Artificial intelligence tools like ChatGPT have grown rapidly in popularity, but recent data shows that they are still far from displacing Google in the world of search. Industry analysts and independent research provide a detailed picture of how people are using AI for search-like tasks and how that compares to traditional search engines.
ChatGPT’s Usage Growth in Numbers
Since its launch, ChatGPT has experienced remarkable growth in overall usage. In December 2023, OpenAI reported that the system was handling around 1 billion prompts per day. By July 2025, this figure had climbed to an estimated 2.5 billion daily prompts, reflecting both the popularity of the free interface and, increasingly, heavy API usage. Many businesses now integrate OpenAI’s GPT models directly into their products, contributing to this surge.
However, only a portion of these prompts can truly be described as “search-like.” A joint study conducted by Harvard researchers and OpenAI examined user interactions and concluded that approximately 21.3% of all prompts involve information-seeking behavior similar to how people use search engines. Translating that percentage to overall daily volume means that ChatGPT currently handles about 66 million search-intent prompts every day.
That number sounds significant, but it pales in comparison with traditional search engines.
Google’s Global Search Dominance
Google remains the clear leader in global search activity. In 2024 alone, the company processed more than 5 trillion searches, which works out to roughly 14 billion searches per day on average. Some independent estimates that draw on traffic and user behavior data suggest the real figure is even higher, closer to 16 billion daily searches worldwide.
By comparison, ChatGPT’s 66 million daily search-like prompts represent less than half a percent of Google’s daily traffic. Even DuckDuckGo, which is considered a niche privacy-focused search engine, still drives more referrals to websites than ChatGPT. This highlights how massive Google’s scale remains and how AI tools are still small players in terms of direct discovery.
How AI Search Compares to Traditional Search
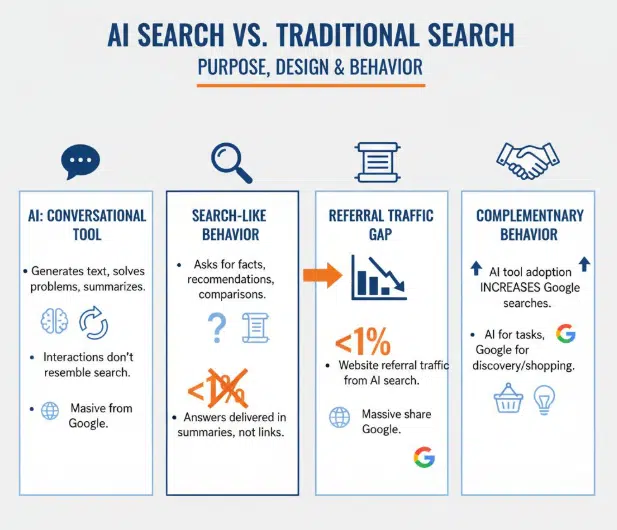
The difference between AI and search engines is not just about volume — it is also about purpose and design.
-
AI as a conversational tool: ChatGPT was designed to generate text, solve problems, or provide summaries, rather than act solely as a gateway to web pages. This means many interactions do not resemble search at all.
-
Search-like behavior: When users ask ChatGPT for factual information, recommendations, or comparisons, those prompts overlap with traditional search queries. Yet ChatGPT rarely drives users directly to websites, because the answers are delivered in the form of summaries.
-
Referral traffic gap: Data from BrightEdge, a digital marketing analytics company, shows that AI search contributes less than 1% of overall website referral traffic, compared to the massive share driven by Google.
-
Complementary behavior: Interestingly, research from SparkToro and Datos suggests that when people adopt AI tools, their Google searches often increase rather than decrease. Users may consult AI for certain tasks while still turning to Google for discovery, shopping, or in-depth exploration.
Historical Perspective on Scale
Back in March 2025, estimates suggested that Google was more than 370 times larger than ChatGPT in terms of search referrals. That gap has narrowed somewhat due to ChatGPT’s rapid adoption, but Google remains vastly bigger, now around 210 times larger when focusing strictly on search-intent interactions.
The context is important. AI adoption has soared, but relative to the massive infrastructure and daily usage of traditional search, it is still in its early stages. Google and other engines like Bing maintain dominance because of decades of investment in crawling, indexing, ranking, and delivering referral traffic across billions of websites.
Why This Matters for SEO and Digital Strategy
For businesses, content creators, and marketers, these trends carry practical lessons:
-
Google still dominates discovery: With billions of daily searches, optimizing for Google remains the single most important strategy for visibility.
-
AI is supplementary, not yet primary: While AI may influence behavior, its share of referral traffic is still minimal. Businesses should view it as an emerging channel rather than a replacement.
-
Adaptation is key: Content should be structured in ways that work for both Google’s algorithms and AI summarization models, focusing on clarity, authority, and accuracy.
-
Future-proofing: As AI use grows, being prepared for voice queries, conversational formats, and summarized answers will matter more in the coming years.
The Future of AI and Search
Google has already begun introducing AI Overviews into search results, where users get summarized answers alongside links. This hybrid approach shows how the lines between traditional search and AI response are blurring.
At the same time, ChatGPT and other generative models are experimenting with real-time browsing, search integrations, and personalization features. These could increase the percentage of search-like prompts over time and make AI more influential in certain industries.
Still, the scale difference cannot be overstated. With trillions of searches annually, Google is deeply entrenched as the world’s discovery engine. ChatGPT, while growing, represents an emerging channel rather than a direct replacement.
The information is collected from MSN and Yahoo.