In today’s digital world, physical IDs are starting to feel outdated. Whether you’re opening a bank account, registering on a crypto platform, or accessing healthcare services, electronic identity documents (eIDs) are taking center stage. And driving this transformation is a secure, seamless technology known as NFC ID verification.
According to the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO), more than 140 countries now issue electronic passports. In the EU, nearly every country has adopted electronic national ID cards—except for Bulgaria and Switzerland.
What’s fueling the popularity of eIDs? The answer is simple: they’re harder to forge, easier to verify remotely, and well-suited for fast, secure onboarding. With NFC verification, any NFC-enabled smartphone can serve as a reader, making identity checks more accessible than ever.
From finance to healthcare, businesses in regulated industries are embracing NFC ID verification to protect user data, improve compliance, and streamline onboarding. It’s also becoming a key tool in patient verification automation, especially in telemedicine, where verifying someone remotely is a daily necessity.
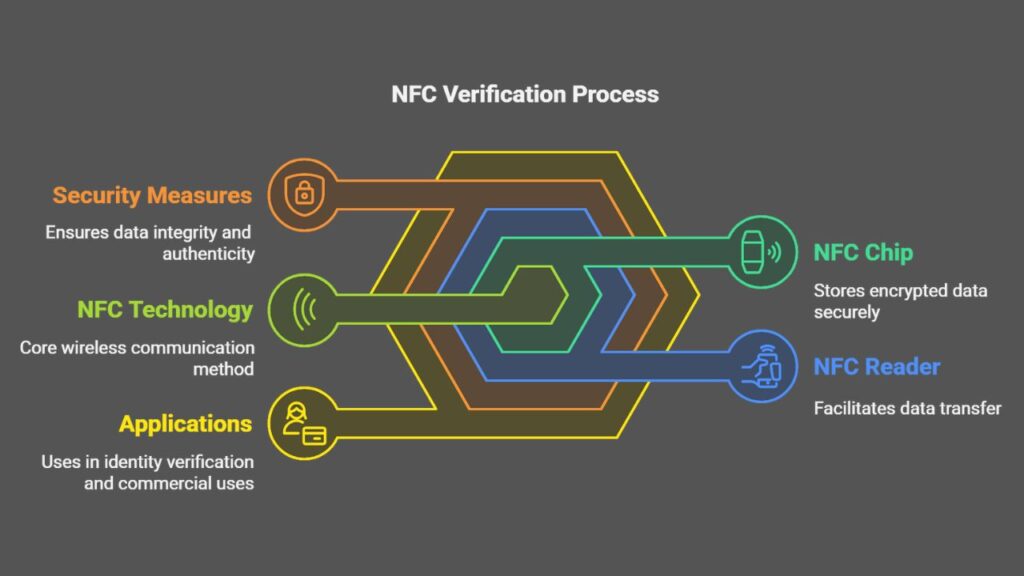
What Is NFC Verification and How Does It Work?
Near Field Communication (NFC) is a short-range wireless communication technology that enables data transfer between a chip (like the one embedded in an eID) and a reader (typically a smartphone).
It’s based on the same core principles as RFID but with a much shorter range—just about 4 cm. That proximity adds a layer of security, making NFC verification ideal for sensitive processes like identity checks.
Electronic passports and ID cards store personal data and biometric info on an encrypted chip. This chip, protected by cryptographic signatures, ensures the document is authentic and hasn’t been tampered with.
Initially created for border control, eIDs have expanded into commercial use, and NFC ID verification is now used across industries to remotely verify users.
Why Businesses Are Switching to NFC ID Verification
1. It’s More Secure
Traditional ID checks often rely on photos—easy targets for fraudsters using AI-generated fakes or screenshots on a screen. With NFC ID verification, the user must physically present a document with an embedded chip that’s almost impossible to replicate.
Even better, some companies are adopting zero-trust to mobile principles. That means verification results generated on a user’s smartphone aren’t accepted at face value—instead, they’re rechecked server-side. This blocks attackers from altering outcomes like changing a failed verification to a passed one.
2. It’s Accessible and User-Friendly
Smartphones with NFC capability are everywhere. By 2020, over 90% of phones already supported it. Consumers are used to using NFC for contactless payments, so using it for ID checks feels familiar.
With NFC verification, there’s no need for users to upload photos or fill out lengthy forms. The chip is scanned, the data is read automatically, and the process is done in seconds. It’s fast, accurate, and far less prone to user error.
For companies, this means better conversion rates and fewer customer support tickets. For users, it means a seamless onboarding experience.
3. It Reduces Friction
Poor lighting, bad angles, blurry cameras—these are all common reasons why photo-based ID checks fail. In contrast, NFC ID verification only requires a user to hold their ID near their phone.
In some cases, data from the chip can be cross-verified with visual and machine-readable zones (MRZ), strengthening the process even further. But even if that’s not done, successful chip verification alone is a strong indicator of authenticity.
Real-World Examples of NFC Verification in Action
- UBS (Switzerland) now requires all new clients to submit electronic IDs during onboarding. They even issue Qualified Electronic Signatures (QES) for clients to use across services.
- Bitazza (Thailand) rewards customers who complete NFC verification by increasing their spending limits within the crypto platform.
- Other companies offer flexibility—still accepting non-biometric IDs—but the trade-off is added friction, like mandatory video interviews or extended waiting times.
The Drawbacks of NFC Verification (and How to Navigate Them)
Even with all its benefits, NFC ID verification does have a few challenges:
Limited Document Availability
Not all countries issue biometric IDs. In markets like India, most documents remain non-electronic. Even in countries that do issue eIDs, older non-NFC documents may still be valid. Businesses relying solely on NFC verification might miss out on certain user groups.
Device Compatibility
While most modern phones support NFC, budget smartphones might not. This creates access barriers. To ensure inclusivity, companies may need to offer alternate flows, like video calls or in-person checks, though these add cost and complexity.
Restricted Chip Data Access
Government-issued eIDs contain sensitive data, but not all of it is accessible to businesses. For example, biometric data like fingerprints is off-limits. That means NFC ID verification for commercial use typically focuses on verifying chip integrity and cross-checking visual data.
To enhance this process, companies often combine it with facial biometrics—asking for a selfie and comparing it with the photo on the chip to confirm the user is who they claim to be.
Regula’s NFC Verification Solutions
Regula offers robust tools to help businesses implement reliable, scalable NFC ID verification:
- Support for over 14,000 eID types from 250+ countries and territories
- Full authenticity checks, including data cross-verification from chip, MRZ, barcodes, and visual zones
- Server-side validation to detect manipulation attempts and maintain verification integrity
Whether you’re onboarding banking customers or automating patient identity checks in healthcare, Regula’s tools make NFC verification secure, smooth, and scalable.
NFC ID Verification Is the Future
In a world where trust is digital, NFC ID verification is quickly becoming the new standard. It’s fast, secure, and ideal for everything from banking to healthcare—and especially valuable in scenarios where remote, frictionless verification is critical.
With more countries issuing eIDs and more users equipped with NFC-enabled devices, the time to embrace NFC verification is now.