Have you ever stared at a tracking page that never moves? You feel the drag of slow last-mile delivery. Fact: Driver errors cause most road crashes and jam supply chains. Autonomous vehicles can change that.
This post shows ten real-life use cases for autonomous vehicles, from autonomous trucks to aerial delivery. You will learn how computer vision, IoT, and predictive maintenance keep fleets on the road.
You will see action in ports, warehouses, and grocery aisles. Keep reading.
Key Takeaways
- Autonomous delivery pods use AI, computer vision, and IoT to cut last-mile costs by up to 50%. StreetDrone’s Pix-E and Nuro’s grocery bots run live in cities like Houston, Phoenix, Manchester, and London.
- Self-driving freight trucks lower logistics costs 30–50% and could generate $300–400 billion by 2035. FedEx saves 700,000 miles per day, and real-time route optimization trims operating costs 15%.
- Warehouse drones and robots hit 99.9% inventory accuracy. They cut labor needs by 80% and boost productivity by 130%. Pyka’s Pelican drone carries five-pound parcels up to 40 miles with GPS precision.
- Autonomous port cranes, AGVs, and RFID scanners speed container handling and cut idle time by 30%. Flexport and Waymo use predictive maintenance and data analytics to keep cargo moving.
- Smart forklifts from Gideon Brothers scan aisles with 3D vision and AI. They drive inventory accuracy to 99.9% and free workers from heavy lifting, while predictive maintenance prevents breakdowns.
Autonomous Delivery Vehicles
Driverless delivery vans glide through city streets by using computer vision, AI, and IoT sensors to map every turn. Keep reading to watch these delivery robots master last-mile grocery runs.
Last-Mile Delivery
Cities launch small pods on sidewalks for last-mile delivery. Autonomous delivery vehicles use computer vision and artificial intelligence to dodge traffic and curb errands fast. AI-based systems cut logistics costs by up to 50 percent, saving billions.
Sensor data from LiDAR and cameras help manage fleets and ease traffic flow.
StreetDrone’s Pix-E roams urban streets, carrying packages straight to your door. Its IoT sensors map curbside spots and avoid curious pedestrians. This model shows how the shipping industry can automate deliveries in rain, sleet, or shine.
Next, we explore autonomous grocery delivery.
Autonomous Grocery Delivery
After last-mile trucks, grocery pods hit city sidewalks. They use computer vision, laser scanners, and IoT sensors for reliable obstacle detection. Each pod holds up to 50 pounds of fresh produce.
AI tools tap data analytics and machine learning to run autonomous driving systems and optimize routes. Fleet managers track pods on dashboards and schedule predictive maintenance to cut costs.
The United States has the highest concentration of autonomous vehicle startups. Nuro runs live grocery trips in Houston and Phoenix. British firms trail behind with pilots in Manchester and London.
Each ride cuts traffic congestion and trims fuel consumption. Autonomous driving boosts road safety and supply chain visibility.
Autonomous Freight Trucks
Self-driving trucks chase long hauls, using computer vision and internet of things sensors to dodge road damage and sudden traffic jams. They ping a fleet management platform for upkeep alerts and tap predictive maintenance plus real-time route optimization to cut downtime.
Long-Haul Freight Transportation
Autonomous trucks cut logistics costs by 30 to 50 percent. They could unlock $300 to $400 billion in revenue by 2035. Waymo, TuSimple and Embark test fleets with advanced sensors and machine learning.
These teams feed data analytics from computer vision to refine routes. They apply predictive maintenance to trim downtime and boost uptime.
Poor driver behavior causes most road accidents, hurting global supply chain efficiency. Driverless rigs track traffic flow in real time, they adjust courses via route optimization.
IoT devices stream maintenance alerts to cut breakdown risk. AI-powered systems steer on highways, they slash crash odds. Smart transportation hubs share data with intelligent transportation systems.
They boost fuel efficiency and support sustainable transportation.
Real-Time Route Optimization
Shifting focus from cross-country hauls, fleets now rely on real-time route optimization. GPS tracking, IoT sensors, and data analytics feed machine learning algorithms that spot jams and reroute trucks.
The system cuts operating costs by 15% and boosts fuel efficiency.
FedEx saves 700,000 miles each day by tweaking paths on the go. Managers get instant supply chain visibility and can tweak plans fast. Service levels jump by 65% as fleets dodge delays.
This approach ties into intelligent transportation systems for smoother urban mobility.
Autonomous Drones in Logistics
Drones sweep shelves with computer vision and connect to the IoT, feeding a warehouse management system in real time. Then they hit the sky on micro flight paths, to airdrop parcels with pinpoint accuracy.
Warehouse Inventory Management
AI runs inventory management tasks with IoT sensors and computer vision. It hits 99.9 percent accuracy on counts. A warehouse management system and data analytics spot errors fast.
Managers cut labor by 80 percent and boost productivity by 130 percent.
Siemens, GE, and Shell use predictive maintenance on conveyors and lifts. That tech stops breakdowns before they occur. Companies save on maintenance costs and gain supply chain visibility.
Artificial intelligence and smart gear keep goods moving.
Aerial Package Delivery
Drones lift parcels from warehouses to porches. Pyka’s Pelican, a pilotless aircraft, uses computer vision to dodge trees and wires. It hauls five-pound loads for up to forty miles and lands with GPS precision.
Local shops in the US and Canada join test programs today.
AI data analytics picks the fastest path. FedEx cuts 700,000 miles each day. That slash lowers fuel use and carbon emissions. IoT links every drone to traffic sensors, so urban streets breathe easier and gridlock eases.
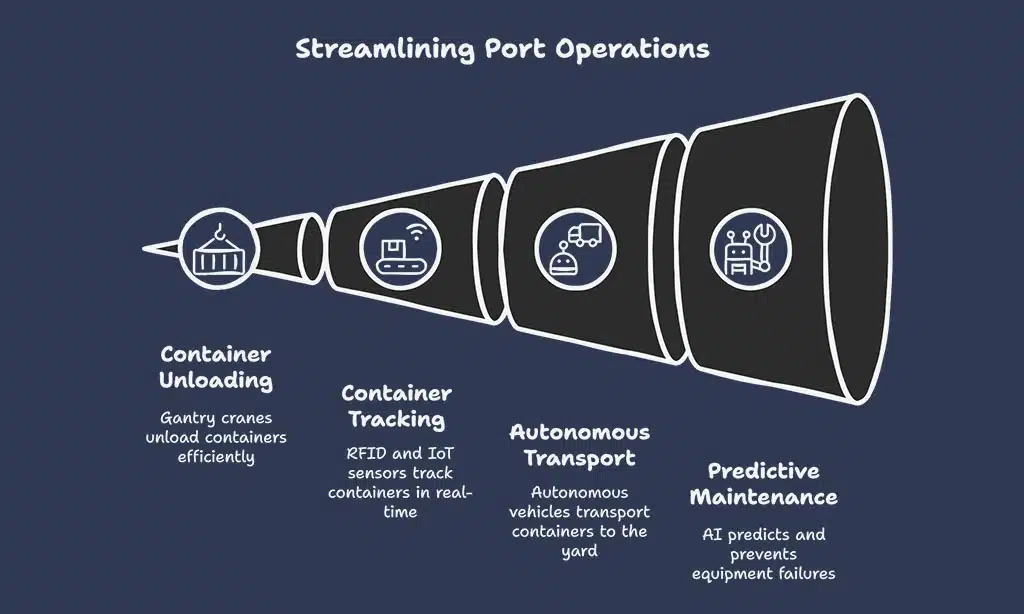
Automated Port Operations
Gantry cranes with computer vision and RFID scanners unload ships fast, they sync with a terminal operating system to guide each container to its yard. Tugger vehicles, small AGVs, ping IoT sensors to avoid roadblocks, and predictive maintenance spots a weak motor before it can halt the dock.
Container Loading and Unloading
Autonomous vehicles power cranes and trucks. They streamline container loading and unloading at ports. Robotics arms lift boxes with AI and machine vision. IoT sensors track weight and location in real time.
Data analytics guides each move on the dock. Flexport and Waymo tap these tools to speed up tasks. A fleet management system cuts idle time by 30 percent.
Port teams face a driver shortage but AVs step in to handle container tasks. AI powered cargo tracking ensures safe, quality loads. IoT devices send alerts to operations staff. Ports gain full supply chain visibility.
This transition leads into Smart Warehousing Solutions.
Smart Warehousing Solutions
Robots, connected sensors, and data analytics help warehouses cut errors, speed orders, and boost space use like a well-choreographed dance; keep reading to see how they work.
Autonomous Forklifts and Robots
Gideon Brothers pallet movers use AI and 3D vision to move pallets. They scan aisles with computer vision in the blink of an eye. IoT links each bot to the warehouse network. These autonomous forklifts handle heavy loads without help.
AI in warehousing boosts productivity by 130% and drives inventory accuracy to 99.9%. That cut of 80% in workforce needs frees people for other tasks. Data analytics batches orders in seconds, and predictive maintenance flags issues before they stall a shift.
Fleet management and autonomous navigation tools tie each unit into a smooth operation.
Enhanced Safety in Logistics Operations
SafeAI retrofits construction gear into autonomous vehicles, boosting safety and cutting human risk. The platform uses computer vision and IoT sensors to sound alarms when it spots unstable ground.
Fleet managers tap data analytics to spot odd patterns in real time, solving hitches before they become crashes. Maersk runs AI models on shipping logs, flagging threats fast, like a guard dog on patrol.
That kind of risk management keeps ports humming and cargo moving.
Siemens, GE, and Shell pour money into predictive maintenance, so machines get tune ups before they fail. AI forecasts fleet needs with forecast accuracy as sharp as a hawk, trimming delays and saving fuel.
Driverless trucks link to intelligent transportation systems, easing traffic congestion in busy hubs. Lift trucks in smart warehouses sync with the cloud; they haul pallets without a hitch.
Workers crack jokes over lunch, saying bots never steal cookies, but they sure boost supply chain visibility and make shipments on time.
FAQs
1. How do autonomous vehicles speed up last-mile delivery?
They use smart maps, computer vision, and IoT sensors to pick the best roads. They dodge traffic congestion like ninjas in a crowd. Customers get their boxes fast, cheaper, straight to the porch.
2. What role does predictive maintenance play in fleet management?
Each truck, van, or car sends data analytics to a control room. They flag a bolt that loosens or a tire that needs air. This cuts downtime, boosts reliability, and keeps the logistics network humming like a tight drum.
3. How do warehouse robots help in logistics?
These warehouse robots, called autonomous forklifts, zip down aisles. They pick and place boxes, stack pallets, and track stock. They free human hands for other tasks, and they shine in the food supply chain or any transit systems.
4. Can driverless taxis fit into public transportation?
Yes, these driverless taxis join buses and trains to ease urban mobility. They act like friendly sidekicks to main transit systems. During rush hour, they slip through gaps, smoothing traffic flow analysis and curbing traffic incidents.
5. How do data analytics and the internet of things boost supply chain visibility?
Smart vehicles and shelves talk via IoT. They send location, temperature, and load info. Software runs demand forecasting, sets surge pricing, and picks buffer stock. The whole chain glows in real time.
6. Are autonomous trucks and self-driving cars safe, and how do they manage risks?
They run on artificial intelligence and computer vision that scan every inch ahead. They test in smart cities and truck yards, they learn from tiny hiccups. This builds trust in the trucking industry and pads sustainable transportation goals.