This guide is designed for beginner to intermediate cryptocurrency holders who are hearing the buzz about quantum computing and want to separate the science fiction from the immediate security reality. If you hold assets on a hardware wallet, an exchange, or in DeFi protocols, this roadmap applies to you.
We will not drown you in theoretical physics. Instead, we will focus on defensive Crypto security: specific, actionable steps you can take today to “quantum-proof” your setup, and exactly what signals you need to monitor over the coming years.
The Promise: By the end of this guide, you will understand:
- Why “quantum apocalypse” headlines are often misleading.
- The difference between “encryption” and “signing” (and why it saves your Bitcoin).
- The “Vault vs. Spending” strategy that drastically reduces your risk surface.
- A clear, staged checklist to upgrade your personal security hygiene without panic.
Note for Advanced Users: Look for the “Technical Callout” sections. These will briefly touch on specific algorithms (like Schnorr vs. ECDSA) and protocol-level migrations (like Ethereum’s Account Abstraction) relevant to developers and power users.
Quantum Threat Model For Crypto
To protect your assets, you first need to understand the weapon. Quantum computers are not just “faster” supercomputers; they operate on fundamentally different math. While a supercomputer tries to solve a maze by running every possible path one by one (very fast), a quantum computer looks at the entire maze at once and collapses the probability to find the exit instantly.
What Quantum Computers Can Break (And What They Can’t)
The quantum threat to crypto boils down to one specific algorithm: Shor’s Algorithm.
Shor’s Algorithm is efficient at breaking asymmetric cryptography (also known as Public-Key Cryptography). This is the math used to generate your private key and derive your public key from it.
- The Risk: If a quantum computer becomes powerful enough, it could theoretically look at your public key (which is visible on the blockchain after you transact) and calculate your private key. With the private key, an attacker can sign transactions and drain your wallet.
- The Targets: Algorithms like RSA and Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC)—which secure Bitcoin, Ethereum, and most of the internet—are vulnerable.
What They Can’t Break (Easily): Quantum computers are not very good at breaking hashing (like SHA-256 used in Bitcoin mining and address generation) or symmetric encryption (like AES used to encrypt your password manager vault).
- Takeaway: Your private keys are at risk if exposed, but the “digital walls” protecting encrypted files (like a 7-Zip file of your seed phrase) are much stronger, provided you use strong passwords.
The Two Big Crypto Exposure Paths
When analyzing your risk, you must distinguish between two different types of attacks.
1. Signature Exposure (The “Key Break” Risk)
This is the direct threat to your funds. In most blockchain systems (like Bitcoin and Ethereum), your “address” is a hash of your public key. Hashing is quantum-resistant. However, when you send a transaction, you must reveal your full public key to the network to verify your signature.
- The Danger Zone: Once your public key is revealed to the network, a sufficiently powerful quantum computer could derive your private key.
- Why It Matters: If you reuse addresses (send funds out of an address and keep the remaining balance in the same address), your public key remains visible on the blockchain forever. Your remaining funds are now sitting ducks for a future quantum attacker.
2. Data Longevity Risk (“Harvest Now, Decrypt Later”)
This risk applies less to the blockchain and more to your communications and backups.
- The Concept: Attackers (nation-states or criminal organizations) are scraping encrypted internet traffic today. They cannot read it yet. They are storing it in massive data centers to decrypt 10 or 15 years from now when quantum computers are available.
- Who Should Care: If you emailed a photo of your seed phrase to yourself in 2018, or if you store your private keys in a cloud backup that isn’t quantum-proof, that data is already “harvested.” When the tech matures, the attacker will unlock your seed phrase and drain your funds—even if you haven’t touched them in years.
Practical Timelines: What ‘Prepare Now’ Really Means
Don’t panic. Experts generally estimate “Q-Day” (the day a quantum computer is strong enough to break Bitcoin’s encryption) is likely 5 to 15 years away (roughly 2030–2040).
- The “Mosca Theorem”: We need to worry when the time it takes to migrate our systems is longer than the time until the threat arrives.
- Current Status: We are in the “Preparation” phase. NIST (National Institute of Standards and Technology) has finalized post-quantum standards (ML-KEM, ML-DSA) as of 2024/2025. Blockchains are beginning to form research teams (e.g., Ethereum’s PQ team formed in Jan 2026).
- Your Job: You do not need to move all your funds tomorrow. You need to adopt good hygiene today so that when the migration tools arrive, your funds aren’t already compromised by bad habits (like address reuse).
Storage Fundamentals That Still Matter Most (Quantum Or Not)
Before worrying about futuristic supercomputers, ensure you aren’t vulnerable to today’s $5 wrench attack or a simple phishing email.
Custody Options Ranked By Control And Risk
Self-Custody (Cold Storage / Hardware Wallets)
- Control: 100%.
- Risk: User error (losing keys) or physical theft.
- Quantum Context: Best option, provided you avoid address reuse. You control when you upgrade.
Multisig (Multi-Signature) Vaults
- Control: High (requires m-of-n keys to sign).
- Risk: Complexity setup.
- Quantum Context: Extremely strong. Even if one key is compromised by a quantum computer, the attacker still needs the others (which might be totally different hardware/locations).
Institutional Custody (Coinbase Prime, BitGo, etc.)
- Control: Low (you trust them).
- Risk: Regulatory freeze or bankruptcy.
- Quantum Context: Institutions will likely handle the quantum migration for you. If you trust them to stay solvent, this is the “hands-off” route.
Exchange Hot Wallets (Binance, Kraken standard accounts)
- Control: None. “Not your keys, not your coins.”
- Risk: Hackers, insolvency, phishing.
- Quantum Context: Risky. If the exchange is slow to upgrade their cold storage, your funds are at risk.
Hot Wallet vs Cold Wallet (The Real Security Tradeoff)
Think of your crypto storage like your physical money:
- Hot Wallet (The Wallet in Your Pocket): MetaMask, Phantom, or an exchange app on your phone. Connected to the internet. Convenient for buying coffee or trading NFTs. Keep only what you are willing to lose.
- Cold Wallet (The Bank Vault): Ledger, Trezor, Coldcard. Never connected to the internet directly. Keys are generated and stored on a specialized chip. This is for life savings.
The Quantum Rule: Your “Vault” (Cold Wallet) should almost never send outgoing transactions. It should mostly receive. Every time you sign a transaction from your Vault, you potentially expose a public key.
Seed Phrase Rules That Prevent Most Catastrophic Losses
If you mess this up, quantum computers won’t matter because a regular scammer will get you first.
- Offline Generation: Your seed phrase (the 12 or 24 words) must be generated on a device that is not connected to the internet (like a hardware wallet).
- Analog is King: Write it on paper or punch it into steel.
- The “No-Go” List (Instant compromise):
-
- Taking a photo of your seed words.
- Saving it in a password manager (unless you are an expert using specific encryption).
- Typing it into a computer to “print it out.”
- Storing it in Google Drive/iCloud/Dropbox.
- Geographic Separation: If your house burns down, do you lose your crypto? Store a secondary steel backup at a trusted relative’s house or a bank safety deposit box.
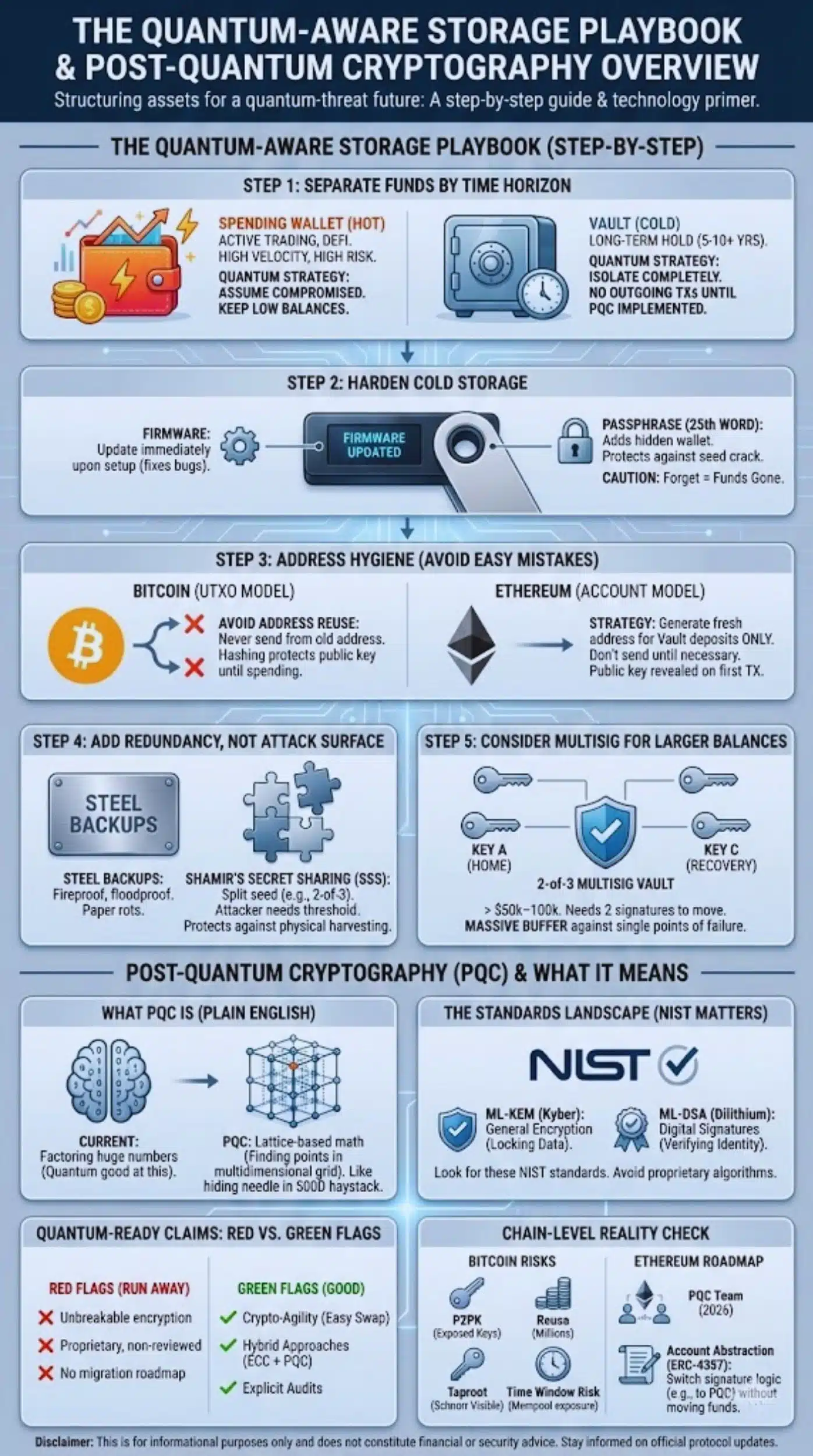
The Quantum-Aware Storage Playbook (Step-By-Step)
Here is how to structure your assets today to minimize future quantum risk.
Step 1 — Separate Your Funds By Time Horizon
Do not mix your “trading stack” with your “retirement stack.”
- Spending Wallet (Hot): Active trading, DeFi farming, NFT minting. High velocity. High risk.
- Quantum Strategy: Assume these keys are already compromised. Keep balances low.
- Vault (Cold): Assets you plan to hold for 5–10+ years.
- Quantum Strategy: Isolate this completely. These addresses should ideally never have outgoing transactions until post-quantum cryptography is implemented on the blockchain.
Step 2 — Harden Cold Storage (Hardware Wallet + Offline Backups)
If you are setting up a new Cold Wallet (Vault):
- Firmware: Update the device firmware immediately upon setup (manufacturers fix crypto bugs regularly).
- Passphrase (The “25th Word”): Most hardware wallets allow you to add a custom passphrase to your seed. This creates a hidden wallet.
- Why: Even if a quantum computer (or a thief) cracks your standard 24 words, they cannot access the hidden wallet without your custom passphrase.
- Caution: If you forget this passphrase, the funds are gone forever.
Step 3 — Address Hygiene (Avoid The Easy Quantum-Later Mistakes)
This is the most technical but most important step for Bitcoiners.
- Avoid Address Reuse: When you send Bitcoin, most modern wallets automatically send the “change” to a new address. This is good. Never manually re-use an old address that you have sent funds from.
- The Logic: An address that has received funds but never sent them has not revealed its public key to the network (it only revealed the hash). A quantum computer cannot derive the private key from the hash.
- For Ethereum/EVM Users: Ethereum uses an account-based model, not UTXO (Unspent Transaction Output). Your public key is revealed as soon as you send your first transaction.
- Strategy: For your “Vault,” generate a fresh address that only receives deposits. Do not send from it until necessary.
Step 4 — Add Redundancy Without Adding Attack Surface
You need backups, but every copy of your seed is a potential leak.
- Steel Backups: Paper rots and burns. Steel plates (like Cryptosteel or Billfodl) are fireproof and floodproof.
- Shamir’s Secret Sharing (SSS): Some modern wallets (Trezor Model T, Keystone) allow you to split your seed into 3 parts (e.g., need 2 of 3 to recover).
- Quantum Benefit: An attacker finding one part of your seed has zero information. They need the threshold amount. This protects against physical theft “harvesting.”
Step 5 — Consider Multisig For Larger Balances
If you hold significant wealth (> $50k–100k equivalent), consider a 2-of-3 Multisig.
- How it works: You need 2 signatures to move funds. You hold Key A (Home) and Key B (Office); a trusted partner or service holds Key C (Recovery).
- Quantum Resistance: This acts as a massive buffer. Even if a weakness is found in one hardware wallet manufacturer’s random number generator, or if one key is theoretically exposed, the attacker remains locked out.
- Checklist: Ensure you use different hardware vendors (e.g., one Ledger, one Trezor, one Coldcard) to avoid supply chain attacks.
Post-Quantum Cryptography (PQC) And What It Means For Wallets
You will see terms like “PQC” or “Quantum-Resistant” marketed by wallet companies. Here is what they mean.
What is PQC
Post-Quantum Cryptography (PQC) refers to new encryption and signature algorithms that are designed to be impossible for both classical and quantum computers to crack. Instead of relying on factoring huge numbers (which quantum computers are good at), PQC relies on complex math problems like lattice-based cryptography (finding points in a multidimensional grid). It’s like hiding a needle in a haystack, but the haystack has 500 dimensions.
The Standards Landscape (Why NIST Matters)
The entire tech industry has been waiting for the US government (NIST) to pick the winners. As of August 2024, they finalized the first set:
- ML-KEM (formerly CRYSTALS-Kyber): For general encryption (locking data).
- ML-DSA (formerly CRYSTALS-Dilithium): For digital signatures (verifying identity).
Why this matters to you: When a wallet or blockchain claims to be “Quantum Ready,” check if they are using these NIST-standardized algorithms. If they are using a proprietary “home-cooked” algorithm, run away.
What To Look For In ‘Quantum-Ready’ Claims
- Red Flags:
- “Unbreakable encryption” (nothing is unbreakable, just computationally infeasible).
- Proprietary algorithms not peer-reviewed.
- No roadmap for how users migrate old keys to new keys.
- Green Flags:
- Crypto-Agility: The wallet is built to swap out algorithms easily.
- Hybrid Approaches: The wallet uses both a classical algorithm (ECC) AND a post-quantum algorithm. If the new PQC turns out to have a bug, the old ECC still protects you. If ECC breaks, PQC protects you.
- Audits: Explicit security audits checking the PQC implementation.
Chain-Level Reality Check (Bitcoin/Ethereum As Examples)
Your wallet is only as secure as the blockchain it lives on.
Bitcoin: Where The Risk Shows Up First
Bitcoin is relatively resistant due to its use of SHA-256 hashing for addresses (P2PKH). However, there are vulnerable pockets:
- P2PK (Pay-to-Public-Key): Used in the very early days (2009–2010), including Satoshi’s coins. These public keys are exposed.
- Reuse: Millions of addresses have been reused.
- Taproot (P2TR): While an upgrade, Taproot uses Schnorr signatures. Once you spend from a Taproot address, the public key is visible.
The “Time Window” Risk: When you broadcast a Bitcoin transaction, it sits in the “Mempool” for ~10 minutes before being mined. During this window, your public key is exposed. A futuristic quantum attacker could see your transaction, calculate the private key instantly, and broadcast a new transaction sending your money to them with a higher fee, effectively “stealing” the transaction before it confirms.
What A Migration Could Look Like (High-Level)
Bitcoin is slow to change, which is a feature, not a bug.
- Soft Fork Upgrade: Developers will likely introduce a new address type (P2QSH – Pay to Quantum Script Hash) utilizing a quantum-safe signature scheme (like Lamport signatures or ML-DSA).
- The Migration: You will create a new quantum-safe wallet and send your funds from your old Ledger to this new address. This transaction will likely need to be done carefully to avoid the “Time Window” risk mentioned above.
Ethereum And Smart-Contract Ecosystems
Ethereum faces a different challenge. It is an account-based system, meaning public keys are often revealed earlier.
- The Roadmap: The Ethereum Foundation formed a dedicated Post-Quantum team in early 2026.
- Account Abstraction (ERC-4337): This is Ethereum’s ace in the hole. It turns your wallet into a “Smart Contract Wallet.” This allows you to change the logic of how you sign transactions without moving funds. You could theoretically switch your wallet’s required signature from ECDSA (vulnerable) to a PQC algorithm (safe) simply by sending an upgrade transaction.
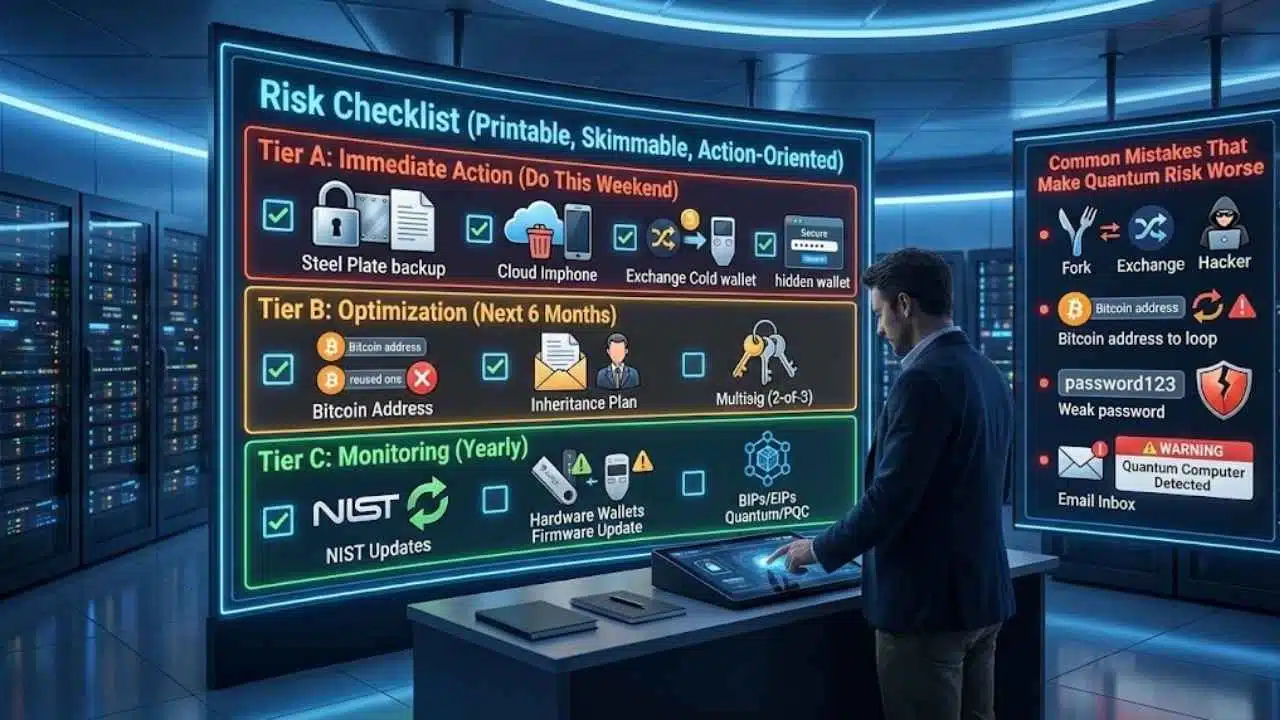
Risk Checklist (Printable, Skimmable, Action-Oriented)
Use this tiered checklist to gauge your readiness.
Tier A: Immediate Action (Do This Weekend)
- Audit your backup: Do you have a physical copy of your seed? Is it steel?
- Cloud clean-up: Delete any photos of seed phrases from your phone/cloud.
- Exchange check: Move long-term hold assets off exchanges to a cold wallet.
- Passphrase: If you have >$10k, set up a “hidden wallet” with a passphrase.
Tier B: Optimization (Next 6 Months)
- Address Review: Check your Bitcoin habits. Are you reusing addresses? Stop immediately.
- Inheritance Plan: If you die, is your family locked out? Or (worse) does the lawyer have the keys? Set up a simple instruction letter stored separately from the keys.
- Multisig Investigation: If your portfolio grows, begin learning about 2-of-3 multisig setups (e.g., Unchained, Casa, or DIY with Sparrow Wallet).
Tier C: Monitoring (Yearly)
- NIST Updates: Watch for updates on ML-KEM/ML-DSA implementation.
- Hardware Updates: Check if Ledger/Trezor releases “Quantum-Ready” firmware updates.
- Protocol Proposals: Keep an eye on Bitcoin BIPs or Ethereum EIPs related to “Quantum” or “PQC.”
Common Mistakes That Make Quantum Risk Worse
- “I’ll just wait for the fork”: If you leave your crypto on an exchange assuming they will handle it, you are trusting their security team against the world’s best hackers.
- Address Reuse: We cannot stress this enough. Reusing addresses removes the natural “hashing shield” that Bitcoin offers.
- Weak Passphrases: Using a “25th word” passphrase like “password123” is useless. It must be high-entropy (random).
- Phishing via Fear: Scammers will soon start sending emails: “URGENT: Quantum Computer Detected. Move your funds to this ‘Safe’ wallet now!” Never click these. Legitimate upgrades will take years and will be announced on official protocol websites, not via email.
Wrap-Up: A Calm Plan For A Noisy Future
The arrival of quantum computing is not an “end of crypto” event; it is a Y2K-style upgrade cycle. It is manageable, foreseeable, and preventable.
The vulnerability is rarely the math itself—it is the human holding the keys. If you practice rigorous cold storage hygiene, avoid address reuse, and maintain physical backups, you are already 99% more secure than the average user.