The signing of the India-EU trade deal on January 27, 2026, marks a decisive shift in the global economic order. By connecting 2 billion people and 25% of global GDP, the pact moves beyond mere commerce to create a strategic, technology-driven corridor that hedges against a volatile US-China trade landscape.
The scene at Hyderabad House in New Delhi was one of quiet triumph. Indian and EU leaders commemorated the conclusion of negotiations on what European officials have called the “mother of all deals”. For nearly two decades, negotiations between India and the European Union were famously “stuck in a loop,” hampered by seemingly insurmountable gaps in market access, data privacy, and professional mobility.
However, the geopolitical pressures of the mid-2020s acted as a powerful centrifuge. With a return to protectionist stances in Washington and the “China Plus One” strategy becoming a survival imperative for Brussels, the cost of inaction finally outweighed the pain of concession. The result is the India-EU trade deal, a 24-chapter masterclass in “de-risking” that provides a democratic alternative to the tech and manufacturing monopolies of the East and West.
The Great Supply Chain Reset: A Multi-Polar Anchor
The core of the India-EU trade deal is tariff liberalisation, which will reduce or eliminate duties on most traded goods over a phased schedule:
- EU exports to India: 96.6% of goods by value will see reduced or zero tariffs.
- Indian exports to the EU: 99.5% of exports by value will receive preferential access.
This liberalisation opens new opportunities for Indian labour-intensive sectors such as textiles, leather goods, marine products, and gems, which previously faced tariff disadvantages compared with other Asian competitors. At the same time, European firms gain broader access to India’s manufacturing base, machinery, chemicals, pharmaceuticals, and premium automobiles, creating immediate incentives to diversify supply chains.
| Sector | Previous Tariff (Avg) | New FTA Rate (Phased) | Projected Impact |
| Textiles & Apparel | 10% – 12% | 0% | Parity with Vietnam/Bangladesh; strong export growth expected. |
| Luxury Automobiles | 70% – 110% | 40% (Quota based) | Surge in European luxury marques; local assembly. |
| Wines & Spirits | 150% | 75% down to 20% | Market expansion for EU SMEs; growth in Indian hospitality. |
| Pharma & MedTech | 5% – 7% | 0% | India as a MedTech hub for the EU; lower healthcare costs. |
| Machinery | 7.5% – 15% | 0% | Reduced CAPEX for Indian manufacturing setups. |
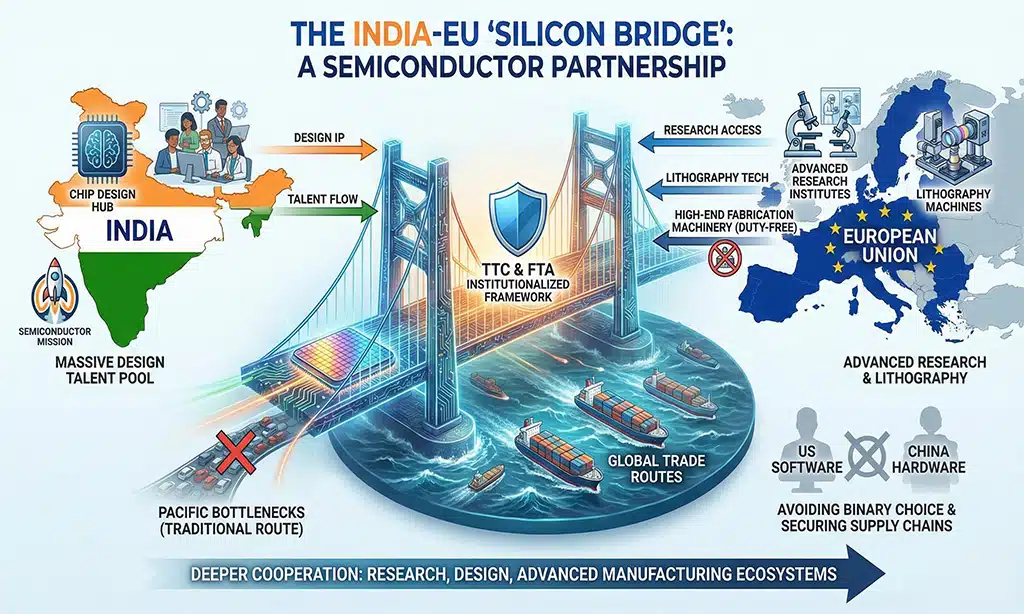
Semiconductors and the “Silicon Bridge”
Beyond the movement of containers, the India-EU trade deal anchors a high-stakes partnership in critical and emerging technologies. Both New Delhi and Brussels share a desire to avoid being caught in a binary choice between American software and Chinese hardware.
The centre of this effort is the Trade and Technology Council (TTC), which has now been institutionalized by the FTA. A key pillar is the semiconductor partnership. While India is still building its fabrication plants, it possesses a massive pool of chip design talent. The EU, meanwhile, holds the keys to advanced research infrastructure and lithography. The agreement positions India and the EU for deeper cooperation in semiconductor research, design talent, and advanced manufacturing ecosystems that bypass the traditional bottlenecks of the Pacific.
This partnership isn’t just about sharing blueprints. It’s about securing the upstream. The FTA removes duties on high-end European machinery required for semiconductor fabrication, which makes up a substantial share of fabrication capital expenditure. This significantly lowers the barrier for India’s “Semiconductor Mission” to scale.
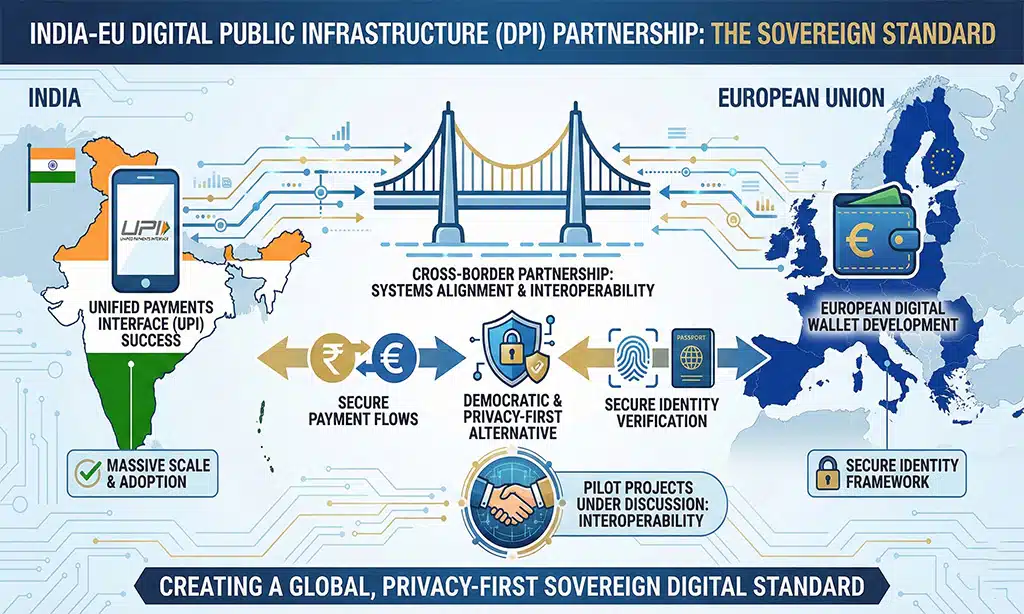
Digital Public Infrastructure: The Sovereign Standard
A radical arc of this partnership involves Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI). Europe is currently developing its own European Digital Wallet, and they are looking closely at India’s success with the Unified Payments Interface (UPI).
Aligning these systems creates a cross-border, secure payment and identity framework. This isn’t just about easier travel; it’s about providing a democratic, privacy-first alternative to the dominant private-sector payment giants. Pilot projects around interoperability in digital payments are under discussion, with both sides identifying this as a priority area.
The Mobility of “Brains and Bits”
Trade in 2026 is as much about people as it is about products. A standout feature of the agreement is the European Legal Gateway, which addresses India’s long-standing demand for the mobility of skilled professionals.
The FTA establishes a predictable, fast-track visa framework for ICT professionals, engineers, and researchers. Crucially, it includes a roadmap for Social Security Agreements, aiming to address double social security contributions, a long-standing concern for Indian service providers. This “Brain Circulation” ensures that the technical partnerships built on paper are implemented by experts on the ground, fostering a shared ecosystem for AI and 6G development.
| Strategic Dimension | Status Before 2026 | Status After FTA (2026) |
| Trade Volume | $136 billion | Targeted $200 billion by 2030 |
| Tech Alignment | Fragmented / Divergent | Unified standards in AI, 6G, and Semiconductors |
| Supply Chain Hub | China-centric | India-EU resilient corridor |
| Digital Payments | Visa / Mastercard dominant | Interoperable UPI-EU Digital Wallet pilots |
| Professional Visas | State-by-state patchwork | Standardized “Legal Gateway” for ICT/R&D |
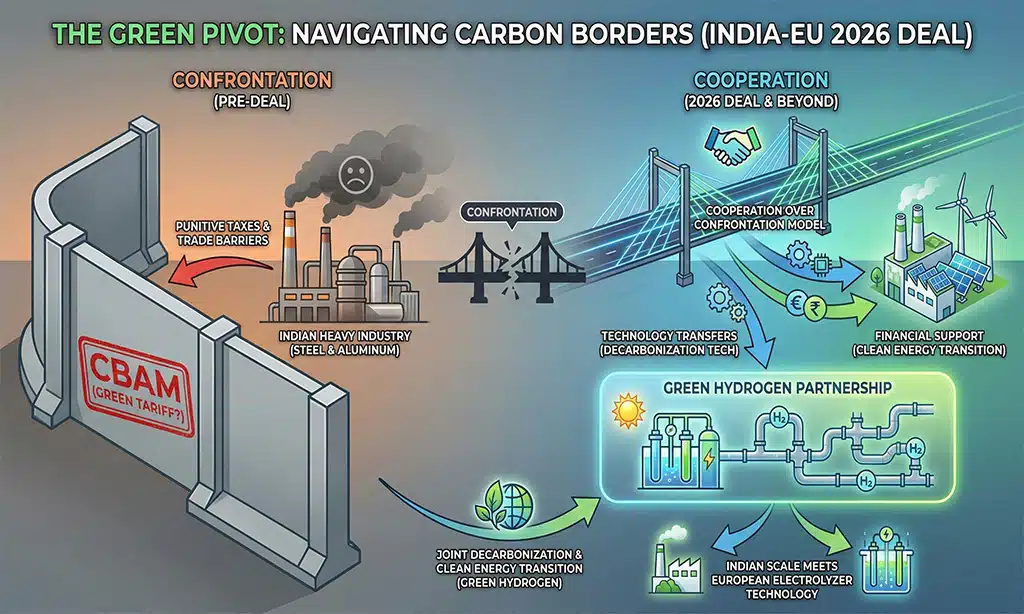
The Green Pivot: Navigating Carbon Borders
The agreement also addresses the “Carbon Question.” India had long been wary of the EU’s Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM), fearing it would act as a “green tariff” on its steel and aluminum.
The 2026 deal solves this through a “Cooperation over Confrontation” model. Instead of punitive taxes, the EU has committed to technology transfers and financial support to help Indian heavy industry decarbonize. This has paved the way for a Green Hydrogen Partnership, where Indian scale meets European electrolyzer technology. Both sides have signalled intent to cooperate on decarbonisation and clean energy transitions, including green hydrogen.
Expert Perspectives: A Strategic Hedge or Economic Gamble?
While the mood in New Delhi and Brussels is celebratory, analysts remain divided on the long-term execution. Proponents argue that the deal is a necessary strategic hedge. In an era where “weaponized trade” is a common tool of statecraft, having a massive, rules-based partner provides a safety net.
However, some economists warn of the “Execution Gap.” India’s domestic industry will now face much stiffer competition from high-efficiency European firms. On the European side, some labour unions have expressed concern that the mobility of Indian professionals might depress wages in the tech sector. Maintaining neutrality, the deal includes bilateral safeguard mechanisms, an “emergency brake” either side can pull if a sudden surge in imports threatens to wipe out a domestic industry.
Strategic Autonomy Through Supply Chains and Technology
At its core, the India-EU trade deal is about rebuilding supply chains for a more uncertain world. Over the last few years, disruptions caused by the pandemic, wars, sanctions, and US-China trade tensions exposed how fragile global supply networks had become. Europe’s dependence on East Asia for manufacturing inputs and India’s reliance on external technology ecosystems proved costly. This agreement responds directly to those lessons. By integrating Indian manufacturing capacity with European capital, standards, and technology, the deal aims to create more resilient, diversified supply chains that are less vulnerable to single-country shocks.
What makes this shift meaningful is that it is not limited to physical goods. Modern supply chains are increasingly driven by technology layers such as design, software, data, automation, and advanced machinery. The India-EU trade deal reflects this reality. Alongside tariff liberalisation, it pushes regulatory cooperation and standards alignment in technology-intensive sectors, allowing firms to plan long-term investments with greater certainty. For European companies, India becomes more than a consumer market. It becomes a manufacturing and technology partner. For Indian firms, access to the EU market comes with exposure to advanced production processes, compliance regimes, and innovation ecosystems. In this sense, supply chains and tech are inseparable in the agreement. The deal does not just move factories. It reshapes how value is created, shared, and secured across borders, giving both sides greater strategic autonomy without retreating from global trade.
From Trade to Technology Trust: A New Economic Architecture
Beyond supply chains, the India-EU trade deal places technology cooperation at the heart of the relationship. This is a significant evolution. Earlier trade agreements focused primarily on goods and tariffs, treating technology as a secondary issue. In contrast, this deal recognises that control over technology standards and ecosystems now defines economic power. Areas such as semiconductors, digital infrastructure, clean energy technologies, and advanced manufacturing are no longer neutral commercial spaces. They are strategic assets. By building structured cooperation in these domains, India and the EU are attempting to reduce exposure to technological chokepoints concentrated in the Pacific region.
Equally important is the emphasis on trust and predictability. Technology investments require stable rules on data governance, intellectual property, and regulatory alignment. The agreement signals an effort to harmonise approaches where possible while respecting sovereignty. This is particularly relevant for digital public infrastructure, AI, and future connectivity technologies, where fragmented rules can quickly become barriers to scale. By aligning supply chains with technology frameworks, the deal lowers long-term risk for businesses and investors. It also strengthens the human layer of tech cooperation. Skilled professionals, engineers, and researchers are positioned as enablers of this partnership, ensuring that supply chain resilience is backed by knowledge flows. Taken together, these elements show that the India-EU trade deal is not just about moving goods faster or cheaper. It is about building a trusted supply chain and technology architecture that can endure geopolitical volatility and shape global trade norms in the years ahead. With these foundations in place, attention now turns to how the agreement will be rolled out in practice.
What Next: The Implementation Roadmap
The signing was the finish line for negotiators, but it is the starting gun for businesses. The agreement now moves through legal scrubbing, translation, and ratification processes in the EU and India.
- Mid-2026: Legal scrubbing and translation into all official EU languages.
- Late 2026: Formal ratification and first phase of tariff reductions.
- Early 2027: Launch of the first “Sectoral Hubs”, dedicated zones in India for European firms to leverage the zero-duty regime.
Investors should watch these hubs closely. As the India-EU trade deal matures, it will not only change what we buy but also how we build. It creates a new “Democratic Supply Chain” designed to remain resilient long after the current geopolitical storms have passed.