across networks.
- Conduct regular security risk assessments and vulnerability scans – Schedule monthly scans to identify weak spots in your systems before hackers find them.
- Maintain detailed records of data processing activities – Document every action involving patient data, including who accessed what information and when they did it.
- Train developers and staff on HIPAA security practices – Regular training sessions keep your team updated on the latest privacy safeguards and data protection requirements.
- Establish breach detection, reporting, and response procedures – Create clear steps for identifying data breaches within minutes and reporting them to authorities within 72 hours.
- Limit PHI storage duration to necessary timeframes only – Delete patient records when they’re no longer needed for care or legal requirements to reduce privacy risks.
- Document and audit all third-party access to PHI – Track every vendor, contractor, or partner who touches patient data with signed agreements and regular compliance checks.
Brazil’s General Data Protection Law (LGPD) Overview
Brazil’s LGPD mirrors many GDPR principles but adds its own unique twist to data protection. Web developers working with Brazilian users must adapt their privacy policies and consent management systems to meet LGPD’s specific requirements.
How is LGPD similar to and different from GDPR?
Brazil’s General Data Protection Law (LGPD) and the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) share many core privacy principles. Both laws focus on data minimization, purpose limitation, and transparency when companies handle personal data.
Data subjects get similar rights under both regulations, including the ability to access, correct, and delete their information. Companies must keep records of data processing activities and conduct regular compliance audits under both frameworks.
Data breach notification requirements exist in both laws, requiring companies to inform authorities and affected individuals.
Key differences set these regulations apart in important ways. LGPD provides 10 legal bases for processing data, while GDPR offers only 6 options for companies. LGPD allows certain data processing without consent in specific circumstances, giving businesses more flexibility than GDPR.
The scope of LGPD covers all companies processing data in Brazil, even if those businesses operate outside the country. Both regulations include consent, legitimate interest, and contractual necessity as lawful bases for data processing.
These similarities and differences shape how web developers must approach privacy compliance across different markets.
What steps should developers take to comply with LGPD?
Brazil’s General Data Protection Law creates strict rules for handling personal data. Developers must follow specific steps to meet LGPD requirements and avoid hefty fines.
- Collect only the data you truly need for your web application’s core functions. Data minimization helps reduce privacy risks and makes compliance easier to manage.
- Get clear, explicit user consent before processing any personal information. Users must understand what data you collect and why you need it.
- Create privacy notices in Portuguese that explain your data practices in simple terms. These notices must be easy to find and understand for all users.
- Build user-friendly features that let people access, correct, or delete their personal data quickly. Data rights are a cornerstone of LGPD compliance.
- Set up data breach detection systems that can spot problems fast. You must notify authorities within 72 hours of discovering a breach.
- Assign a Data Protection Officer to oversee your privacy compliance efforts. This person becomes your go-to expert for all LGPD questions.
- Run regular audits of your data processing activities to check LGPD alignment. These reviews help catch issues before they become bigger problems.
- Check that all third-party tools and data processors meet LGPD standards too. Your compliance depends on your partners’ privacy practices as well.
- Implement strong data encryption for information at rest and in transit. Multi-factor authentication adds another layer of protection for sensitive systems.
- Create clear data retention policies that specify how long you keep different types of information. Storage limitation prevents you from hoarding unnecessary personal data.
ePrivacy Directive (Cookie Law) Overview
The ePrivacy Directive makes websites ask users before placing cookies on their devices, and it covers all tracking technologies that store information on user computers. This regulation works alongside GDPR to protect people’s online privacy, requiring clear consent management systems and transparent privacy notices about data collection practices.
What are the rules for cookie use and consent?
Cookie consent rules protect user privacy and give people control over their personal data. Websites must follow strict guidelines about how they collect and use this information through cookies.
- Prior consent must be obtained before placing most cookies on user devices, except for strictly necessary cookies that make websites function properly.
- Clear information about cookie types, purposes, and retention periods must be provided to users before they give consent.
- Consent must be freely given, specific, informed, and unambiguous, meaning users cannot be forced or tricked into accepting cookies.
- Granular choices allow users to select which specific cookies they want to activate rather than accepting all cookies at once.
- Withdrawal of consent must be as easy as giving it, with simple opt-out options available at all times.
- Consent records must be maintained and stored to demonstrate compliance with data protection regulations during audits.
- Cookie banners cannot use dark patterns or misleading design elements that manipulate users into giving consent.
- Strictly necessary cookies for basic website functionality can be used without explicit user consent but still require transparency.
- Non-compliance with cookie requirements can result in significant financial penalties and damage to consumer trust.
What are best practices for implementing cookies?
Smart cookie management protects user privacy and keeps your website compliant with data protection laws. Following these practices builds consumer trust while avoiding legal troubles.
- Display a prominent cookie banner to inform users and collect consent – Place your banner where visitors can easily see it before any non-essential cookies load on your site.
- Use a CMP, such as Usercentrics, to automate cookie consent collection and management – These tools handle the technical work of tracking user choices and managing consent across your entire website.
- Avoid loading non-essential cookies before obtaining user consent – Wait for explicit permission before activating analytics, marketing, or preference cookies that aren’t required for basic site function.
- Categorize cookies by purpose (e.g., analytics, marketing, preferences) – Group your cookies into clear categories so users understand exactly what data you collect and why you need it.
- Only collect and store cookies that are necessary for the site’s functionality – Practice data minimization by removing any cookies that don’t serve a specific, essential purpose for your web application.
- Provide users with the ability to update or withdraw cookie preferences at any time – Add a clear link in your privacy policy or footer that lets visitors change their consent choices whenever they want.
- Integrate consent signals with analytics and marketing tools to respect user choices – Connect your consent management platform with Google Analytics, advertising networks, and other third-party services to honor user decisions.
- Regularly review and update the cookie policy to reflect current use – Check your privacy notices quarterly to make sure they accurately describe all cookies your site actually uses and their purposes.
Data Protection Act 2018 (UK) Overview
The UK’s Data Protection Act 2018 works alongside UK GDPR to protect personal data after Brexit. Web developers must follow both laws when building sites for UK users, creating a dual compliance challenge that affects data processing and privacy policies.
How does the UK’s Data Protection Act relate to GDPR after Brexit?
Brexit changed how data protection works in the UK, but the changes are smaller than you might think. The Data Protection Act 2018 works hand in hand with UK GDPR to create a complete privacy framework.
UK GDPR mirrors the EU GDPR’s seven foundational principles exactly. This means businesses still follow the same core rules they knew before Brexit.
The Data Protection Act 2018 modifies certain GDPR provisions for UK-specific contexts. It adds special rules for law enforcement data processing that don’t exist in regular GDPR. UK organizations must comply with both UK GDPR and the Data Protection Act 2018 to stay legal.
The Act provides additional guidance for special category and criminal offense data. Data transfers from the UK to the EU remain permitted under adequacy agreements, which keeps business flowing smoothly.
The Act retains GDPR’s accountability, transparency, and data subject rights, so consumers still get strong protection. UK Information Commissioner’s Office (ICO) oversees both UK GDPR and the Data Protection Act, making enforcement clear and simple.
What developer changes are needed for UK compliance?
The UK’s Data Protection Act 2018 works alongside UK GDPR after Brexit. Developers must make specific changes to stay compliant with UK data privacy laws.
- Update privacy policies to reference UK GDPR and Data Protection Act 2018 instead of EU versions. Replace old policy language with UK-specific terms and legal requirements.
- Appoint a UK representative or data protection officer if your company processes personal data of UK residents from abroad. This person handles UK compliance matters and user requests.
- Review all data processing contracts with third parties to align with UK law requirements. Update agreements to reflect post-Brexit data protection rules and transfer mechanisms.
- Build mechanisms that let UK data subjects exercise their rights easily. Create systems for data access, deletion, and portability requests from UK users.
- Check that data transfers to and from the UK follow post-Brexit transfer rules. Set up proper safeguards for international data flows involving UK personal data.
- Run regular audits of your data practices to check compliance with UK-specific regulations. Test your systems against UK GDPR requirements and document findings.
- Train your development team and staff on UK data privacy requirements. Make sure everyone knows the differences between UK and EU rules.
- Use privacy automation tools to streamline compliance tasks and manage user rights requests. These tools help handle consent management and data subject requests efficiently.
Takeaways
Data privacy regulations shape how we build websites today. These seven laws protect people’s personal information across different countries and industries. Web developers must follow these rules to keep user data safe and avoid costly fines.
Privacy by design helps developers create better websites from the start. This approach builds trust with users who worry about how companies use their data. Smart developers know that good data protection leads to happy customers and successful businesses.
FAQs on Data Privacy Regulations For Every Web Developer
1. What is GDPR and why should web developers care about it?
GDPR stands for General Data Protection Regulation. It’s like the big boss of data privacy laws that covers how you handle personal data from European users. Web developers must follow GDPR compliance rules or face hefty fines, so it’s not something you can ignore.
2. How do data minimization and purpose limitation work together?
Data minimization means collecting only what you actually need, like ordering just enough pizza for your team instead of buying ten boxes. Purpose limitation requires you to use that data only for what you told people you’d use it for.
3. What’s the difference between a data controller and data processor?
A data controller decides why and how personal data gets processed, while a data processor handles the actual work. Think of it like a restaurant owner (controller) telling the chef (processor) what to cook.
4. Do I need a Data Protection Officer for my website?
Not always, but you might need a DPO if you process lots of sensitive personal information or do large-scale monitoring. It depends on your business size and what kind of data you’re handling.
5. How can privacy by design help with consumer trust and data security?
Privacy by design builds data protection right into your systems from day one, like installing good locks when you build a house instead of adding them later. This approach strengthens consumer trust because users see you take their privacy seriously. Plus, it makes data security much easier to manage.
6. What are the key data protection principles I should follow?
The main principles include lawfulness, fairness, and transparency in how you collect data. You also need storage limitation rules, proper data retention policies, and strong integrity and confidentiality measures. Don’t forget about data rights either, users can ask to see or delete their information.