Emerging markets are shaping the next chapter of the smartphone industry. Many countries still have millions of first-time smartphone buyers. Even more people are upgrading from older phones with slow processors and weak batteries. At the same time, mobile internet is becoming cheaper in many regions. That mix creates a huge wave of demand.
This is why the fastest-growing smartphone brands in emerging markets are gaining attention. In these regions, buyers often look for value, durability, and long battery life more than prestige. They want a phone that lasts all day, charges fast, and survives daily use. They also want great cameras for social media, even on a tight budget.
Another key reason is the rise of affordable 4G and 5G phones. As networks expand, buyers want devices that can take advantage of faster speeds. Brands that can deliver solid specs at the right price grow faster than brands that focus only on premium phones. That is also why local distribution and after-sales service matter so much.
What This Article Covers
| What You’ll Learn | Why It Matters |
| The top 10 fastest-growing brands | Helps you understand who is gaining share and why |
| Growth drivers in emerging markets | Explains what actually moves sales in these regions |
| How brands compete by price and features | Shows how value phones win against big rivals |
| What’s next through 2030 | Gives a realistic view of future growth opportunities |
Methodology: How We Chose The Fastest-Growing Brands
We built this list using clear and practical signals. We focused on brands that are expanding in real-world sales presence, not just online buzz. We also looked at how brands perform in regions where price sensitivity is high. The goal is to reflect momentum that can be seen in both shipments and market presence. This approach helps keep the article fair and data-informed.
We treated “fast-growing” as a combination of growth factors. A brand may grow fast in one region due to strong offline retail. Another may grow through aggressive online pricing and rapid model releases. Some brands grow because they serve the entry-level market better than anyone else. Others grow because they dominate the mid-range upgrade cycle.
We also kept the definition of “emerging markets” broad and practical. It typically includes countries across South Asia, Southeast Asia, Africa, Latin America, and parts of Eastern Europe. These markets often share similar conditions: rising smartphone adoption, expanding mobile internet, and a large base of budget-conscious buyers.
How Growth Was Evaluated
| Signal | What It Reveals |
| Year-over-year momentum | Whether the brand is gaining speed, not just holding position |
| Market share movement | Whether it is winning against close competitors |
| Strength in entry and mid-range segments | Where most emerging-market volume sits |
| Distribution footprint | Whether the brand can scale beyond big cities |
| Service and trust factors | Whether it can retain users and reduce churn |
Key Trends Driving Smartphone Growth In Emerging Markets
Emerging markets do not grow the same way mature markets do. Many buyers in these regions prioritize practical value. They want a phone that feels “complete” even at a lower price. That means fewer compromises on battery, display, and camera quality. It also means brands must optimize costs without damaging user experience.
Offline retail still plays a massive role. In many countries, a large share of buyers still prefer walking into a shop. They want to hold the phone, compare models, and negotiate pricing. Retailers also influence decisions through recommendations and promotions. Brands with strong retail incentives and service centers often win here.
Financing is another major driver. Installment plans, trade-ins, and carrier bundles make smartphones affordable for more people. When the monthly cost is low, more buyers can upgrade sooner. This helps brands scale quickly. It also increases competition, because buyers have more choices at the same monthly payment.
Finally, regional customization matters more than many people think. Dual SIM support, strong network tuning, good low-light camera output, and heat management can influence buyer satisfaction. Brands that listen to these local needs can grow faster than brands that copy-paste strategies from the West.
Top Growth Drivers In Emerging Markets
| Trend | Why It Helps Brands Grow |
| Value pricing | Expands the buyer base quickly |
| Battery and durability focus | Builds trust and reduces returns |
| Offline retail strength | Wins customers outside big cities |
| Financing and bundles | Makes upgrades possible for more users |
| Local features and tuning | Improves satisfaction and word-of-mouth |
10 Fastest-Growing Smartphone Brands In Emerging Markets
This list highlights brands that are gaining traction across emerging regions. Some are global giants. Others are region-first players that mastered local needs. The mix is important because growth does not come from one strategy. It comes from execution, price discipline, and strong distribution.
You will see a pattern across most of these brands. They tend to release multiple models at key price points. They also emphasize battery, camera, and display quality. They partner with retailers and carriers to widen reach. And they keep marketing focused on practical benefits rather than luxury.
Below are the brands, followed by deeper detail for each one.
The 10 Brands And Their Main Growth Advantage
| Brand | Core Advantage In Emerging Markets |
| Xiaomi | Strong specs for the price, fast product refresh cycles |
| Transsion (Tecno/Infinix/itel) | Deep localization and entry-level dominance |
| Samsung | Broad lineup, trusted brand, strong service network |
| Realme | Youth positioning and aggressive value strategy |
| vivo | Offline retail power and camera-focused mid-range |
| OPPO | Retail visibility and strong design appeal |
| Lava | Local relevance and value-first domestic strategy |
| HONOR | Premium-feel mid-range devices at competitive prices |
| Motorola | Strong regional footholds and clean software experience |
| HMD (Nokia/HMD) | Trust, durability positioning, and entry-level accessibility |
1. Xiaomi
Xiaomi grows by making “value” feel exciting. It often delivers strong displays, fast charging, and capable processors at aggressive prices. That helps it win first-time buyers and upgraders. It also keeps momentum by launching frequently. This makes the brand feel fresh and competitive. In many markets, Xiaomi thrives where online shopping is strong.
Xiaomi’s product strategy is also flexible. It can push entry-level models in one market and mid-range models in another. It also uses sub-brands and series differentiation to cover more price points. This allows it to fight multiple rivals at once. For budget users, it competes on specs. For mid-range users, it competes on features like camera stabilization and AMOLED displays.
Another advantage is ecosystem pull. Many buyers like having affordable earbuds, wearables, and smart devices from the same brand. This supports repeat purchases and loyalty. Over time, Xiaomi can become a “default” choice for value-focused buyers in emerging markets.
2. Transsion Holdings (Tecno, Infinix, itel)
Transsion is built around emerging markets from the start. It has mastered what many global brands struggled to do. It understands local buyer needs and local retail realities. It also targets the biggest volume segments: entry-level and affordable mid-range. This gives it a huge advantage in markets where first-time smartphone adoption is still rising.
The company’s multi-brand approach is key. Itel often targets ultra-budget buyers. Tecno commonly targets mainstream users who want better cameras and designs. Infinix often appeals to younger buyers who want performance and big screens. This segmentation helps Transsion cover a wide range without confusing buyers.
Transsion also benefits from strong offline distribution. In many African and South Asian markets, the offline channel is still dominant. Retailers know Transsion models well. Service and repair support is also important, and Transsion often builds that locally. When a phone is easier to repair, more buyers trust the brand.
3. Samsung
Samsung’s emerging-market growth comes from reach and trust. In many countries, Samsung is the brand that people recognize first. That matters for buyers who do not want to take risks on unknown names. Samsung also offers a wide range of models. It can compete in budget, mid-range, and premium at the same time. This is a major advantage in diverse markets.
Samsung’s mid-range phones often drive volume. These models usually offer reliable cameras, steady software support, and strong build quality. Buyers also value Samsung’s service network. When customers know they can find service centers easily, they are more likely to buy. This is especially true in smaller cities.
Samsung also works well with carriers and retailers. Promotions, bundles, and installment offers make Samsung devices easier to buy. While Samsung faces intense price pressure from value brands, its brand trust and distribution help it remain one of the fastest movers in many emerging regions.
4. Realme
Realme is often positioned as the “young and fast” brand. It grows by offering feature-rich phones at low prices. It also markets aggressively through online channels. In markets where social media and e-commerce are strong, Realme can scale quickly. Many buyers see it as a smart alternative to older, slower budget models.
Realme’s success often comes from timing. It launches new phones rapidly and pushes headline features down into cheaper tiers. That may include fast charging, high refresh-rate displays, or large batteries. Realme also focuses on performance for the price, which helps it win students and young professionals.
Another reason Realme grows fast is its clear competition strategy. It often targets the same buyers as Xiaomi and OPPO sub-lines. When it wins, it wins through a simple message: more features for less money. In emerging markets, that message works.
5. vivo
vivo grows through offline excellence. In many emerging markets, vivo is visible everywhere in retail stores. It invests in retailer relationships, sales staff, and strong in-store promotion. This is a big advantage outside major cities. It also focuses heavily on camera and battery experiences, which matter to everyday buyers.
vivo’s lineup often targets the mass mid-range. These are the phones people buy when they want an upgrade without going premium. vivo typically emphasizes portrait photos, video performance, and stable software features. It also tends to deliver balanced hardware that feels smooth for daily use.
vivo’s growth strategy is steady, not random. It builds a strong local presence, then expands deeper. That helps it keep sales stable even during economic shifts. In emerging markets, stability can be a competitive advantage.
6. OPPO
OPPO is strong in regions where brand image and offline reach matter. It invests heavily in marketing and retail presence. Many buyers recognize OPPO through ads, sponsorships, and store visibility. This helps OPPO compete even when the spec sheets are similar to rivals.
OPPO also focuses on design and camera appeal. Many users want a phone that looks premium, even if it is mid-range. OPPO often delivers that “premium feel” with sleek finishes and good displays. It also focuses on fast charging, which is a practical feature people notice quickly.
OPPO’s challenge is price competition. Emerging markets are aggressive, and rivals undercut quickly. But OPPO can still grow because it plays a different game. It wins through retail power, marketing, and brand desire.
7. Lava
Lava is a strong example of a local brand strategy. It can grow quickly when it focuses on domestic demand and value positioning. In some emerging markets, buyers like local brands for practical reasons. Pricing can be more competitive. Distribution can be better in smaller cities. Local service and repair can also be faster.
Lava’s growth often depends on its ability to deliver solid entry-level phones. For many buyers, the first smartphone must be reliable and affordable. Lava can compete there. It can also benefit from local manufacturing narratives and policy support in certain markets.
Local brands like Lava may not dominate globally, but they can be fast-growing within their home region. In emerging markets, regional wins can be massive in volume. That makes Lava a brand to watch.
8. HONOR
HONOR has regained attention by offering strong mid-range devices that feel premium. Many HONOR phones focus on sleek designs, high-quality screens, and capable cameras. This helps the brand compete with both value brands and mainstream giants. In emerging markets, the “premium feel at mid-range price” approach can generate fast growth.
HONOR also benefits from a clear brand reset. It positions itself as modern and independent. In many regions, it partners with retail and carrier channels to widen availability. That is crucial for scale, especially where offline buying remains common.
HONOR’s opportunity is large because many emerging-market buyers are upgrading into the mid-range. If HONOR captures those upgraders, it can grow quickly. That is why it often appears in discussions of rising smartphone momentum.
9. Motorola
Motorola continues to be important in emerging markets, especially in Latin America. It often wins through a clean software experience and strong mid-range value. Many buyers like the simplicity of Motorola’s Android approach. They also trust the brand name, which helps with repeat purchases.
Motorola is also good at balancing price and build. It often focuses on solid, practical devices rather than flashy features that inflate costs. For buyers who want a phone that “just works,” Motorola is attractive. Carrier partnerships can also strengthen Motorola’s growth in certain markets.
Motorola’s growth depends on defending its strongholds and expanding where competitors are weaker. In emerging markets, that can happen quickly if Motorola targets the right price band and distributes well.
10. HMD (Nokia / HMD-Branded Phones)
HMD’s Nokia-branded phones still carry strong recognition in many emerging markets. That recognition matters, especially among buyers who want reliability. Many customers associate Nokia with durability, even if the modern smartphone market has changed. This trust can support growth in entry-level segments.
HMD also targets accessible price points. In emerging markets, entry-level phones remain a large part of volume. When HMD offers competitive battery life and sturdy builds, it can attract first-time buyers. It can also appeal to buyers who want a simple, dependable phone.
HMD’s future growth depends on how well it adapts to modern expectations. Buyers now want good cameras, smooth performance, and strong value. If HMD meets those expectations at the right price, it can remain a fast-growing player in certain emerging regions.
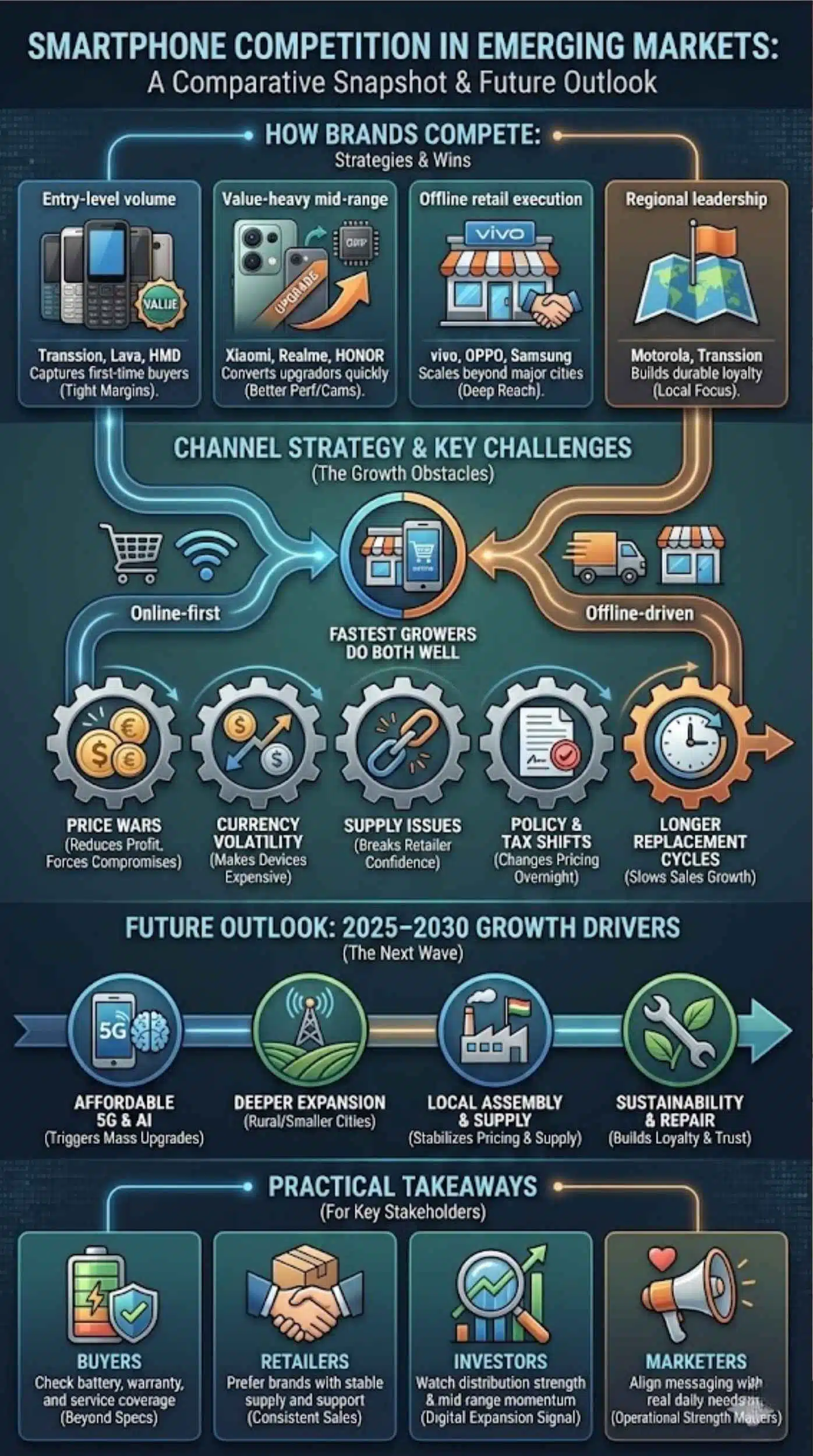
Comparative Snapshot: How These Brands Compete
Emerging-market competition is not one-dimensional. Some brands win through price. Others win through retail reach. Some win because they understand local needs better. This section helps you compare strategies without getting lost in brand hype.
In the entry-level tier, volume is huge but margins are tight. Brands like Transsion and some local players can dominate by controlling distribution and costs. In the mid-range tier, buyers upgrade for better cameras and performance. That is where Xiaomi, Realme, HONOR, Samsung, vivo, and OPPO fight hardest.
Another key factor is channel strategy. Online-first brands can grow fast where e-commerce is strong. Offline-driven brands can grow deeper into smaller cities. The fastest growers are often the ones that can do both well.
Strategy Comparison
| Strategy | Brands That Fit | Why It Wins |
| Entry-level volume | Transsion, Lava, HMD | Captures first-time buyers |
| Value-heavy mid-range | Xiaomi, Realme, HONOR | Converts upgraders quickly |
| Offline retail execution | vivo, OPPO, Samsung | Scales beyond major cities |
| Regional leadership | Motorola, Transsion | Builds durable loyalty |
Challenges Facing Smartphone Brands In Emerging Markets
Fast growth comes with hard problems. Price wars can destroy margins. Currency changes can force sudden price hikes. Supply chain disruptions can delay launches and frustrate retailers. These issues can slow a brand even when demand is strong.
Regulation and import policy also matter. Some governments adjust taxes, tighten rules, or encourage local assembly. That can change which brands have an advantage. Brands that rely heavily on imports may struggle with cost shocks. Brands with local assembly options can respond faster.
Another challenge is that replacement cycles can lengthen. When incomes tighten, people keep phones longer. That makes growth harder, especially after the first wave of adoption. It also increases the need for real upgrades that feel worth it.
Brands that solve these challenges tend to keep growing. They manage pricing carefully. They build stronger service networks. They maintain stable supply. In emerging markets, operational strength is often as important as innovation.
Key Risks And Their Impact
| Risk | What It Does |
| Price wars | Reduces profit and forces compromises |
| Currency volatility | Makes devices suddenly expensive |
| Supply issues | Breaks retailer confidence |
| Policy and tax shifts | Changes pricing overnight |
| Longer replacement cycles | Slows sales growth after adoption rises |
Future Outlook: 2025–2030 Growth Drivers To Watch
The next growth wave will be shaped by affordable 5G, better financing, and smarter mid-range phones. Buyers will expect features that used to be premium. AI-based camera tools, voice features, and battery optimization will spread into cheaper phones. That will raise baseline expectations across emerging markets.
Another major trend is deeper expansion into smaller cities and rural areas. As network coverage improves, demand expands beyond major urban centers. Brands that build local distribution and service will win these new buyers. This is where offline strategy remains critical.
Local assembly and supply chain localization will also matter more. It can reduce costs and improve pricing stability. It can also help brands respond faster to policy changes. Over time, operational flexibility may separate the winners from the short-term hype brands.
Finally, sustainability and repairability may become bigger issues. Some markets are pushing stronger consumer rights and repair options. Brands that offer better durability and support may build stronger trust and loyalty.
What To Watch Next
| Trend | Why It Will Matter |
| Affordable 5G | Triggers mass upgrades |
| AI features in mid-range | Creates new buying reasons |
| Financing growth | Expands access for more users |
| Local assembly | Stabilizes pricing and supply |
| Service and repair focus | Builds loyalty and reduces churn |
What This Means For Consumers And Businesses
For consumers, fast-growing competition is mostly good news. It pushes prices down and features up. It improves choices in every price tier. It also encourages better service and warranties as brands fight for loyalty.
For retailers, the best brands are the ones with consistent supply and low return rates. A brand can sell well for a few months, then fade if it cannot support retailers. Strong after-sales networks also help retailers sell with confidence.
For businesses and investors, emerging-market smartphone growth signals broader digital expansion. More smartphone adoption means more mobile banking, e-commerce, online learning, and content consumption. Brands that win the smartphone layer often benefit in accessories and services too.
If you are choosing a phone, do not focus only on the brand name. Look at service availability, warranty terms, battery reputation, and real-life performance. In emerging markets, those factors often matter more than small differences in specs.
Practical Takeaways
| Audience | Best Advice |
| Buyers | Check battery, warranty, and service coverage |
| Retailers | Prefer brands with stable supply and support |
| Investors | Watch distribution strength and mid-range momentum |
| Marketers | Align messaging with real daily needs |
Final Thoughts: Why Emerging Markets Decide The Next Smartphone Winners
The global smartphone story is shifting. Premium phones still matter, but the biggest growth comes from emerging economies. That is where adoption is still rising and upgrades are accelerating. It is also where buyers demand the most value for every dollar.
The fastest-growing smartphone brands in emerging markets are winning because they understand practical needs. They focus on battery, camera, reliability, and price discipline. They build distribution networks that reach smaller cities. They support customers through service and repair. And they keep improving quickly.
If you want to predict the next leaders in smartphones, watch what happens in emerging markets. The brands that master these regions build scale, loyalty, and momentum. Those strengths can shape the global market for years.
Summary Of The Growth Formula
| Growth Factor | What It Looks Like |
| Right price bands | Strong options under $200–$300 |
| Real daily value | Battery, durability, and camera upgrades |
| Channel execution | Offline + online expansion |
| Trust and service | Repairs, warranty, and support visibility |
| Smart differentiation | Features that matter, not gimmicks |
FAQs
Which brand is growing the fastest in emerging markets right now?
Growth depends on the region and price segment. Entry-level leaders can grow fastest where first-time buyers dominate. Mid-range leaders can grow fastest where upgrades are rising. The best approach is to track the brand that is gaining share in your specific country.
Why are emerging markets so important for smartphone brands?
Emerging markets still have large pools of first-time smartphone buyers. They also have a growing group of people upgrading from older phones. That creates higher potential volume than many saturated markets.
Are budget phones the main driver of emerging-market growth?
Yes, entry-level and affordable mid-range phones drive most volume. But the mid-range is becoming more important as more users upgrade for better cameras and performance.
What features matter most for buyers in emerging markets?
Battery life, fast charging, durable build, strong signal performance, and a good main camera matter a lot. After-sales service can also be a deciding factor.
Will 5G increase smartphone sales in developing countries?
It often does. When affordable 5G phones appear and network coverage expands, many users upgrade earlier than they otherwise would. The impact is strongest where carriers bundle phones with data plans.
Can local smartphone brands compete with global brands long-term?
Local brands can win in specific markets, especially when they understand distribution and service better. Global brands still have scale advantages, but local brands can grow fast with the right focus.