In the battle against climate change, carbon farming has emerged as a vital strategy for reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting sustainable land use.
Among global leaders in this field, New Zealand has carved a unique niche, leveraging its rich natural resources, innovative policies, and commitment to environmental stewardship.
New Zealand’s carbon farming initiatives are not only addressing climate challenges at home but also serving as a model for the rest of the world.
By focusing on sustainable agricultural practices, technological innovation, and international collaboration, the country is paving the way for effective climate solutions that are both scalable and impactful.
This comprehensive guide explores New Zealand’s carbon farming initiatives, their key practices, and the global impact of their strategies, showcasing the pivotal role of New Zealand in global carbon farming initiatives and why the country stands out in the fight against climate change.
Understanding Carbon Farming and Its Global Importance
Carbon farming involves adopting land management practices that increase the amount of carbon stored in soil and vegetation while reducing emissions.
These practices include reforestation, agroforestry, regenerative agriculture, and improved soil management.
By absorbing more carbon dioxide from the atmosphere than is released, carbon farming serves as a powerful tool in mitigating climate change.
Why Carbon Farming Matters Globally
With rising carbon emissions driving global warming, carbon farming offers a scalable, nature-based solution.
It not only helps sequester carbon but also promotes biodiversity, enhances soil health, and improves agricultural resilience.
Global adoption of these practices could significantly reduce the impacts of climate change while supporting sustainable development goals.
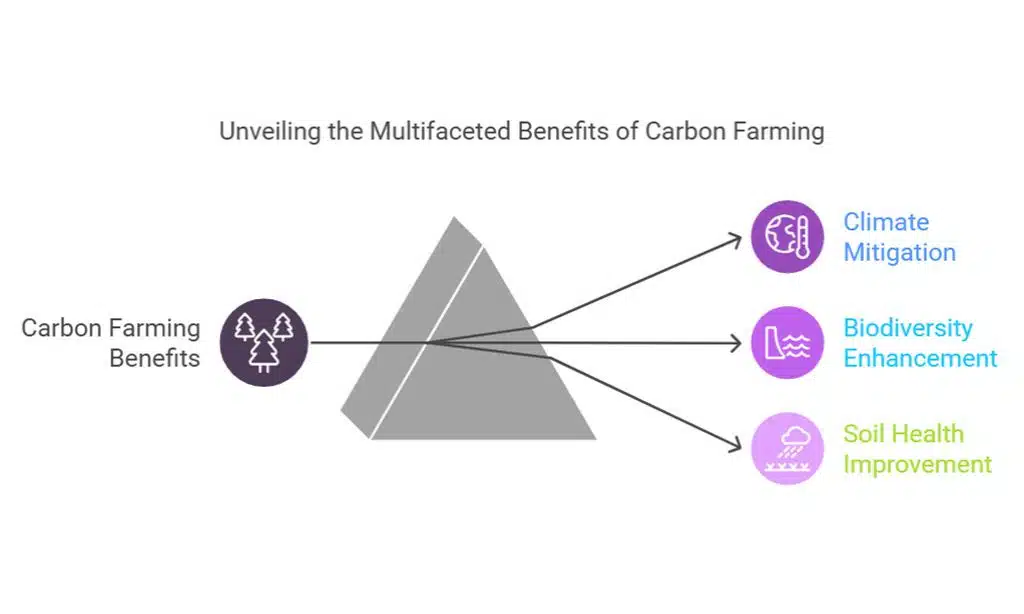
Key Benefits of Carbon Farming:
| Benefit | Description |
| Climate Mitigation | Reduces atmospheric CO2 levels effectively. |
| Biodiversity Enhancement | Supports diverse ecosystems and habitats. |
| Soil Health Improvement | Boosts fertility and prevents degradation. |
New Zealand’s Role in Carbon Farming
New Zealand’s leadership in carbon farming initiatives stems from its robust environmental policies, innovative farming techniques, and dedication to meeting global climate goals.
The country’s unique geographical and climatic conditions make it an ideal environment for implementing effective carbon farming practices, setting a benchmark for others to follow.
New Zealand’s Unique Position in Carbon Farming
New Zealand’s diverse landscapes and temperate climate create optimal conditions for carbon farming.
The country’s extensive forests, fertile soils, and rich biodiversity contribute to its capacity for large-scale carbon sequestration.
Native plant species, such as totara and manuka, are particularly effective at capturing and storing carbon, making reforestation a key component of New Zealand’s strategy.
Environmental Factors Supporting Carbon Farming
| Factor | Description |
| Climate | Temperate, ideal for diverse vegetation. |
| Soil Quality | High organic matter content. |
| Native Flora | Efficient carbon capture and storage potential. |
Policy Framework Supporting Carbon Farming
The New Zealand government has established a strong policy framework to support carbon farming initiatives:
- Emissions Trading Scheme (ETS): The ETS incentivizes landowners to engage in carbon farming by allowing them to earn carbon credits for planting forests and adopting sustainable practices.
- Zero Carbon Act: Enacted in 2019, this law commits New Zealand to achieving net-zero carbon emissions by 2050.
- He Waka Eke Noa: This industry-government partnership helps farmers transition to lower-emission practices.
These policies ensure that carbon farming aligns with both national and international climate objectives.
Case Example: The ETS has encouraged the establishment of more than 500,000 hectares of new forests, significantly increasing New Zealand’s carbon sequestration capacity.
New Zealand’s carbon farming initiatives reflect a strong commitment to balancing environmental health with economic incentives.
Key Carbon Farming Practices in New Zealand
Agroforestry integrates trees and shrubs into farmland, enhancing carbon storage while maintaining agricultural productivity. In New Zealand, agroforestry practices include:
- Planting shelterbelts and riparian buffers.
- Incorporating perennial crops alongside livestock grazing.
- Establishing mixed-species plantations to maximize carbon capture and biodiversity.
Case Study: Successful Agroforestry Projects
The “Taranaki Carbon Farming Initiative” demonstrates the benefits of agroforestry. By combining forestry with livestock grazing, this project has increased carbon sequestration, reduced soil erosion, and improved farm profitability.
Such examples highlight the tangible impact of New Zealand’s carbon farming initiatives.
Agroforestry Benefits
| Practice | Benefit |
| Shelterbelts | Wind protection and carbon capture. |
| Mixed-species Planting | Enhances biodiversity and carbon storage. |
| Riparian Buffers | Reduces water pollution and captures carbon. |
Regenerative Agriculture Techniques
Regenerative agriculture focuses on restoring soil health, improving water retention, and enhancing biodiversity. New Zealand farmers are adopting methods such as:
- No-till farming to preserve soil structure.
- Cover cropping to prevent soil erosion and increase organic matter.
- Rotational grazing to improve pasture productivity and carbon storage.
These practices not only sequester carbon but also boost resilience against climate variability, making them integral to New Zealand’s carbon farming initiatives.
Practical Example: A regenerative farm in Canterbury reported a 30% increase in soil organic carbon over five years, showcasing the long-term benefits of these methods.
Technology and Innovation in Carbon Farming
New Zealand is leveraging cutting-edge technology to enhance its carbon farming efforts.
Examples include:
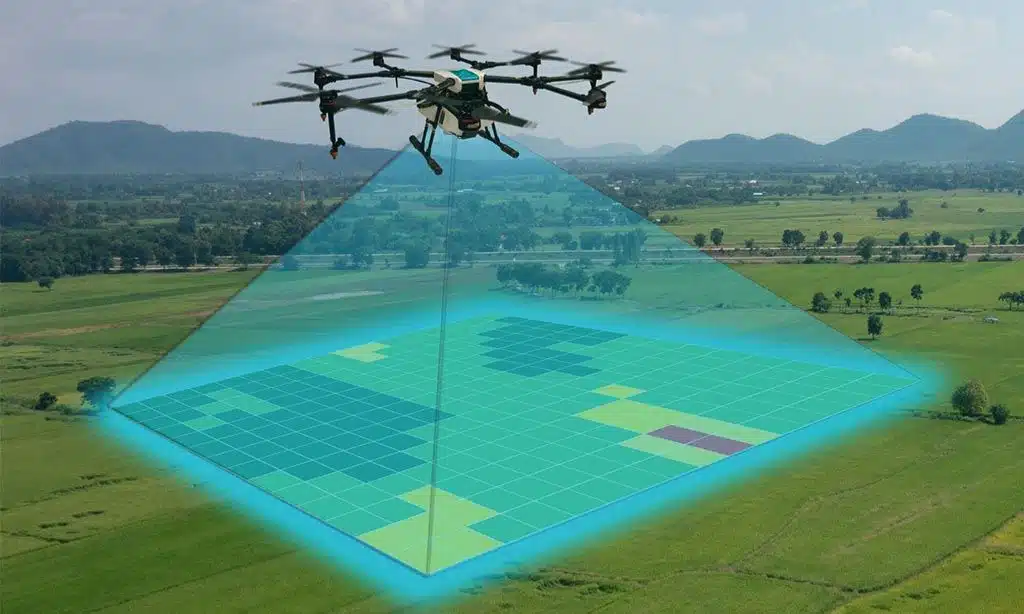
- Drones and Satellite Imagery: Used for monitoring forest growth, assessing soil health, and mapping carbon stocks.
- Digital Tools for Carbon Credits: Platforms like “Toitū Envirocare” assist landowners in calculating and trading carbon credits.
Key Technologies in Carbon Farming
| Technology | Application |
| Drones | Forest monitoring and data collection. |
| Satellite Imagery | Carbon stock mapping and land analysis. |
| Digital Tools | Simplifies carbon credit management. |
The Role of New Zealand in Global Carbon Farming Initiatives
New Zealand actively collaborates with global institutions to promote carbon farming.
For instance:
- United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC): New Zealand contributes to international discussions on carbon farming as part of its climate commitments.
- Global Research Alliance on Agricultural Greenhouse Gases: The country co-leads efforts to reduce emissions from agriculture worldwide.
Example: New Zealand’s expertise has supported Pacific nations in adopting sustainable carbon farming practices tailored to their unique ecosystems.
Such collaborations enhance the global influence of New Zealand’s carbon farming initiatives.
Exporting Knowledge and Technology
New Zealand’s expertise in carbon farming is increasingly sought after by other nations. By sharing best practices and technological innovations, New Zealand helps other countries enhance their carbon sequestration efforts.
Success Stories
Programs like the “Pacific Carbon Farming Initiative” have enabled island nations to adopt sustainable practices, drawing inspiration from New Zealand’s model.
Challenges: Despite its success, New Zealand faces obstacles such as funding gaps and the need for scalable solutions to include smaller landholders.
Key Challenges in Carbon Farming
| Challenge | Description |
| Land Use Conflicts | Balancing agriculture and forestry demands. |
| Funding | High investment requirements. |
| Scalability | Adapting practices for smaller farms. |
Economic and Environmental Benefits of Carbon Farming
Carbon farming contributes to New Zealand’s economy in several ways:
- Carbon Credits: Landowners earn revenue through the ETS by selling carbon credits.
- Job Creation: Expanding carbon farming creates employment opportunities in forestry, technology, and consulting.
Economic Contributions of Carbon Farming
| Contribution | Impact |
| Carbon Credits | Additional revenue streams for landowners. |
| Job Creation | Employment in sustainable industries. |
Environmental Gains
The environmental benefits of carbon farming include:
- Reduced Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Increased carbon sequestration helps offset emissions from agriculture and energy.
- Enhanced Biodiversity: Reforestation and agroforestry support diverse ecosystems.
- Improved Soil Health: Sustainable practices restore soil fertility and prevent erosion.
Future Outlook for Carbon Farming in New Zealand
Innovations on the Horizon
Emerging technologies promise to revolutionize carbon farming in New Zealand:
- Biochar production for soil enhancement and carbon storage.
- AI-driven tools for precision farming and carbon monitoring.
Scaling Carbon Farming Efforts
Strategies for scaling carbon farming include:
- Engaging Small-Scale Farmers: Offering incentives and technical support to encourage participation.
- Public-Private Partnerships: Collaborating with businesses to fund large-scale projects.
Example: The “Smallholder Carbon Farming Support Program” aims to integrate small farms into the ETS, ensuring inclusivity and widespread adoption. These efforts highlight the adaptability of New Zealand’s carbon farming initiatives to diverse farming contexts.
Interactive Elements
Comparative Table: New Zealand’s Carbon Farming Policies vs. Global Leaders
| Policy Area | New Zealand | Australia | EU | USA |
| Carbon Credits | ETS-based system | ERF initiatives | CAP funding mechanisms | 45Q tax credit system |
| Climate Goals | Net-zero by 2050 | Net-zero by 2050 | Fit for 55 plan | Net-zero by 2050 |
| Agroforestry Practices | National integration | Regional initiatives | Extensive implementation | Pilot programs |
Takeaway
New Zealand’s carbon farming initiatives underscore the country’s commitment to addressing global climate challenges.
By combining innovative practices, strong policy support, and international collaboration, New Zealand has positioned itself as a leader in carbon farming.
As the world looks for sustainable solutions to combat climate change, New Zealand’s carbon farming initiatives offer a blueprint for others to follow, proving that small nations can make a big impact.
The journey ahead may be filled with challenges, but with continued innovation and global cooperation, New Zealand’s carbon farming model holds the potential to transform agriculture and climate solutions worldwide.