Storing data safely is a big concern for VPS users. Hard drive failures can lead to data loss, downtime, and frustration. Many wonder how to protect their files while improving system performance.
RAID (redundant array of independent disks) helps solve these problems. It uses multiple disk drives to boost storage capacity, speed, and data safety. This blog explains different RAID configurations like RAID 0 and RAID 1 and why they matter in VPS storage.
Stay with us to learn how RAID keeps your data safe and your system running smoothly!
Key Benefits of Using RAID in VPS Storage
RAID boosts data safety by spreading copies or pieces of files across multiple drives. It also helps keep systems running smoothly even if a drive fails.
Data Redundancy
Data redundancy means storing copies of the same data on different drives. This protects against drive failure in VPS storage systems. For example, RAID 1 mirrors all data on two separate disks, ensuring no loss if one fails.
Some RAID levels like RAID 5 and RAID 6 store parity information across multiple drives. This balance between performance and protection ensures high availability while preventing total data loss.
Enhanced Performance
RAID storage boosts system performance. RAID 0 uses data striping, splitting files across drives. This setup increases read and write speeds but lacks fault tolerance. For better balance, RAID 10 combines striping and mirroring.
It provides faster access while protecting against drive failure.
Hardware RAID controllers can also improve speed by managing tasks directly without taxing the CPU. SSDs in a RAID array make systems even quicker due to their high-speed operations.
These setups are ideal for demanding tasks like VPS hosting or database management.
Improved Fault Tolerance
Improved fault tolerance protects data during drive failure. Using RAID levels like RAID 1, RAID 5, or RAID 10 ensures smoother recovery and reduces downtime. For example, in RAID 1, if one hard disk fails, the mirrored copy on the second drive stays safe.
RAID arrays like RAID 5 use parity to rebuild data even after a single drive breaks down. This setup balances performance and safety well. Combining multiple drives into a single logical unit also spreads risks across all disks, boosting data protection while maintaining storage capacity.
Different RAID Configurations Explained
RAID setups offer unique ways to balance speed, safety, and storage. Each type works differently to meet specific needs in data storage and protection.
RAID 0: Striping for Performance
Striping splits data across multiple hard drives. This helps improve read and write speeds. RAID 0 uses this method but does not offer fault tolerance or backup options. If one drive fails, all data is lost.
It works well for tasks needing speed, like video editing or gaming.
This setup increases system performance by allowing drives to work together. For example, two 1TB drives will provide a total of 2TB storage space and faster access times. Unlike mirrored setups in RAID 1, it focuses only on speed and storage capacity without redundancy features.
RAID 1: Mirroring for Redundancy
RAID 1 copies data to two drives at the same time. This is called mirroring and helps protect against drive failure. If one hard disk fails, the other disk still has all the data. You only lose space equal to one drive because everything is stored twice.
For example, with two 1TB drives, your usable storage is just 1TB.
This setup improves data safety but does not boost write speeds like RAID 0. It works well for important files where protection matters more than extra capacity or speed. Many businesses use RAID 1 in servers or VPS storage for reliability.
Solid-state drives (SSDs) paired with this configuration can further enhance performance while ensuring high fault tolerance over time.
RAID 10: Combining Performance and Redundancy
RAID 10 combines the benefits of RAID 0 and RAID 1. It uses both striping and mirroring to provide speed and redundancy. Data is split across multiple drives for faster performance, while each drive has a mirror copy for protection.
This configuration requires at least four hard disks or SSDs. Half of the storage capacity is used for data mirroring, so space efficiency reduces compared to other setups. If one drive fails, data remains safe due to the mirrored copies.
It’s ideal for systems needing high-speed access and strong fault tolerance, like databases or VPS hosting environments.
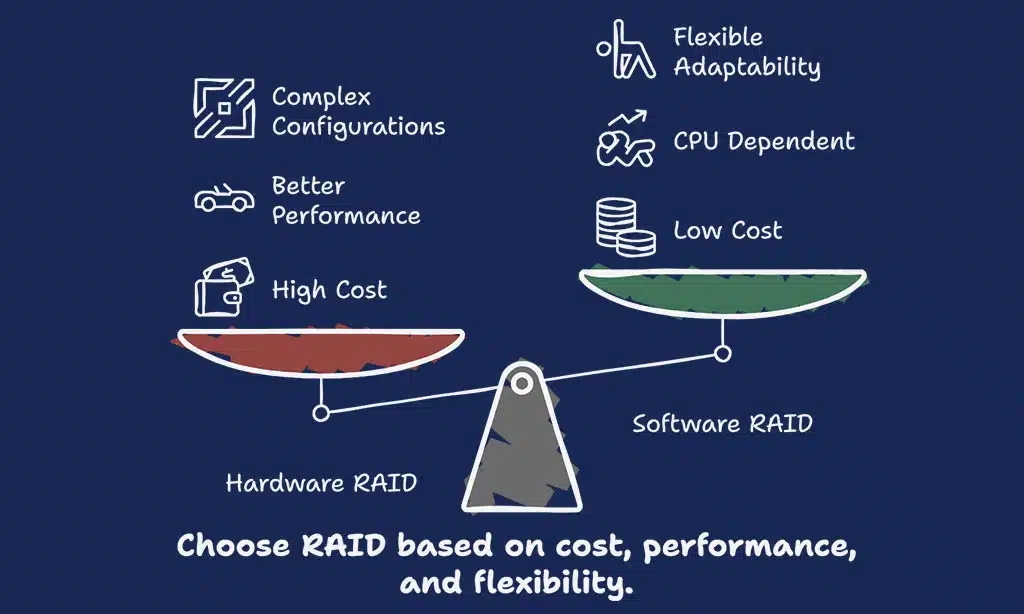
RAID Controllers: Hardware vs. Software
RAID controllers manage how drives work together—learn the differences between hardware and software options to pick what fits your needs best.
Advantages and Limitations of Hardware RAID
Hardware RAID uses a dedicated controller for storage management. It enhances system performance and supports complex RAID configurations like RAID 5 or nested RAID levels. Faster write speeds and data redundancy improve data safety during drive failures.
The independent controller reduces CPU load, improving system performance in data centers or PCs running virtual private servers.
Still, hardware RAID has limitations. The cost of the controllers can be high, impacting budgets in smaller setups. Compatibility issues may arise with specific motherboards or NAS devices.
If the controller fails without backups, accessing stored data might become difficult. Drive replacements often require specific models for proper function, limiting flexibility when upgrading storage capacities.
Advantages and Limitations of Software RAID
Software RAID uses the operating system to manage data storage. This makes it cheaper since no extra hardware is needed. It works well for small systems or budget setups. Many VPS providers use software RAID for its flexibility.
It can run across different drives and adapt quickly.
Despite its benefits, it relies heavily on the CPU. This can slow performance during heavy tasks like file storage or backups. If the OS fails, access to RAID may stop until fixes are made.
Software RAID often lacks advanced features found in hardware options, like self-monitoring tools or checksums for higher fault tolerance.
Challenges of RAID in VPS Storage
RAID setups can be costly and may still risk data loss without proper backups—read on to uncover more challenges.
Cost Considerations
Using RAID configurations can increase costs. Hardware RAID controllers often cost more than software setups. High-performance drives, like SSDs, also raise prices. For instance, RAID 1 requires double the storage since data is mirrored on two disks.
Maintenance and upgrades add to expenses too. If a drive fails in nested RAID levels like RAID 10 or RAID 5, you’ll need compatible replacements quickly. Larger datacenters might find network attached storage with robust fault-tolerance pricier but necessary for reliability.
Budget planning becomes essential for balancing performance and cost.
Potential for Data Loss Without Backups
RAID configurations can fail, leaving data at risk. Drive failure in systems like RAID 0 offers no safety net since it lacks redundancy. Even with RAID 5 or RAID 10, multiple failures could result in permanent loss.
Backups are vital for true data protection. No matter the RAID level, relying on it alone risks losing critical files during faults or corruption. Cloud backups and external storage solutions add an extra layer of resilience against unexpected issues.
Takeaways
Understanding RAID configurations makes managing VPS storage easier. These setups boost data safety, speed, and fault tolerance. Options like RAID 1 or RAID 10 suit different needs, balancing protection and performance.
Both hardware and software solutions have unique benefits for flexibility or efficiency. Picking the right setup depends on your budget and goals. Have you thought about how these setups can improve your system’s reliability? Start applying what you’ve learned today to keep your data safer and faster!
FAQs on Role of RAID Configurations in VPS Storage
1. What is RAID in VPS storage?
RAID stands for Redundant Array of Independent Disks. It combines multiple drives to improve data safety, fault tolerance, and system performance.
2. How do RAID configurations protect against data loss?
RAID configurations like RAID 5 or RAID 0+1 use striping with parity or mirroring to prevent data loss during drive failure.
3. What are the main types of RAID setups?
There are hardware RAID and software RAID setups. Hardware uses physical raid controllers, while software relies on operating systems or tools like storage spaces.
4. Can I increase both speed and redundancy with a single configuration?
Yes, hybrid RAIDs such as nested levels (like RAID 10) combine faster write speeds from striping with redundancy from mirroring for better performance and protection.
5. Is backup still needed if I use a RAID setup?
Yes, backups remain essential even with raid storage since it cannot fully replace robust backup strategies for complete data protection.
6. Where is RAID commonly used today?
RAID is widely used in web hosting, network-attached storage (NAS), edge computing, the cloud, and Internet of Things (IoT) devices to ensure reliable data availability and virtualization efficiency.