Energy-saving smart home devices are everywhere now, but not all of them save energy. Some “smart” gadgets add convenience while quietly increasing electricity use through always-on standby power, constant Wi-Fi activity, extra hubs, and feature bloat. Others deliver real savings by reducing heating and cooling waste, cutting standby loads, optimizing major appliances, and helping people see exactly where money is leaking out of their homes.
The difference is not branding. It is systems thinking. A home’s energy bill is largely shaped by a few big categories: heating and cooling, water heating, lighting, refrigeration, laundry, and electronics standby power. The best energy-saving smart home devices target these categories directly, using automation and feedback to reduce waste without making daily life harder.
This guide breaks down which smart home devices actually reduce energy costs, how they work, how to avoid “smart” purchases that raise your bill, and how to build a smart home setup that delivers measurable savings in 2026 and beyond.
How Smart Homes Save Energy In The Real World
A smart home saves money when it changes behavior and system performance in measurable ways. It does not matter if a device has an app, voice control, or futuristic marketing. What matters is whether it reduces energy consumption while keeping comfort and safety stable.
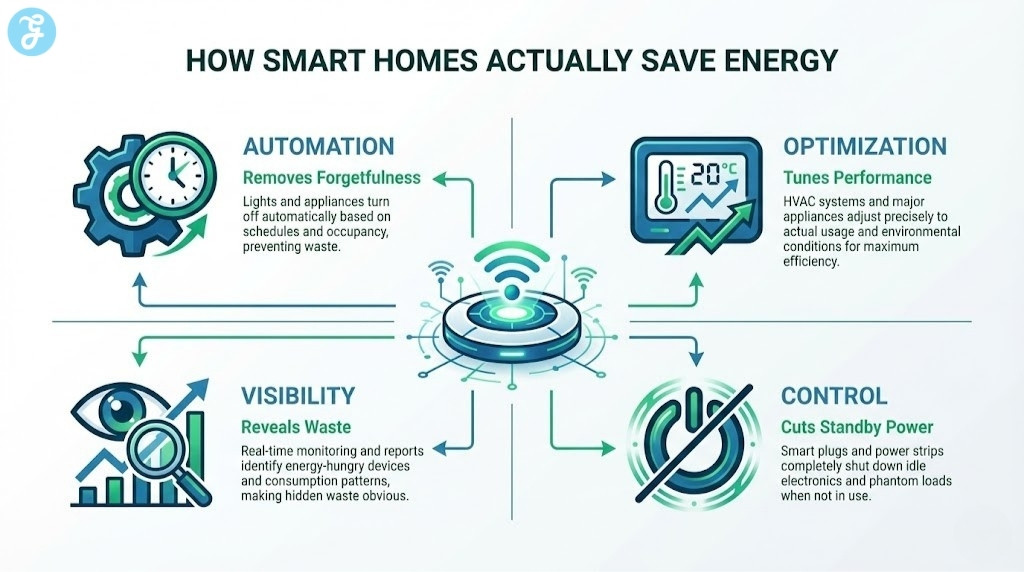
In most households, savings come from four mechanisms.
The Four Mechanisms Of Real Energy Savings
-
Automation that prevents waste when people forget
-
Optimization that tunes heating, cooling, and appliances to actual usage
-
Visibility that reveals what is consuming power and when
-
Control that reduces idle loads and standby power
Energy-saving smart home devices that rely only on “cool features” often underperform. Devices that solve a specific waste pattern are the ones worth buying.
Savings Mechanism Table
| Mechanism | What It Does | Example Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Automation | Removes forgetfulness | Lights and plugs turn off automatically |
| Optimization | Tunes systems precisely | HVAC runs less while comfort stays |
| Visibility | Reveals hidden waste | Identify standby loads and overuse |
| Control | Reduces idle consumption | Cut phantom power draw overnight |
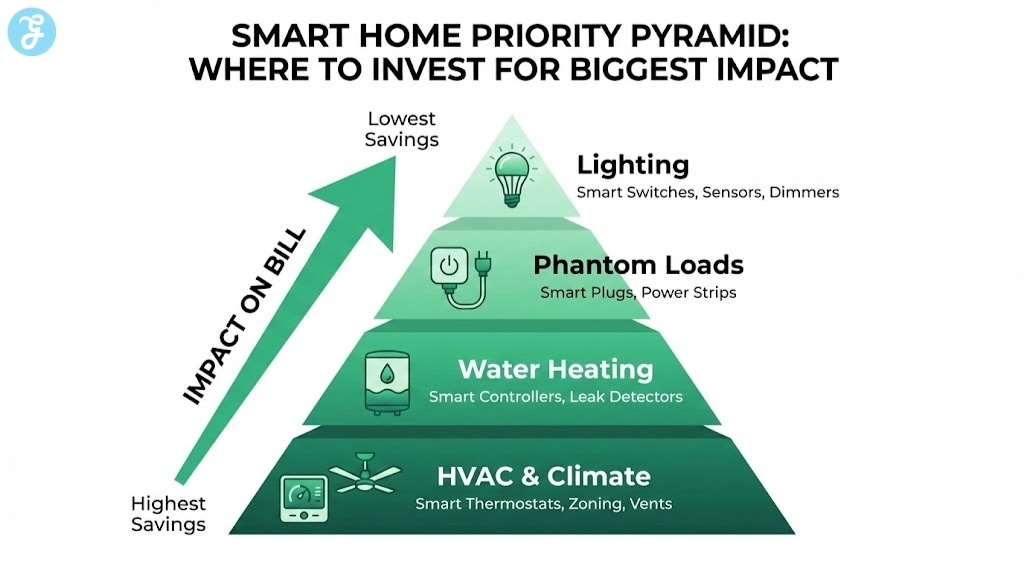
Start With The Biggest Energy Winner: Heating And Cooling
In many homes, heating and cooling is the largest energy expense. That makes HVAC control the best place to start if you want meaningful savings.
Smart Thermostats That Actually Pay Off
A smart thermostat is one of the most proven energy-saving devices because it reduces heating and cooling waste. But it works best when it learns schedules, detects occupancy, and avoids over-conditioning an empty home.
Strong features include:
-
Adaptive scheduling that learns patterns
-
Geofencing or occupancy sensing to reduce energy when no one is home
-
Smart setback temperatures that reduce waste without discomfort
-
System health insights and filter reminders
-
Compatibility with heat pumps and multi-stage systems
Weak “smart” thermostats are basically app-controlled thermostats. Real savings comes from automation and learning, not remote control.
Smart Thermostat Decision Table
| Feature | Why It Matters | What To Avoid |
|---|---|---|
| Occupancy detection | Prevents empty-home heating/cooling | Manual-only scheduling |
| Learning schedules | Reduces daily waste | “Smart” without automation |
| Heat pump support | Avoids inefficient behavior | Poor compatibility |
| Data insights | Helps tune settings | No usage reporting |
Smart Vents And Zoning: Powerful, But Risky If Misused
Smart vents and zoning systems can reduce HVAC waste by directing heating and cooling where it is needed. This can help in homes with uneven temperature distribution or underused rooms.
But smart vents can also create pressure issues in HVAC systems if installed incorrectly. That can reduce efficiency and damage equipment.
When Smart Vents Make Sense
-
You have rooms that are rarely used
-
Your home has temperature imbalance across floors
-
You have a system designed for zoning or can safely add it
-
You want better comfort without heating/cooling every space equally
Smart Vent Risk Table
| Benefit | What It Improves | Risk |
|---|---|---|
| Targeted comfort | Less HVAC waste in unused rooms | Pressure imbalance if too many vents close |
| Zone control | Better room-to-room efficiency | Requires correct HVAC design |
| Automation | Reduced manual adjustments | Can cause short cycling |
If you do not understand HVAC constraints, a smart thermostat plus better insulation and sealing often delivers safer savings.
The Hidden Winner: Smart Water Heating Control
Water heating is often a major household cost. Smart control can reduce waste by preventing heating when hot water is not needed and by optimizing temperature settings.
Energy-Saving Water Heating Options
-
Smart water heater controllers for electric tanks
-
Heat pump water heaters with smart scheduling
-
Leak detection shutoff systems that prevent catastrophic waste
-
Smart recirculation pumps that run only when needed
One common waste source is recirculation systems running continuously, keeping pipes hot all day. Smart recirculation control can reduce that dramatically.
Water Heating Table
| Device Type | How It Saves | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Smart controller | Schedules heating | Electric tank water heaters |
| Heat pump water heater | High efficiency + smart control | Long-term upgrades |
| Smart recirculation | Runs only when needed | Homes with recirc systems |
| Leak shutoff | Prevents waste and damage | All homes, especially older plumbing |
Leak detection also connects directly to sustainability. Preventing water loss reduces energy wasted in pumping and heating water.
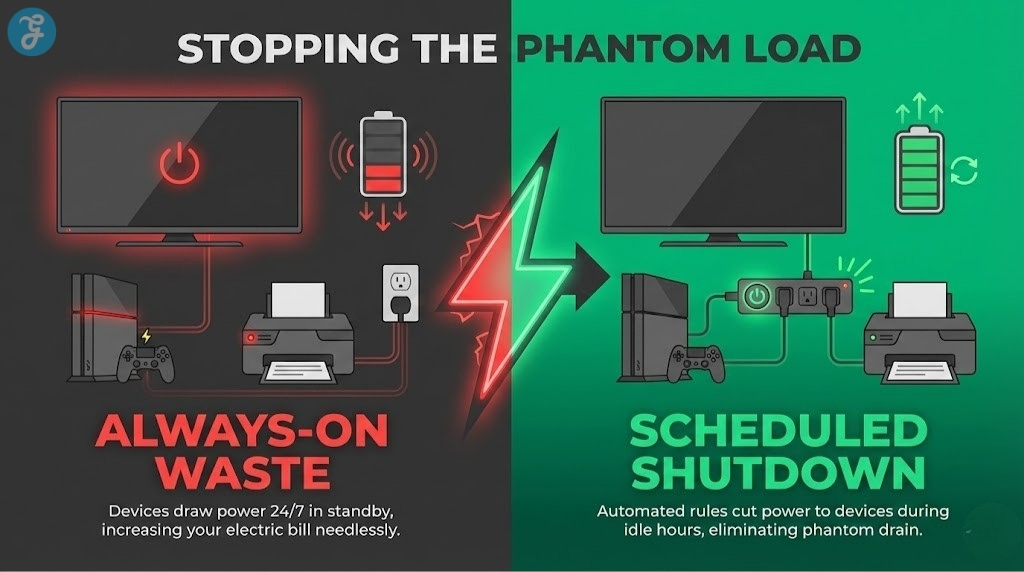
Smart Plugs And Power Strips: The Best Low-Cost Entry Point
Phantom loads, also called standby power, can add up across a home. TVs, game consoles, routers, speakers, chargers, printers, and kitchen appliances can draw power even when “off.”
Smart plugs and smart power strips reduce this by scheduling shutdowns, detecting idle states, and cutting power when devices are not in use.
What Smart Plugs Do Well
-
Turn off entertainment systems overnight
-
Cut power to office equipment after work hours
-
Control space heaters safely with timers and rules
-
Track energy usage for specific devices
Smart Plug Use Case Table
| Use Case | Rule | Result |
|---|---|---|
| TV and console | Off after midnight | Lower standby load |
| Home office | Off weekends | Reduced idle power |
| Kitchen devices | Off overnight | Less waste |
| Holiday lights | Schedule daily | Predictable control and savings |
This is where energy-saving smart home devices become practical quickly because setup is simple and savings begin immediately.
Smart Lighting: Savings Are Real, But Often Smaller Than People Think
LED bulbs already use far less energy than older lighting. That means the biggest lighting savings come from reducing “on time,” not from switching bulbs alone.
Smart lighting helps by:
-
Turning lights off automatically
-
Using occupancy sensors in hallways and bathrooms
-
Dimming lights during low-need periods
-
Using daylight sensors to reduce artificial lighting
Lighting Strategy Table
| Strategy | Best Device | Best Location |
|---|---|---|
| Occupancy-based off | Motion sensor or smart switch | Bathrooms, hallways |
| Dimming | Smart dimmer | Living rooms, bedrooms |
| Daylight response | Light sensor automation | Rooms with large windows |
| Schedules | Smart switch | Outdoor lighting |
For most homes, smart switches deliver better value than dozens of smart bulbs, because they reduce always-on connections and simplify control.
Smart Appliances: Where The Real Savings Are And Aren’t
Many smart appliances focus on features and notifications rather than energy reduction. A “smart fridge” is rarely an energy saver just because it has a screen. However, some appliance features can reduce waste.
Appliance Features That Can Save Money
-
Smart laundry scheduling to run during lower-cost electricity periods
-
Alerts that prevent leaving doors open on freezers and fridges
-
Energy monitoring to detect abnormal consumption
-
Heat pump dryers that reduce energy compared to older electric dryers
Appliance Value Table
| Appliance Category | Strong Energy Feature | Weak Feature |
|---|---|---|
| Laundry | Off-peak scheduling, heat pump tech | App notifications only |
| Refrigeration | Door alerts, abnormal load detection | Screens and entertainment |
| Dishwashers | Eco modes and scheduled runs | “Smart” without energy control |
| HVAC-related | Smart integration | Unconnected “smart” features |
If you want appliance savings, prioritize efficiency ratings and durable performance first. Smart features should support, not replace, baseline efficiency.
Home Energy Monitoring: The Device That Changes Behavior
One of the most effective energy-saving smart home devices is not something that directly controls power. It is a home energy monitor. These devices show where energy is going, making waste obvious.
Energy monitoring can help you:
-
Identify a failing appliance drawing too much power
-
Spot high standby loads
-
Learn which habits drive peak costs
-
Track the impact of changes over time
Monitoring Helps You Find These Common Problems
-
Old refrigerators with rising energy consumption
-
Space heaters running longer than expected
-
Always-on entertainment systems
-
Inefficient HVAC cycling patterns
-
Poor insulation leading to long heating/cooling runtimes
Energy Monitoring Table
| What You Learn | What You Can Do | Likely Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Standby loads | Add smart strips | Lower baseline usage |
| HVAC patterns | Adjust schedules and settings | Lower heating/cooling cost |
| Appliance anomalies | Repair or replace | Prevent long-term waste |
| Peak usage | Shift loads | Lower bills in time-of-use plans |
Monitoring turns energy savings into a measurable plan instead of guesswork.
Smart Home Automation Rules That Deliver Real Savings
The biggest mistake people make is buying devices without building rules. Savings come from automation, not from having an app.
High-Impact Automation Rules
-
Thermostat setback when no one is home
-
Smart plug shutdown of entertainment systems overnight
-
Occupancy-based lighting in key rooms
-
Water heater scheduling based on household patterns
-
Leak detection alerts and automatic shutoff
-
Peak-hour load reduction if you have time-of-use pricing
Automation Bundle Table
| Bundle | Devices | What It Targets |
|---|---|---|
| Comfort saver | Smart thermostat + sensors | Heating and cooling waste |
| Phantom load killer | Smart strip + plug rules | Standby power |
| Water saver | Leak sensor + smart shutoff | Water and energy waste |
| Visibility pack | Energy monitor | Hidden consumption patterns |
If you implement one bundle at a time, the setup stays manageable and the savings are easier to track.
The Rebound Effect: When Smart Homes Increase Energy Use
Some smart homes increase energy use because convenience encourages more consumption. This is called the rebound effect.
Examples include:
-
Running HVAC more because it is easy to control
-
Leaving lights on because automation “will handle it” but rules are not set well
-
Adding many always-on devices that draw standby power
-
Installing multiple hubs and cameras that run 24/7
Green smart homes are not about adding devices everywhere. They are about reducing waste where it matters most.
Rebound Risk Table
| Smart Feature | How It Can Backfire | Fix |
|---|---|---|
| Always-on devices | Adds baseline power draw | Choose low-power devices and reduce hubs |
| Over-automation | More comfort use than before | Set boundaries and schedules |
| Cameras everywhere | 24/7 streaming and storage | Use motion-triggered settings |
| Too many gadgets | Complexity and extra load | Focus on high-impact categories |
Energy-saving smart home devices should reduce total consumption, not shift it.
Cybersecurity And Privacy: The Cost You Should Not Ignore
Smart devices connect to networks. Poor security can create privacy risk and long-term cost. While this is not “energy,” it affects sustainability because insecure devices get replaced sooner and cause unnecessary churn.
Practical smart home security actions include:
-
Choose brands with long software support
-
Keep firmware updated
-
Use strong Wi-Fi security settings
-
Segment smart devices on a separate network if possible
-
Avoid unknown brands with unclear update policies
A device that stops receiving updates quickly becomes a replacement candidate, which undermines sustainability.
Smart EV Chargers: A Surprisingly Powerful Home Energy Tool
Energy-saving smart home devices are not limited to lights and thermostats. If you own an electric vehicle, a smart EV charger can become one of the most meaningful tools for controlling home electricity costs. Charging is a large load. When it happens at the wrong time, it can push you into higher rate tiers or peak pricing windows. When scheduled properly, it can reduce cost without changing your driving habits.
A smart charger can help by:
-
Scheduling charging for off-peak hours
-
Limiting maximum charging power to avoid demand spikes
-
Coordinating with solar generation if you have rooftop panels
-
Tracking charging costs and usage patterns over time
Smart EV Charging Table
| Feature | What It Does | Why It Saves Money |
|---|---|---|
| Off-peak scheduling | Charges when rates are lowest | Reduces cost per kWh |
| Power limiting | Prevents demand spikes | Avoids higher peak charges |
| Solar matching | Uses daytime generation | Cuts grid consumption |
| Reporting | Tracks cost and usage | Helps optimize routines |
Even without solar, off-peak scheduling alone can improve household cost control significantly.
Smart Blinds And Curtains: Lower HVAC Costs Without Touching The Thermostat
Windows are a major driver of heating and cooling demand. Sunlight can heat rooms aggressively. Poorly insulated windows can leak heat in winter. Smart blinds and shades help manage this passively by controlling sunlight and heat transfer.
They save energy by:
-
Blocking summer heat gain during peak sun hours
-
Allowing winter sunlight to warm rooms naturally
-
Reducing the need for daytime cooling in sunny rooms
-
Improving comfort so you rely less on HVAC extremes
Smart Shade Strategy Bullets
-
Close shades automatically during afternoon heat
-
Open shades in winter mornings to capture sunlight
-
Pair with temperature sensors for room-based rules
-
Combine with occupancy rules so unused rooms stay protected
Smart Shades Table
| Season | Automation Rule | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Summer | Close during peak sun | Lower cooling load |
| Winter | Open during sunny hours | Reduce heating demand |
| Year-round | Close at night | Better insulation effect |
These devices are most effective in homes with large windows or strong sun exposure.
Smart Ceiling Fans And HVAC Coordination
Ceiling fans do not cool air, but they improve comfort. When used correctly, they allow higher thermostat setpoints in summer or better warmth distribution in winter. This reduces HVAC energy use without reducing comfort.
Energy-saving smart home devices in this category work best when they coordinate with the thermostat and occupancy sensors.
Useful automation includes:
-
Turn fans on only when someone is in the room
-
Increase fan speed when indoor temperature rises
-
Turn fans off automatically after a set idle period
-
Reverse direction seasonally for better air distribution
Fan Automation Table
| Rule | When It Runs | Why It Helps |
|---|---|---|
| Fan on with occupancy | Room is in use | Avoids wasting fan power |
| Fan boost on heat | Temp exceeds threshold | Supports higher thermostat setting |
| Fan off after idle | No motion detected | Eliminates unnecessary runtime |
| Seasonal direction | Winter vs summer | Improves comfort efficiency |
Fans use far less energy than HVAC, so using fans strategically is often a net win.
Dehumidifiers, Air Quality Sensors, And The Comfort-Efficiency Link
Humidity can drive perceived discomfort more than temperature. In humid climates, lowering humidity can reduce the need to overcool your home. In dry climates, managing air quality can reduce unnecessary ventilation and filtration overuse.
Smart humidity sensors and air quality monitors help by making conditions measurable and triggering targeted actions.
They can support savings when paired with:
-
HVAC dehumidification modes
-
Smart dehumidifiers that run only when needed
-
Ventilation systems that avoid constant operation
-
Alerts that prevent overuse of energy-heavy filtration
Air Quality And Humidity Table
| Target | Smart Device | Energy Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Humidity control | Humidity sensor + smart dehumidifier | Less overcooling needed |
| Ventilation timing | Air quality monitor | Avoids unnecessary fan runtime |
| Filter efficiency | HVAC monitoring | Prevents wasted airflow restriction |
This category works best when it reduces extreme HVAC settings rather than adding new always-on devices.
A Simple “High-Impact Add-On” Bundle For Bigger Savings
If you already have a thermostat and smart plugs, these add-ons can push savings further without turning your home into a gadget showroom.
Recommended Add-On Bundle
-
Smart shades for sun-facing rooms
-
Smart ceiling fan control for main living areas
-
Smart EV charging schedule if you own an EV
-
Humidity sensors if you live in a humid region
Add-On Bundle Table
| Add-On | Best Fit Home | Main Savings Area |
|---|---|---|
| Smart shades | Large windows, strong sunlight | Reduced cooling and heating |
| Smart fan control | Multi-room comfort issues | Higher thermostat setpoints |
| Smart EV charger | EV owners | Off-peak energy savings |
| Humidity sensors | Humid climates | Less overcooling |
These upgrades stay aligned with the purpose of energy-saving smart home devices: lowering consumption where it matters most, with clear rules and measurable outcomes.
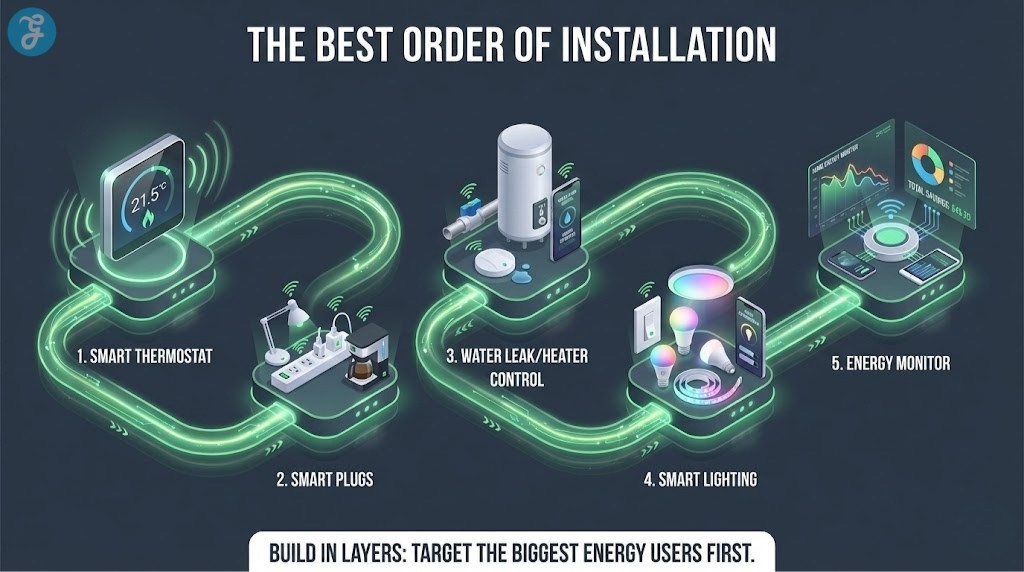
How To Build A Smart Home That Saves Money In 2026
A smart home should be built in layers, starting with the biggest energy drivers.
The Best Order Of Installation
-
Smart thermostat and HVAC optimization
-
Smart plugs and strips for standby loads
-
Water heating control and leak prevention
-
Smart lighting switches and sensors
-
Energy monitoring for visibility and fine tuning
-
Optional upgrades like zoning and smart appliances
This approach keeps spending focused where savings are largest.
At this point, it is helpful to restate the focus keyword naturally. Energy-saving smart home devices deliver the most value when they cut heating and cooling waste, reduce standby loads, and optimize water heating, not when they simply add convenience features.
Ending Thoughts
Energy-saving smart home devices can reduce bills and emissions, but only when they target real waste sources. Smart thermostats and HVAC automation often deliver the biggest impact. Smart plugs and power strips reduce phantom loads with low cost and fast payoff. Water heating control and leak prevention reduce both water and energy waste. Energy monitoring makes invisible consumption visible, helping households take action confidently.
The best smart home is not the one with the most gadgets. It is the one with the smartest rules, the fewest wasted kilowatt-hours, and the longest-lasting devices. When automation reduces waste without increasing baseline power draw, smart homes become a real sustainability tool, not just a convenience upgrade.