Integrated Sustainable Waste Management (ISWM) is a modern and holistic approach to answering the question: what is integrated sustainable waste management? It focuses on managing waste in a way that is environmentally sustainable, economically viable, and socially inclusive.
ISWM covers all aspects of waste management, such as waste generation, collection, transportation, recycling, treatment, and disposal. This approach emphasizes sustainability by addressing the environmental, social, and economic impacts of waste.
ISWM prioritizes reducing waste generation, maximizing resource recovery, and minimizing harm to the environment. By involving key stakeholders, including governments, businesses, and communities, ISWM creates a collaborative framework for effective waste management solutions.
Understanding the Core Principles of ISWM
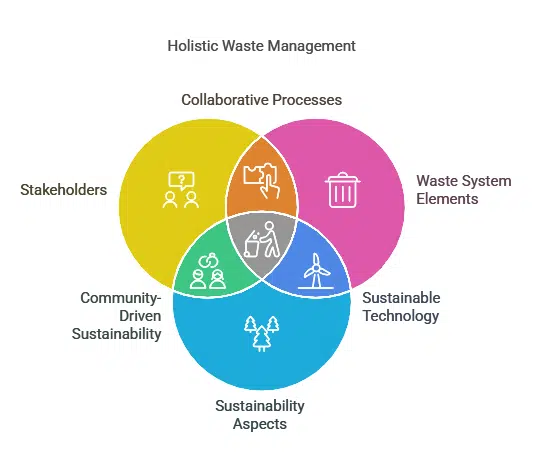
Integrated Sustainable Waste Management is built upon three fundamental dimensions:
- Stakeholders: All parties involved in waste management
- Waste system elements: Technical components of the waste management process
- Sustainability aspects: Factors that ensure the long-term viability of the system
These dimensions work together to create a comprehensive framework for managing waste in an environmentally sound, economically viable, and socially acceptable manner.
The Stakeholder Dimension
ISWM recognizes the importance of involving all relevant parties in the waste management process. This includes:
- Local authorities and government agencies
- Private sector waste management companies
- Informal waste collectors and recyclers
- Community-based organizations
- Residents and businesses
By engaging all stakeholders, ISWM ensures that waste management solutions are tailored to local needs and conditions, promoting greater acceptance and participation.
The Waste System Elements
The technical components of ISWM cover the entire waste management chain:
- Waste generation and separation
- Collection and transportation
- Treatment and processing
- Resource recovery (recycling, composting, energy recovery)
- Final disposal
ISWM aims to optimize each of these elements while considering their interdependencies and potential for integration.
Sustainability Aspects
To ensure long-term viability, ISWM addresses six key aspects of sustainability:
- Environmental protection
- Public health and safety
- Financial sustainability
- Institutional capacity
- Technical feasibility
- Social and cultural acceptability
By considering all these aspects, ISWM strives to create waste management systems that are not only effective but also sustainable in the long run.
The Evolution of Waste Management Practices
To fully appreciate the significance of ISWM, it’s important to understand how waste management practices have evolved over time.
Traditional Waste Management
Historically, waste management focused primarily on collection and disposal, with little consideration for environmental impact or resource recovery. This approach led to numerous problems:
- Overflowing landfills
- Environmental pollution
- Health hazards
- Wasted resources
The Shift Towards Integrated Approaches
As awareness of these issues grew, waste management strategies began to evolve. Key milestones include:
- 1970s: Emphasis on environmental protection and pollution control
- 1980s: Introduction of recycling programs and waste reduction initiatives
- 1990s: Development of integrated waste management concepts
- 2000s: Growing focus on sustainability and circular economy principles
ISWM emerged as a response to the limitations of traditional waste management approaches, offering a more comprehensive and sustainable solution.
Key Components of Integrated Sustainable Waste Management
ISWM encompasses a wide range of strategies and practices, including:
Waste Prevention and Reduction
The most effective way to manage waste is to prevent its generation in the first place. ISWM prioritizes waste prevention through:
- Product design for durability and recyclability
- Promoting sustainable consumption patterns
- Implementing extended producer responsibility (EPR) programs
Resource Recovery and Recycling
ISWM emphasizes the importance of recovering valuable resources from waste streams. This includes:
- Material recycling (e.g., paper, plastics, metals)
- Organic waste composting
- Energy recovery from non-recyclable waste
Efficient Collection and Transportation
Optimizing waste collection and transportation systems is crucial for reducing costs and environmental impact. ISWM approaches include:
- Route optimization
- Use of transfer stations
- Implementation of separate collection systems for different waste streams
Environmentally Sound Treatment and Disposal
For waste that cannot be prevented or recycled, ISWM promotes environmentally sound treatment and disposal methods, such as:
- Sanitary landfills with leachate and gas management systems
- Advanced incineration facilities with energy recovery
- Mechanical-biological treatment (MBT) plants
Public Education and Engagement
ISWM recognizes the importance of public participation in achieving sustainable waste management. Key strategies include:
- Awareness campaigns on waste reduction and proper segregation
- Community-based initiatives for waste management
- Incentive programs to encourage recycling and waste reduction
The Benefits of Integrated Sustainable Waste Management
Implementing ISWM offers numerous benefits for communities, the environment, and the economy:
- Reduced environmental impact
- Improved public health and safety
- Conservation of natural resources
- Job creation in the waste management and recycling sectors
- Cost savings through improved efficiency and resource recovery
- Enhanced community engagement and social cohesion
Challenges in Implementing ISWM
Despite its many advantages, implementing ISWM can be challenging. Common obstacles include:
- Lack of political will and institutional capacity
- Limited financial resources
- Resistance to change from established waste management practices
- Inadequate public awareness and participation
- Technical challenges in implementing new waste management technologies
Global Trends and Statistics in Waste Management
To understand the importance of ISWM, it’s crucial to consider the global waste management landscape:
| Statistic | Value | Source |
| Global municipal solid waste generation (2020) | 2.01 billion tonnes | World Bank |
| Projected global waste generation by 2050 | 3.40 billion tonnes | World Bank |
| Average global municipal solid waste recycling rate | 19% | UNEP |
| Percentage of global waste disposed in landfills | 37% | World Bank |
| Number of people without access to proper waste management services | 2 billion | UNEP |
These statistics highlight the urgent need for more sustainable waste management practices worldwide.
Case Studies: Successful Implementation of ISWM
Several cities and countries have successfully implemented ISWM principles, demonstrating their effectiveness in various contexts:
San Francisco, USA
San Francisco has achieved one of the highest waste diversion rates in the world, with 80% of waste diverted from landfills through recycling and composting programs.
Kamikatsu, Japan
This small town has implemented a zero-waste policy, with residents sorting their waste into 45 categories. As a result, the town recycles 80% of its waste and aims to be completely zero-waste by 2030.
Ljubljana, Slovenia
The capital of Slovenia has implemented a comprehensive ISWM system, including separate collection of biodegradable waste, a regional waste treatment center, and extensive public education campaigns. These efforts have resulted in a 68% separate collection rate and a significant reduction in landfilled waste.
The Future of Integrated Sustainable Waste Management
As global waste generation continues to increase, the importance of ISWM will only grow. Future trends and developments in this field include:
- Increased focus on circular economy principles
- Integration of digital technologies for waste management optimization
- Development of new recycling technologies for complex waste streams
- Greater emphasis on waste-to-energy solutions
- Expansion of extended producer responsibility programs
Takeaways
So, what is integrated sustainable waste management? It is a forward-thinking, sustainable approach that combines environmental, social, and economic factors to address the growing challenges of waste management.
By adopting ISWM, we can create resilient systems that reduce waste, conserve resources, and protect our planet for future generations. Integrated Sustainable Waste Management is more than a method—it’s a necessary step toward a sustainable future.