We all use apps every day. Messaging, shopping, banking—there’s an app for everything. But have you ever thought about how safe they really are? Many of the most popular apps have had serious security flaws in the past. Hackers have exploited these flaws to steal data, take control of accounts, and even spread malware.
Take WhatsApp, for example. In 2019, it faced a major security breach where attackers could install spyware on users’ phones through a simple call.
Instagram has also had its share of problems, including vulnerabilities that exposed personal details of millions of users.
Even Zoom, the widely used video conferencing tool, had critical flaws that let strangers join private meetings and access sensitive information.
These are big names, used by millions every day, yet they have been hacked. This shows that app security is far from perfect, even for companies with huge resources. If big brands can be attacked, smaller businesses with fewer security measures are even more at risk.
How Do Hackers Break Into Apps?
Hackers usually take advantage of coding errors or weak security settings in apps. Many apps store sensitive data like passwords, credit card details, and personal information. If this data is not protected, hackers can steal it.
Some attacks happen through injection flaws, where attackers trick the app into running harmful code.
Others involve broken authentication, which means hackers can bypass login systems and take control of accounts. There are also attacks through insecure APIs, which are the systems apps use to talk to each other.
The problem often starts with developers rushing to release features without giving enough attention to security. It can also happen when apps are not updated regularly. Hackers know this and constantly look for weak points to exploit.
Why Businesses Need Strong Security Testing
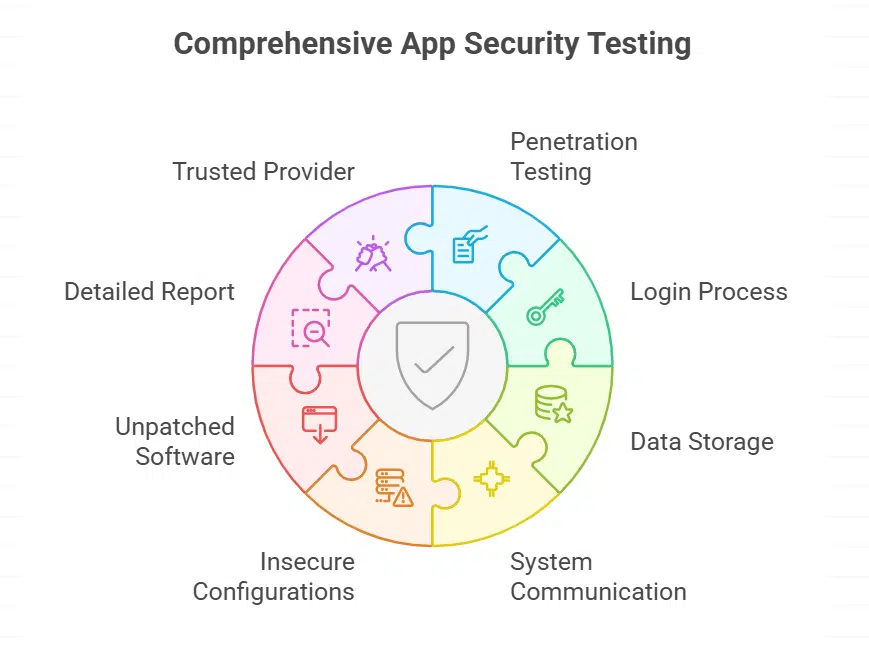
For companies that build or use apps, security testing is not optional. It’s essential. One effective method is application penetration testing by Bishop Fox. This kind of testing simulates real attacks. Experts try to break into the app the same way hackers would. The goal is to find weaknesses before the bad actors do.
Penetration testing checks all parts of the app, including the login process, data storage, and communication with other systems.
It also looks for issues like insecure configurations or unpatched software. Once the testing is done, businesses get a detailed report. This report shows where the app is weak and how to fix those problems.
The benefit of using a trusted provider is experience. These specialists keep up with the latest hacking techniques. They know where to look and what to test. This means businesses get a real picture of their app security, not just a checklist review.
What Can Users Do To Stay Safe?
While businesses work on securing their apps, users can also take steps to protect themselves. First, always keep your apps updated.
Many updates include fixes for security flaws. Second, use strong and unique passwords for every app. A password manager can help with this. Third, be careful with app permissions. If a game asks for access to your contacts or camera, think twice before granting it.
t’s also smart to enable two-factor authentication wherever possible. This adds an extra layer of security in case someone gets your password. Finally, download apps only from official stores like Google Play or the Apple App Store. Apps from unknown sources can be risky.
The Bottom Line
App security is a shared responsibility. Developers need to build safer apps, and businesses must test them properly before release.
At the same time, users should follow basic security practices to reduce risk. Hackers will always try to find ways in, but with the right steps, both companies and individuals can make it much harder for them to succeed.