Malaysia, a vibrant Southeast Asian nation, is known for its diverse culture, natural beauty, and booming economy.
Many expatriates and foreign nationals dream of making Malaysia their second home, and obtaining Permanent Residency (PR) status is one way to achieve this.
In this guide, we will explore everything you need to know about how to get PR in Malaysia, from the benefits of permanent residency to the step-by-step process for applying.
Step-By-Step Application Process To Get PR In Malaysia in 2025
Be it through employment, investment, or special talents, learn how Malaysia’s PR system works for every category. Here is the step-by-step guide to getting PR in Malaysia.
Step 1: Determine Your Eligibility
Identify the pathway that best fits your qualifications and prepare the necessary documents.
Step 2: Gather Required Documents
| Document | Details |
| Passport | Valid passport with sufficient validity. |
| Marriage certificate (if applicable) | Proof of marriage for spouse-based applications. |
| Employment letter | Verification from employer (for employment-based PR). |
| Financial statements | Evidence of financial stability. |
| Medical report | Certificate of good health from a recognized institution. |
| Criminal record clearance | Proof of a clean record from your home country. |
Step 3: Submit Your Application
Submit your application to the Immigration Department of Malaysia or the nearest Malaysian embassy/consulate.
You can find the official submission guidelines and forms on the Immigration Department of Malaysia’s Official Website.
Step 4: Attend an Interview
The immigration office may invite you for an interview to verify your credentials and purpose for applying.
Step 5: Wait for Approval
The approval process can take several months. Be prepared for follow-up inquiries or additional documentation requests.
Step 6: Receive Your PR Card
Once approved, you will be issued a PR card, which serves as proof of your residency status.
Benefits of Permanent Residency in Malaysia
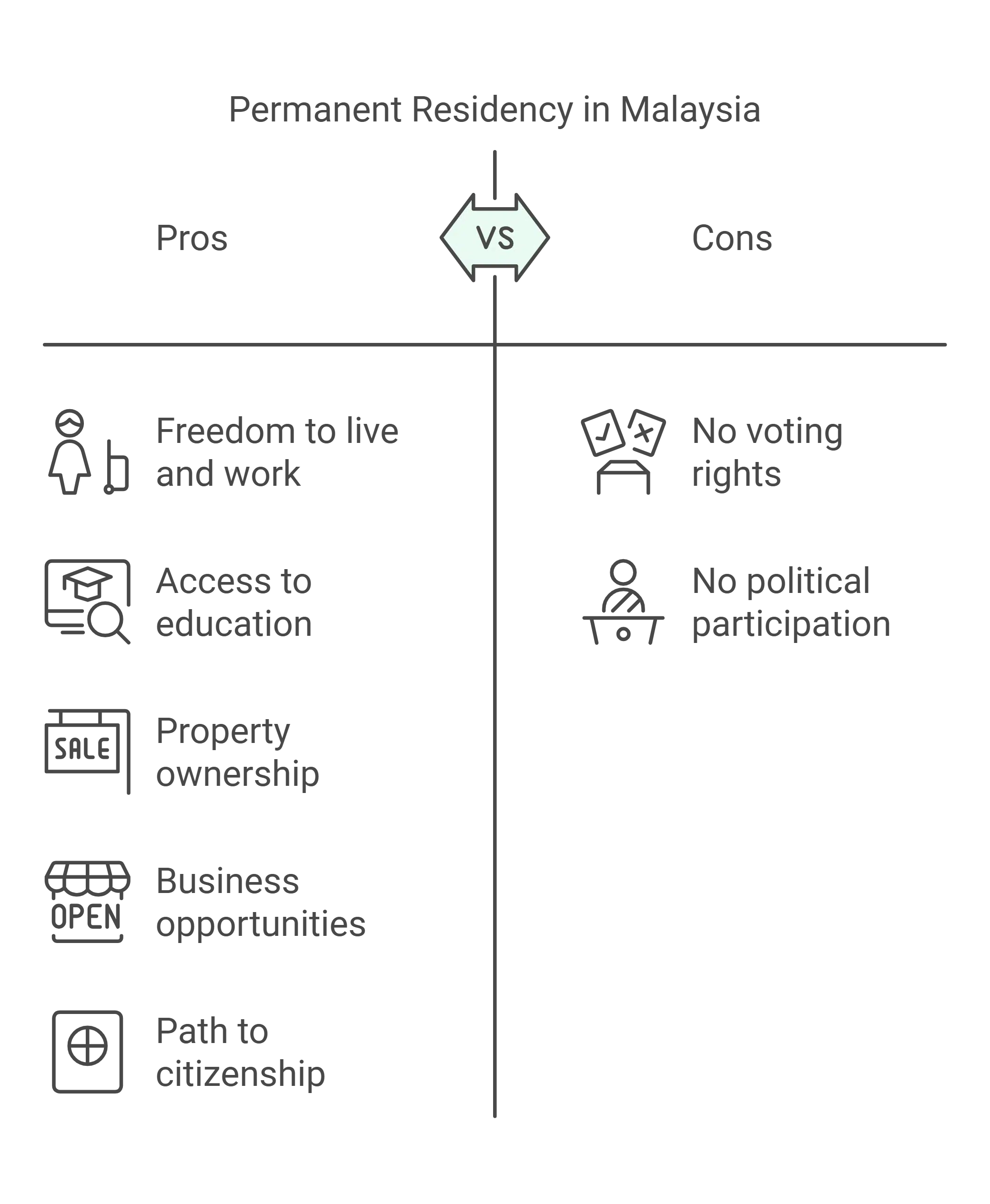
Becoming a permanent resident in Malaysia comes with numerous advantages. However, it’s important to note that while PR status offers many privileges, it does not grant the right to vote or participate in political activities. Below are the key benefits:
| Benefit | Details |
| Freedom to live and work | Reside in Malaysia indefinitely and work without a special visa. |
| Access to education | Enroll your children in local schools and universities at local rates. |
| Property ownership | Purchase property without needing special approval from authorities. |
| Business opportunities | Open and operate businesses without the restrictions placed on foreigners. |
| Path to citizenship | PR status can pave the way to applying for Malaysian citizenship. |
Eligibility Criteria for PR in Malaysia
To qualify for permanent residency, applicants must meet specific requirements. Here are the main pathways and their conditions:
1. Marriage to a Malaysian Citizen
Foreign spouses of Malaysian citizens can apply for PR after five years of continuous residence in the country. it is also noted that, Applicants must also demonstrate financial stability and obtain sponsorship from their Malaysian spouse.
| Requirement | Details |
| Marriage duration | Minimum of 5 years of legal marriage. |
| Proof of financial stability | Evidence of financial means to support yourself. |
| Residence | Reside in Malaysia during the application period. |
2. Employment Pass Holders
Highly skilled professionals with long-term employment in Malaysia can apply for PR after working for five years.
| Requirement | Details |
| Employment duration | Minimum of 5 years in a high-demand field. |
| Employer support | Recommendation letter from your employer. |
| Industry preference | Sectors like healthcare, engineering, and IT are prioritized. |
3. Investment in Malaysia
Investors who contribute significantly to the Malaysian economy are eligible for PR. However, specific investment amounts and criteria can vary, and it’s advisable to consult the latest guidelines from the Malaysian Immigration Department.
| Requirement | Details |
| Investment amount | Minimum RM 1,000,000 in a Malaysian company or bond. |
| Financial proof | Evidence of substantial financial resources. |
| Industry focus | Investment in high-growth sectors is preferred. |
4. Special Talent Route
Applicants with exceptional skills or talents recognized by the Malaysian government can apply for PR.
| Requirement | Details |
| Recognized talent | Proven expertise in a niche or critical field. |
| Endorsements | Endorsement from Malaysian ministries or agencies. |
| Contribution | Demonstrated value to Malaysia’s development. |
5. Point-Based System
Malaysia offers a Point-Based System as one of the pathways to obtain permanent residency (PR). This system evaluates applicants across seven specific criteria, assigning points to each. To be eligible for PR under this system, an applicant must achieve a minimum score of 65 out of a possible 120 points. The criteria are as follows:
- Age: Points are allocated based on the applicant’s age, with certain age brackets receiving higher scores.
- Qualification: Educational and professional qualifications are assessed, with advanced degrees earning more points.
- Duration of Stay in Malaysia: The length of time an applicant has resided in Malaysia contributes to the score, with longer stays resulting in higher points.
- Familiarity with Malaysian Institutions: Understanding and engagement with Malaysian societal and cultural institutions are evaluated.
- Value of Investments: Investments made within Malaysia are considered, with higher investment values garnering more points.
- Working Experience in Malaysia: Professional experience within the country is assessed, with more extended periods of employment leading to higher scores.
- Proficiency in Bahasa Malaysia: Language proficiency is evaluated, with higher fluency levels earning additional points.
Applicants can use the Point System Calculator provided by the Immigration Department of Malaysia to estimate their potential score. It’s important to note that achieving the minimum score does not guarantee approval; the final decision rests with the immigration authorities.
Common Challenges and Tips for Success
- Lengthy Processing Time: Start your application early and ensure all documents are complete.
- Language Barrier: Learn basic Malay to enhance your communication during the process.
- Financial Proof: Maintain detailed financial records to demonstrate your stability.
- Professional Assistance: Consider hiring an immigration consultant for complex cases.
Additional Considerations
- No Formal Points-Based System: Malaysia does not have a formal points-based system for PR applications. Eligibility is assessed based on specific categories and criteria.
- Residency Requirement: For most categories, applicants must have resided in Malaysia for a minimum of 5 consecutive years on a valid long-term pass before applying for PR.
- Documentation: All foreign documents should be certified by the respective foreign missions in Malaysia.
For the most accurate and up-to-date information, it’s recommended to consult the Malaysian Immigration Department’s official website or seek advice from legal professionals specializing in immigration to Malaysia.
Tax Information for Each PR Scheme in Malaysia
Whether you’re an investor, professional, or spouse, understanding Malaysia’s tax policies is key to financial success as a PR. From income brackets to investment tax benefits, here’s a comprehensive look at how taxes apply to PR holders in Malaysia.
1. Points-Based System (General Employment or Investment Pathway)
Tax policies for individuals who qualify under this pathway include:
- Income Tax:
- Resident individuals are taxed on income derived from Malaysia only. Foreign-sourced income is generally exempt from taxation (except remitted income, which is subject to taxation starting in 2022).
- Progressive tax rates range from 0% to 30%:
- Income up to RM 5,000: 0%
- RM 5,001 to RM 20,000: 1%
- RM 20,001 to RM 35,000: 3%
- RM 35,001 to RM 50,000: 8%
- RM 50,001 to RM 70,000: 13%
- RM 70,001 to RM 100,000: 21%
- Above RM 100,000: 24%–30% depending on income brackets.
- Investment Income: Income from local investments, such as dividends, rent, or interest, is taxable in Malaysia.
- Tax Deductions: Individuals may claim deductions for personal, spouse, and child relief; insurance premiums; education fees; and medical expenses.
2. Marriage to a Malaysian Citizen
PRs obtained through marriage are taxed similarly to others but may have additional tax reliefs based on family status:
- Joint Assessment: Spouses can opt for a joint assessment, which allows the higher-earning spouse to declare total family income and claim relief for the non-earning spouse.
- Reliefs: Married PRs can claim child reliefs and personal reliefs (up to RM 3,000 for the non-earning spouse).
- Property Tax: If owning property, the Real Property Gains Tax (RPGT) applies:
- 10% if disposed of within the first five years.
- 5% for disposals after the fifth year.
3. Employment Pass Holders
For professionals granted PR after working in Malaysia, their tax obligations align with employment-related income policies:
- Income Tax: Employment income is taxed progressively based on the rates mentioned above.
- Employee Provident Fund (EPF): Mandatory contributions apply for employees (11% from the employee and 12%-13% from the employer, depending on salary). Contributions to EPF are tax-deductible up to RM 4,000 annually.
- Employment Benefits: Non-monetary benefits like housing or car allowances are taxable under the Perquisite Tax system.
4. Investment in Malaysia
For PR holders who qualify under investment routes, their tax liabilities are focused on business and asset-related income:
- Corporate Tax:
- Flat tax rate of 24% on profits for businesses.
- Smaller companies (with capital below RM 2.5 million) enjoy a preferential rate of 17% on the first RM 600,000 of taxable income.
- Real Property Gains Tax (RPGT): Applicable on profits from property disposals as outlined in the marriage pathway section.
- Dividend Tax: Dividends received from Malaysian companies are tax-exempt in the hands of the recipient since Malaysia operates a single-tier tax system.
5. Special Talent Route
Applicants under this route are often high-earning individuals or self-employed professionals. Tax obligations include:
- Income Tax: Earnings from professional work in Malaysia are taxed progressively based on residency status and the rates mentioned above.
- Self-Employed Professionals:
- Required to file income tax under the “self-assessment system.”
- Deductible business-related expenses include operational costs, professional fees, and depreciation of assets.
- GST/SST Compliance:
- If their annual turnover exceeds RM 500,000, they must register for the Sales and Service Tax (SST) system (rate: 6% for services or 5%–10% for goods, depending on the category).
Common Tax Benefits for All Malaysia PRs
- Double Tax Agreements (DTAs): Malaysia has agreements with several countries to avoid double taxation, ensuring PR holders don’t pay taxes on the same income in multiple jurisdictions.
- Tax Residency Status: PR holders staying in Malaysia for 183 days or more in a tax year qualify as residents and benefit from the progressive tax system, including reliefs and rebates.
- Foreign-Sourced Income: While foreign income is generally tax-exempt, new policies from 2022 impose taxes on remitted foreign income.
Takeaways
Obtaining PR in Malaysia is a significant step toward building a life in this beautiful and diverse country. While the process may seem daunting, proper preparation, understanding of the requirements, and patience can lead you to success.
Whether you are seeking PR through employment, marriage, investment, or talent, Malaysia offers numerous opportunities for those looking to call it home.








































