Choosing the correct AN size for fuel, oil, or coolant systems can have an immense effect on performance and efficiency. Knowing all the elements these players consider in the decision-making is necessary to yield the highest returns. In this guide, we will discuss several important factors you should consider as well as some tips to help you make the best decisions.
Understanding AN Fittings
AN fittings were originally designed for the military and are now common in car and industrial products. They ensure a strong and leak-free connection. They are sized based on their OD in sixteenths of an inch. For example, AN-4 would represent a fitting with a 4/16 or 1/4 inch outside diameter. The first step to choosing the right size is to identify these measurements.
Assessing System Requirements
Each system [fuel, oil, and coolant] has its own needs. Look at the characteristics of the fluid and the required pressure and flow rate of the system. Higher AN sizes may be required for high-pressure systems to ensure durability/performance. On the other end of the spectrum, smaller systems may benefit from smaller fittings for efficiency. Given those needs, which you will assess, this will lead to the decision.
Considering Flow Rates
This means that one key component when deciding the proper AN size is flow rate. Bigger fittings allow for greater flow, reducing the potential for pressure drops and helping to move fluids through the system effectively. The size is determined by how the system can handle the flow its design conveys. Flow rate data is usually stored within the specifications of the vehicle or the system design.
Compatible with Existing Components
Another essential consideration is ensuring compatibility with existing components. Using the same AN size for other ports ensures that leaks do not occur and that the transfer of fluid across systems remains efficient. Referencing manufacturer specs for compatible sizes can help free up time and resources. This phase usually requires looking up information or asking suppliers a few questions.
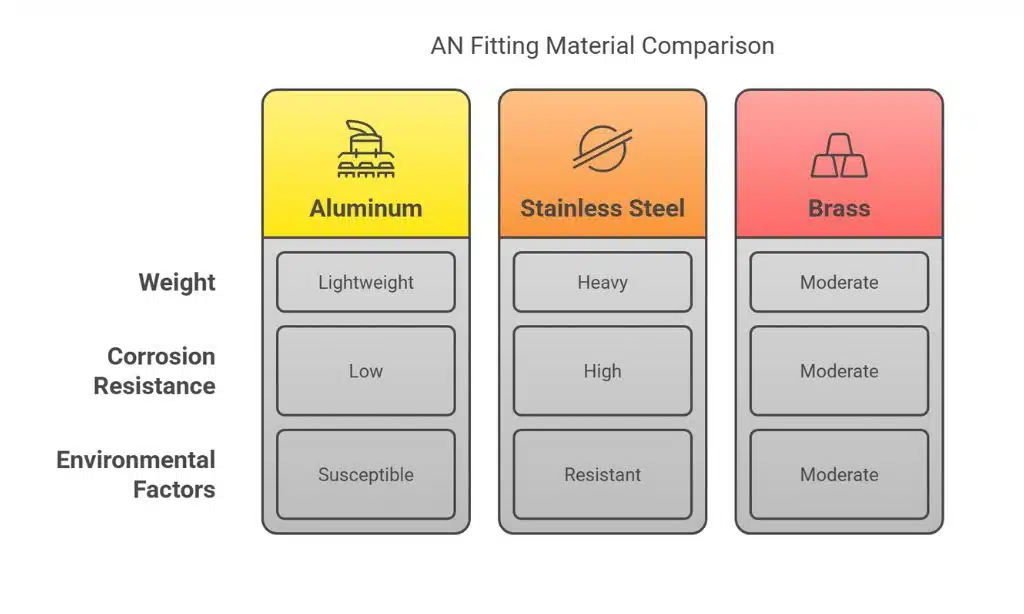
Material and Environmental Considerations
Material choice impacts both performance and longevity. AN fittings are available in various materials, including aluminum, stainless steel, and brass. Each material offers distinct advantages. Aluminum provides lightweight benefits, while stainless steel offers corrosion resistance. When selecting a material, consider environmental factors such as exposure to harsh conditions.
Ease of Installation
Another consideration is whether you can get it in quickly or not. While other fittings do not need special tools or methods to fit, knowing the installation requirements can be beneficial when selecting a user-friendly option. Complex installations may necessitate a consultation of instructional materials and/or professionals.
Budget Constraints
Budget constraints play a role in choosing the sizes of juxtaposed ANs. The cost-quality balance gives design trade-offs for cost and performance. Although higher-quality materials may cost more at the outset, they often deliver enhanced durability and lifespan. To reach a realistic solution, one must weigh budget limitations against performance necessities.
Professional Guidance and Resources
Experts and guides can provide valuable clues to its location. Experienced personnel or detailed documentation might provide recommendations for a specific system. Consulting the right sources leads to much better-informed decisions and can help you avoid some expensive pitfalls.
Testing and Evaluation
Testing and evaluation are essential once one AN size has been selected during experimentation. After installation, make sure the system works as expected. To ensure that the correct fittings have been chosen, you can check the flow of fluid, watch for leaks, and confirm that the fittings operate as they should. Periodic assessments can also increase the longevity of the system.
Conclusion
Selecting an appropriate AN size for fuel, oil, or coolant systems consists of more than one consideration. These are factors such as awareness of system requirements, flow rate analysis, compatibility analyses, and material considerations that empower an informed decision. Moreover, factoring in budget limitations along with quality, as well as obtaining expert opinion, aids in making the optimal choice. Thus, following these guidelines ensures optimal performance and longevity of the systems, as well as better satisfaction and efficiency.