Cryptocurrency trading has gained immense popularity over the years, attracting investors from all over the world. As the market has matured, regulations have tightened, and Know Your Customer (KYC) requirements have become a standard practice for most exchanges. However, there are still some platforms that allow trading without verification, known as non-KYC crypto exchanges.
Understanding the ID requirements for crypto trading is important for anyone looking to enter the crypto market.
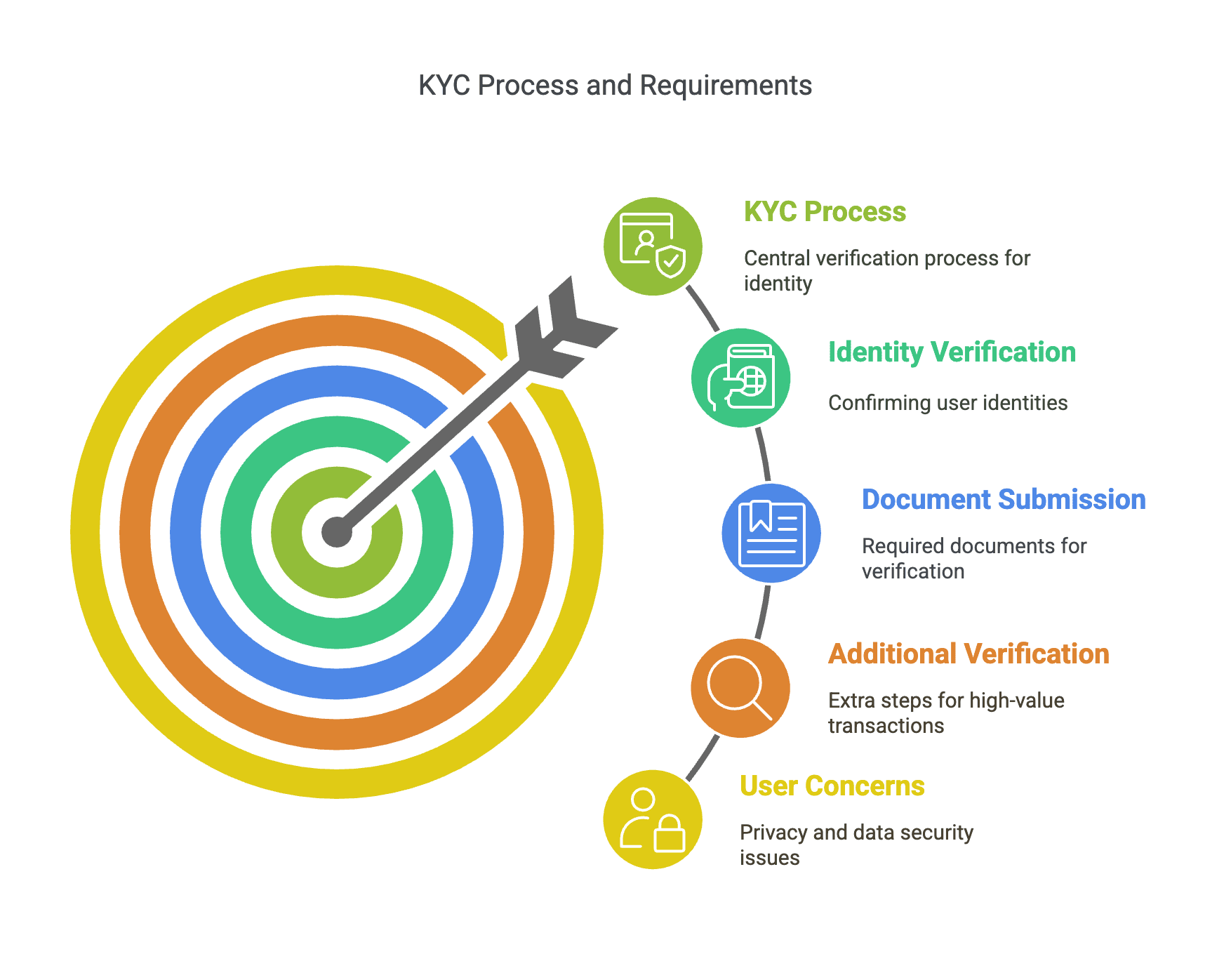
What is KYC?
KYC, or Know Your Customer, is a verification process used by financial institutions and cryptocurrency exchanges to confirm the identities of their users. As well as being a method to verify identity, the primary purpose of KYC is to prevent fraudulent activities and ensure regulatory compliance.
The KYC process typically involves submitting a government-issued identification document, such as a passport, national ID card, or even a driver’s license. On top of this, certain exchanges may need to see proof of residence, such as a utility bill or bank statement, to confirm the user’s address.
In some cases, KYC can be even more intrusive, requiring biometric verification, such as a selfie or facial recognition, which can be a cause for concern for many users when it comes to their privacy.
For users who want to trade large amounts of cryptocurrency, some platforms require further verification, which may include additional documentation like tax identification numbers, employment details, or financial statements.
While KYC isn’t a bad thing, in theory; many traders find it intrusive and don’t want to have to dish out so much personal and financial data, which then becomes vulnerable online.
Types of ID Required for Crypto Trading
Most cryptocurrency exchanges require users to submit government-issued identification to verify their identity. The most commonly accepted forms of ID include passports, national identity cards, and driver’s licenses.
Some exchanges may also need additional documents such as a utility bill or a bank statement to confirm the user’s address. The exact requirements vary depending on the exchange’s jurisdiction and local regulations.
Differences Between KYC and Non-KYC Exchanges
KYC-compliant exchanges generally offer access to fiat-to-crypto transactions, and in some cases, higher withdrawal limits. However, the verification process can be time-consuming, and many users prefer platforms that do not require KYC for ease of access and privacy.
Non-KYC exchanges allow traders to create accounts and execute transactions without submitting identification documents. These platforms are preferred by users who don’t want to wait for lengthy verification, and also highly value their privacy.
Why Many Traders Prefer Anonymity
Privacy is important for many cryptocurrency traders, particularly those who value the decentralized and permissionless nature of digital assets. Some traders prefer to keep their financial activities private for personal reasons, such as avoiding excessive data collection or ensuring financial sovereignty.
In some cases, traders may reside in countries with restrictive financial policies, making it difficult to access traditional banking services or regulated exchanges. Trading on non-KYC platforms can provide greater accessibility and ease of use, as well as better privacy, which is why many traders choose non-KYC platforms.
Regional Variations in ID Requirements
Cryptocurrency regulations tend to be significantly different in each country, affecting the ID requirements imposed by exchanges. In the United States, exchanges must comply with AML and KYC regulations enforced by the Financial Crimes Enforcement Network. Users are required to provide detailed personal information before they can access full trading services.
Some countries, such as Japan and South Korea, have strict regulations, requiring detailed KYC processes before users can trade. In contrast, certain jurisdictions in the Caribbean or Southeast Asia may have exchanges that operate with minimal or no KYC requirements, providing alternative options for traders.