Have you ever waited hours for a package while the tracking app stalled? Many companies still battle slow cloud computing, data gaps, and poor inventory management that lead to missed deliveries and rising costs.
Edge AI in smart logistics combines artificial intelligence with edge computing to process data closer to its source. This boosts real-time decision-making.
In this post, you will see seven edge computing applications that boost operational efficiency, fleet management, predictive maintenance, inventory management, and dynamic routing.
You will learn how iot devices and edge servers cut lag and ensure data security with decentralized data processing. Read on.
Key Takeaways
- IoT devices on trucks send location, fuel, and driver data to edge servers. A global logistics firm cut fuel use and sped deliveries by processing data near trucks and boosted last-mile success while protecting driver privacy.
- Sensors on trucks and forklifts monitor vibration and temperature. Edge AI spots engine or belt issues and alerts teams before breakdowns, cutting repair costs and downtime.
- Production-line cameras and warehouse robots use edge AI to find cracks or dents in real time. A leading e-commerce retailer fixes defects at once, cutting waste and keeping stock moving.
- Edge computing with 5G network slicing processes traffic, weather, and delivery schedules at each hub. Fleet managers reroute trucks instantly for faster deliveries and lower fuel use.
- Refrigerated trucks and pharmaceutical IoT sensors track temperature and humidity at the edge. Teams lock in safe ranges to protect vaccines and perishable goods and meet strict safety rules.
How does real-time fleet tracking improve logistics coordination?
Trucks carry edge devices with location trackers, fuel monitors, and driving pattern analysis modules. These IoT devices send status and position info in real time. Edge computing cuts lag time and trims reliance on cloud-based tracking.
A global logistics firm used edge AI to optimize routes, cut fuel use, and speed up delivery times. Dedicated links and network tweaks keep data flowing fast, with reduced latency for time-sensitive tasks.
Live feeds let staff spot hold-ups, reroute vehicles, and boost last-mile delivery success. Decentralized data processing on trucks tightens data security and shields driver privacy.
What are the benefits of predictive maintenance for vehicles and equipment?
Predictive maintenance taps vibration probes and temperature sensors on trucks and forklifts to forecast breakdowns. Fog computing, a form of edge computing, cuts lag for these alerts.
Neural network inference runs on the device and spots odd patterns in oil pressure and engine heat. It schedules service before belts snap or pumps seize.
Crews swap worn parts during scheduled stops, not during a breakdown. That move trims repair bills, cuts downtime and shrinks operational costs. It boosts energy efficiency by skipping needless checkups.
Plants keep conveyors rolling without surprise halts and fleet management apps flag a sick rig before you lose a load. IoT gateways feed snapshots to cloud infrastructure for extra logging.
How can supply chains use automated quality control?
Sensors on production lines scan each item like hawks, they spot cracks or dents in real time. Edge AI models run on local hardware, they flag flawed goods before shipment, they cut waste and boost consistency.
Factories tap real-time analytics at the edge for instant alerts, workers fix errors on the spot, they keep the line moving. A just-in-time flow only moves approved loads downstream, it trims storage piles, it secures steady stock.
Warehouses link IoT devices and machine learning tools, they log each defect to the cloud, they lock down data security for audits. Dashboards pull live analytics from edge nodes, teams review issue logs fast, they sidestep compliance headaches.
This blend of edge computing, cloud integration, and smart sensors gives supply chain managers full visibility, it holds quality high, it feeds regulators clear records.
What are smart inventory management methods with edge devices?
Smart warehousing by a leading e-commerce retailer uses edge AI robots to scan shelves. They track stock levels and update counts instantly. Edge nodes process real-time data from IoT cameras, sensors and handheld scanners.
Staff get alerts for low stock, avoiding shortages or overstock. Models train on high-quality sensor input, driving AI decisions with machine learning algorithms.
Healthcare hubs like hospitals and pharmacies use edge computing to slash waste. Modular architecture makes it easy to add new gadgets or upgrade systems. Performance monitors flag any slowdowns or errors in inventory flows.
Integration with cloud platforms boosts data privacy and scales operations fast. Staff link picking arms and conveyors to existing networks, and maintain supply chain visibility.
How does dynamic routing optimize navigation in logistics?
Logistics companies use dynamic routing to tweak routes instantly. Edge computing moves data processing close to trucks. The system grabs traffic, weather, and delivery schedules at each hub.
Edge AI refines route planning through split-second analysis. Drivers view the new path on a cab screen via 5G connectivity. Delivery times shrink by minutes. Fuel consumption drops and vehicle wear slows.
Cloud integration acts as a backup during peak routing demand. It stores overflow data when local nodes near capacity. Network slicing with 5G gives each critical task its own channel.
Route recalculation runs with ultra-low latency. Internet of things (iot) sensors feed data from scanners and cameras. Fleet managers track performance metrics using real-time data processing.
This setup boosts operational efficiency and cuts delays.
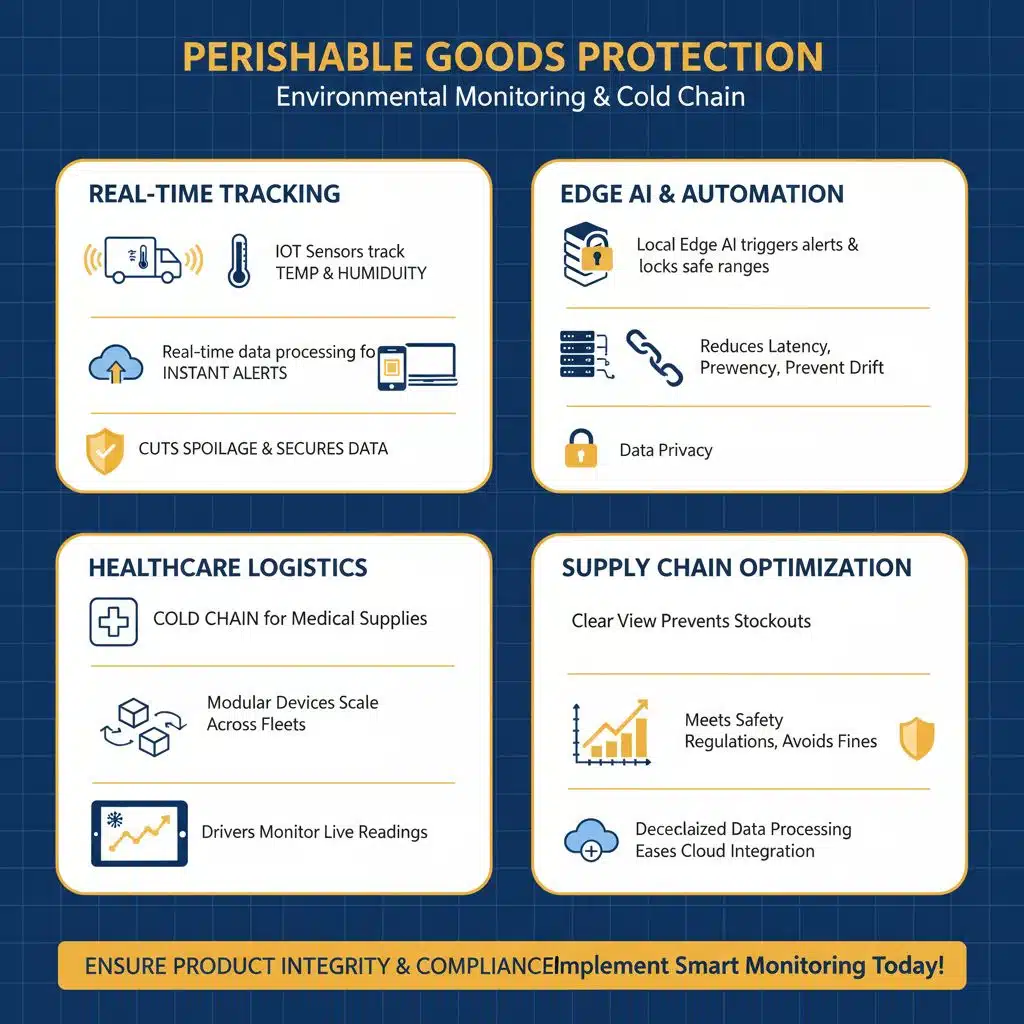
Why is environmental monitoring important for perishable goods?
Refrigerated trucks run edge computing systems that track temperature and humidity for perishable goods. Pharmaceutical firms install IoT sensors to guard vaccine and drug potency.
These units feed real-time data processing, so teams spot any drift at once. Local edge AI then triggers alerts and locks in safe ranges. That step cuts spoilage risk and secures data privacy.
Healthcare logistics also rely on cold chain monitoring for medical supplies. Modular devices scale across fleets as the network widens. Drivers tap dashboards for live readings. Companies meet strict safety rules, avoiding fines and lost stock.
This clear view helps supply chain managers dodge stockouts. Decentralized data processing slashes latency and eases cloud integration.
How do enhanced warehouse automation systems work?
Enhanced warehouse automation systems use edge computing to control automated guided vehicles and robotic arms for picking, packing, and sorting. Smart warehousing integrates edge AI robots that scan shelves, track inventory, and alert teams to replenish stock.
Operators gain instant feedback through IoT devices and real-time analytics on site.
Standardized hardware and software connect each module, so warehouse management remains seamless across fleets of AGVs and robots. Edge AI driven automation monitors performance and triggers rapid response to any operational issues.
Teams tie local systems into cloud integration for advanced inventory management and secure data sharing.
Takeaways
Gear shifts happen fast with edge computing, so fleets hit the road running. Tiny nodes, processors, and sensors share data on site. They check engine health, spot hiccups before they break down.
Teams save money, avoid late-night calls, keep goods fresh. The mix of IoT devices, cloud servers, and blockchain also backs each move. Future steps include 5G links and autonomous vehicles that steer themselves.
FAQs on Top Computing Applications in Smart Logistics
1. What does edge computing bring to smart logistics?
Edge computing moves data work to the truck and warehouse, near IoT devices, not far off in a server hub. It’s like having a warehouse brain in your pocket. It cuts latency, speeds real-time data processing, and boosts operational efficiency.
2. How do IoT devices use edge computing for stock control?
IoT devices send data to a nearby node that processes info fast. You get real-time tracking, you spot low stock right away. Edge computing cuts latency, it powers stock control and smart warehousing.
3. Can edge computing help with predictive maintenance?
Industrial IoT sensors feed data to a local node. It spots a worn part in a heartbeat. That triggers predictive maintenance. It saves money, stops breakdowns before they happen.
4. Do autonomous vehicles use edge computing in logistics?
Sensors in autonomous vehicles use edge computing to run real-time data processing. They map routes, avoid obstacles in seconds. This cuts latency, boosts safety, and drives supply chain management and fleet management forward.
5. How do edge computing and cloud integration work together?
Edge computing handles local work, cloud computing tackles the heavy stuff. They sync via cloud integration. This mix is scalable, it blends local real-time analytics and central big data tasks. It helps with demand forecasting.
6. Does edge computing improve data security and data privacy?
Edge computing keeps data close to the source, within local nodes. It limits visits to server hubs, lowers breach risks. It adds a layer in data management, hardens data security, and boosts data privacy.