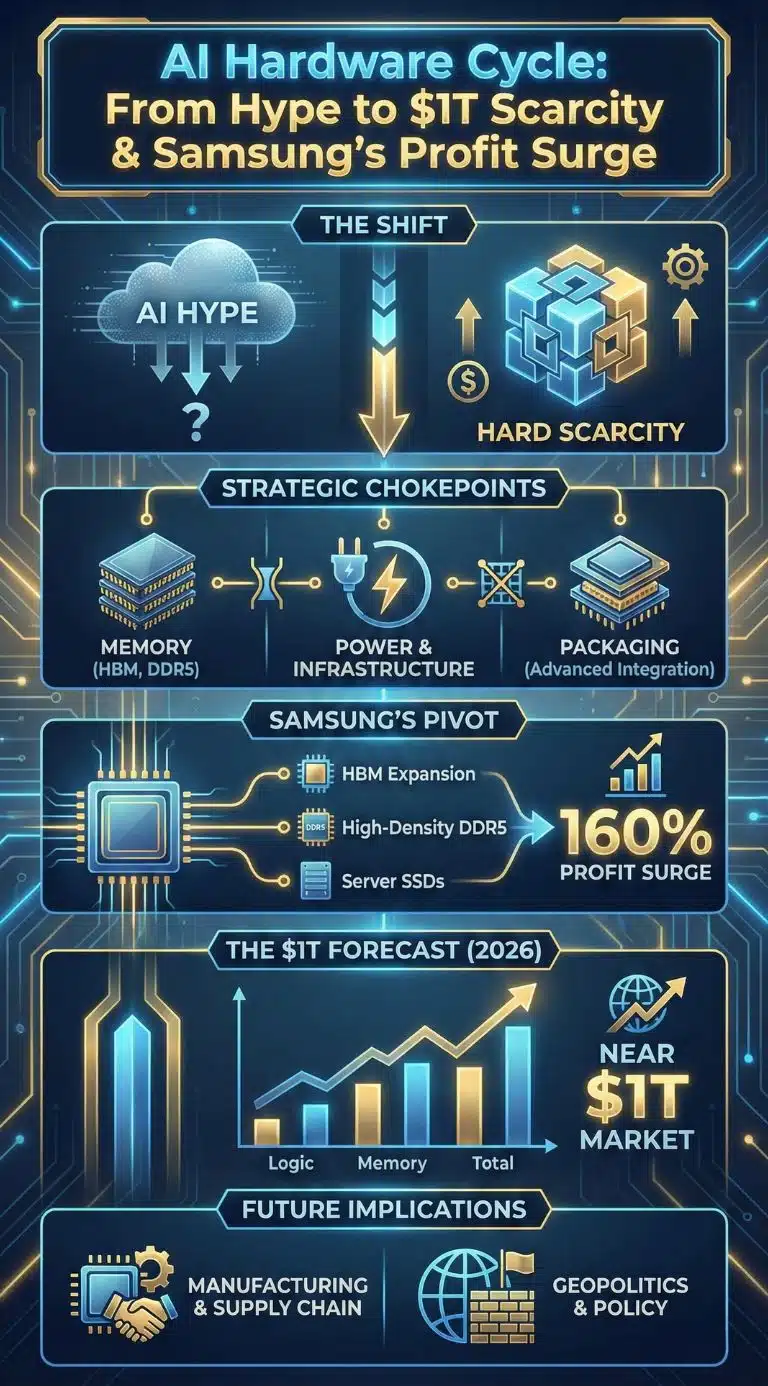
Samsung’s AI chip profit jump is a real-time indicator that the AI hardware cycle has moved from hype to hard scarcity. A projected 160% operating-profit surge signals that memory, power, and packaging are now strategic choke points as the chip market barrels toward a near-$1T year in 2026.
How We Got Here: From The Memory Bust To The AI Infrastructure Cycle
Samsung’s expected profit surge lands at a moment that looks familiar to anyone who lived through past memory booms. When memory prices rise, Samsung’s earnings can move dramatically because the business has high operating leverage. The twist is what is driving the cycle. This is not a smartphone-led rebound or a typical cloud refresh. It is a compute re-architecture: AI training and inference are pulling the entire semiconductor stack upward, from GPUs and advanced logic to DRAM, NAND, interconnect, and packaging.
The near-term setup matters. Memory went through a deep downturn earlier in the decade as pandemic-era demand normalized, inventories piled up, and pricing reset. Producers cut output, delayed capacity, and prioritized profitability. Then AI demand accelerated quickly. When hyperscalers and model builders started deploying large GPU clusters, the system-level bill of materials changed. AI servers typically carry more memory per system, higher bandwidth needs, and more expensive storage and networking. Even modest unit growth in servers can translate into outsized growth in memory bits consumed.
Samsung’s own guidance and product roadmap over 2025 pointed to this pivot: expanding high-bandwidth memory (HBM) shipments, pushing higher-density DDR5 for servers, and preparing next-generation HBM. The message is simple: memory is no longer “just a commodity.” In an AI-heavy world, the right memory, delivered at the right bandwidth and volume, becomes scarce infrastructure.
That sets up the significance of the headline number: a projected 160% year-on-year operating-profit surge. The number itself is impressive. The reason behind it is bigger. It suggests the industry is entering a period where AI changes the pricing power dynamic across memory categories, including “conventional” DRAM products, because capacity is being pulled toward AI-optimized outputs.
Why The Samsung AI Chip Profit Jump Matters Right Now
A profit spike can be dismissed as a cyclical blip. This one is harder to wave away because it aligns with multiple structural indicators:
-
The global semiconductor market is forecast to approach $1 trillion in 2026, with both logic and memory projected to grow strongly.
-
Semiconductor equipment forecasts show sustained investment, including a notable emphasis on back-end assembly, packaging, and test, which are increasingly critical for AI architectures.
-
Data-center electricity demand projections and real-estate market tightness imply that the physical buildout of AI capacity will remain constrained, which tends to keep component demand “inelastic” for longer.
-
Memory pricing signals have strengthened, reflecting tightness that is not easily solved by a single fab expansion.
The most important interpretation is this: the AI boom has matured into a hardware-and-infrastructure boom. That means the winners will be determined by manufacturing execution, supply-chain control, and deployment constraints, not just by model performance or software distribution.
A Quick Snapshot Of The Profit Signal
| Indicator | What’s Happening (As Of January 2026) | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Samsung profitability | Forecast Q4 operating profit up about 160% year-on-year | Suggests a powerful shift in pricing power and product mix |
| Memory pricing strength | Reports of sharp DDR5 moves and improving contract dynamics | Indicates tight supply as AI pulls capacity toward premium outputs |
| Conventional DRAM outlook | Forecasts point to meaningful growth in conventional DRAM pricing | Shows “non-HBM” memory is tightening too, not only niche products |
| Market size trajectory | Semiconductor market forecast near $1T in 2026 | Reframes chips as the core of a multi-year capex cycle |
Memory Is The New AI Bottleneck, Not A Side Character
AI headlines fixate on GPUs. In practice, AI scaling is often limited by memory bandwidth and memory capacity. The reason is mechanical:
-
Training large models moves enormous tensors repeatedly through memory.
-
Inference at scale becomes a throughput-and-latency problem, which also favors high bandwidth.
-
Modern accelerator designs rely on fast, nearby memory to keep compute units utilized.
This is why HBM became the emblem of the AI era. But the deeper story is that AI also changes “ordinary” memory demand. When a server platform is redesigned for AI workloads, it often carries more DRAM per CPU or per accelerator node, more storage per rack, and higher-speed interconnect. Even if total server shipments grow only modestly, memory content per server can rise meaningfully. That pushes bit demand up.
Samsung’s roadmap emphasis on HBM, high-density DDR5, and server SSDs is an attempt to capture the highest-value part of that shift. The market implication is that memory is no longer governed only by consumer electronics refresh rates. It is increasingly governed by data-center buildouts and AI workload intensity, which tend to be less price-sensitive in the early stages of a platform shift.
Winners And Losers In The AI Memory Squeeze
| Segment | Likely Winners | Who Faces Pressure | What To Watch Next |
|---|---|---|---|
| HBM supply | Memory producers that ramp yields and volume fast | Buyers without secure long-term supply | Qualification timelines, multi-sourcing, yield improvements |
| DDR5 DRAM | Suppliers with flexible capacity allocation | OEMs exposed to BOM inflation | Contract pricing resets, inventory discipline |
| NAND and SSD | Vendors with high-end enterprise offerings | Low-end storage suppliers | Enterprise SSD mix, demand elasticity |
| System makers | Firms passing costs while selling “AI-ready” SKUs | Low-margin PC and device brands | Whether AI features translate into durable pricing power |
The Chokepoints Keep Moving: HBM, Packaging, And The Back-End Revolution
One reason the AI hardware boom feels different is where the bottlenecks appear. The limiting factor is not always the most advanced lithography step. Increasingly, constraints show up in packaging, integration, and the ability to assemble complex systems reliably at scale.
AI accelerators and high-end memory stacks demand:
-
Advanced packaging to connect multiple dies with high bandwidth.
-
Specialized substrates and interposers.
-
Tight testing requirements because a defect in one part can reduce the yield of the entire assembled unit.
This is why equipment forecasts that highlight assembly, packaging, and test are not “secondary details.” They are a signal that the industry recognizes the back-end as a strategic frontier. If packaging capacity expands slowly, it can throttle the pace at which AI compute can be delivered, even when wafers are available.
For Samsung, this becomes a two-front battle: scaling memory production while also executing on foundry and packaging capabilities that complement AI system needs. The most competitive players will be those who can offer integrated supply reliability, not only the best single component.
The $1 Trillion Chip Race Is A Forecasted Reality, Not A Clickbait Metaphor
The phrase “$1 trillion chip race” is grounded in market forecasts. Industry projections point to 2026 as a year where the semiconductor market approaches the $1T mark, driven by strong growth in logic and memory. The key analytical takeaway is the composition of that growth:
-
Logic growth reflects AI accelerators, advanced CPUs, and more compute per system.
-
Memory growth reflects the bandwidth and capacity expansion needed to feed that compute.
When both logic and memory are growing strongly, the cycle becomes broader and more synchronized. That can keep the upcycle alive longer because multiple product families reinforce each other. It can also raise the risk of a later correction if capacity expansions overshoot and demand normalizes.
Market Forecast, By Major Product Groups
| Product Group | 2024 (Approx.) | 2025 Forecast | 2026 Forecast | What The Mix Suggests |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Logic | Strong growth | Strong growth | Strong growth | AI compute remains the primary engine |
| Memory | Rebound underway | Accelerating | Very strong | Memory becomes a first-order constraint |
| Total market | Large base | Big expansion | Near $1T | Chips behave like critical infrastructure |
Follow The Power: Electricity And Real Estate Are Now Semiconductor Variables
A subtle but crucial shift is that chip demand is now constrained by power and data-center capacity, not only by budgets.
Electricity demand projections for data centers show rapid growth through 2030, with AI-optimized facilities growing faster than traditional ones. This matters because the ability to deploy chips depends on:
-
Grid connections and transmission upgrades.
-
Cooling and water availability in certain regions.
-
Zoning, permitting, and land constraints.
-
Construction timelines and supply chains for transformers and switchgear.
Meanwhile, data-center market conditions show low vacancy and heavy preleasing in major hubs, implying future capacity is being reserved years in advance. That environment encourages hyperscalers and colocation providers to lock in equipment and component supply earlier. It tends to pull semiconductor orders forward, reinforcing tightness.
This turns the AI hardware boom into an “infrastructure flywheel”:
-
AI demand drives data-center expansion.
-
Data-center expansion drives preleasing and long-term power procurement.
-
Preleasing and power commitments pull forward chip and memory orders.
-
Chips and memory tightness supports pricing and profitability.
-
Profitability funds the next wave of capex.
AI Infrastructure Constraints, In Numbers
| Constraint | Signal | Why It Shapes Chip Markets |
|---|---|---|
| Data-center electricity demand | Projected sharp growth into 2030 | Slows or accelerates chip deployments depending on grid capacity |
| Construction pipeline | Large multi-year buildouts | Encourages forward purchasing of chips and memory |
| Vacancy and preleasing | Tight availability in key hubs | Locks future demand and reduces short-term elasticity |
| Capital intensity | Massive investment requirements | Keeps equipment makers and suppliers in expansion mode |
Geopolitics And Industrial Policy Turn Cycles Into Strategy
Semiconductors are now a strategic priority for governments because they sit at the intersection of economic competitiveness and national security. That reality changes the chip cycle in three ways:
Supply diversification becomes policy, not preference.
Countries want resilient supply chains, which encourages parallel investments. Parallel investments can lift total capex, expand capacity, and potentially create future oversupply if demand does not keep up.
Export controls reshape demand allocation.
Restrictions on advanced chips and equipment affect where high-end compute can be deployed and which firms get priority access. Even without naming every rule, the practical effect is that supply chain planning becomes political. Firms spend more on compliance, requalification, and localization.
Subsidies influence investment timing.
Industrial policy can accelerate projects that might not be economically optimal in a pure market setting. That can keep the upcycle hot longer because it supports demand for tools and construction. It can also intensify a downturn later if too much capacity comes online simultaneously.
For Samsung, this is both risk and opportunity. Samsung can benefit from government-driven demand for localized capacity, but it also faces higher costs and more complex execution. The winners in this geopolitical era will be the firms that can operate across regions without losing yield, speed, and reliability.
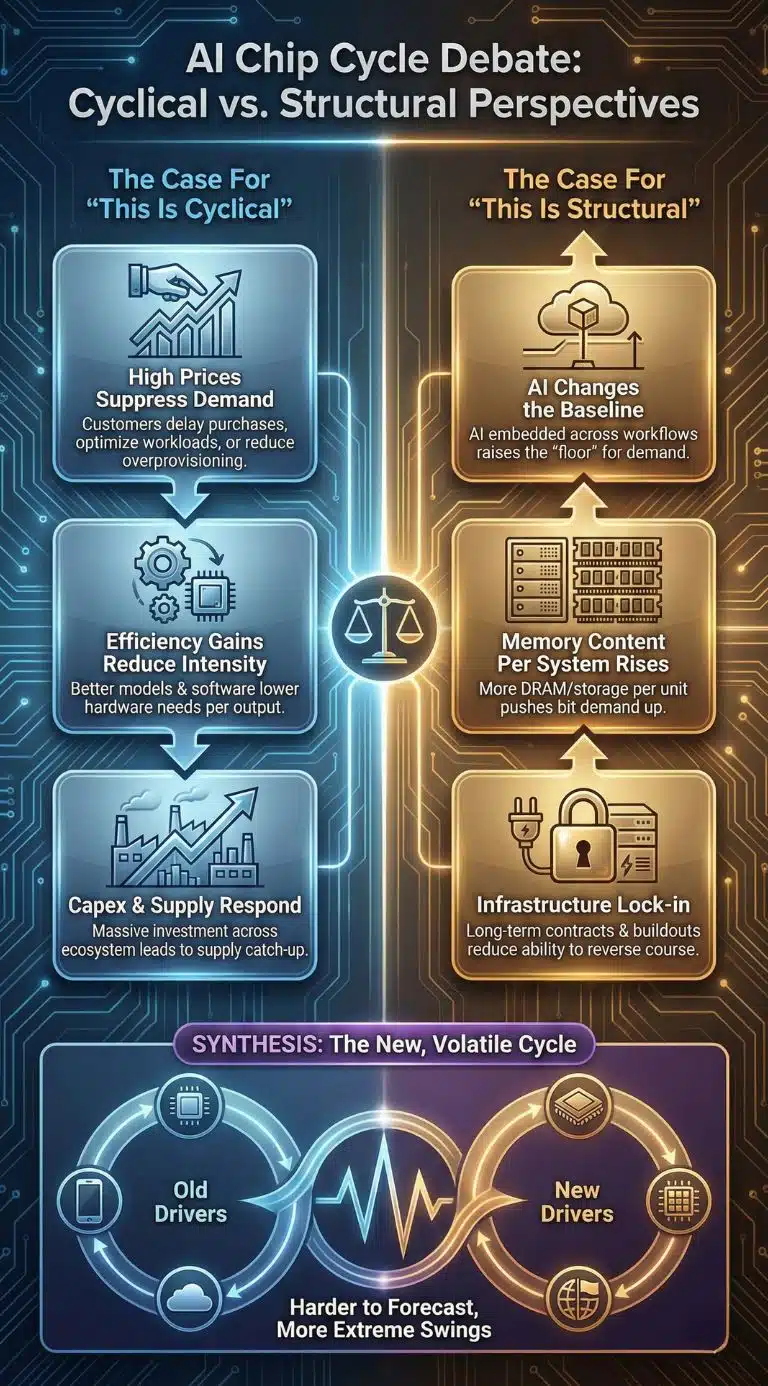
Expert Perspectives And Counterarguments: Is This A Shortage Spike Or A New Era?
A balanced view requires acknowledging the bear case.
The Case For “This Is Cyclical”
High prices can suppress demand.
If memory pricing rises too quickly, device makers and even cloud providers may delay purchases, optimize workloads, or reduce overprovisioning. Semiconductors remain cyclical because customers can pause buying when inventories are sufficient.
Efficiency gains can reduce hardware intensity.
AI software optimizations, better model architectures, quantization, and inference scheduling can reduce the amount of hardware needed per unit of output. If the industry gets significantly more efficient, the demand curve could flatten.
Capex is rising across the ecosystem.
Massive investment by major manufacturers and a strong equipment spending outlook suggest supply will respond. If supply catches up faster than expected, pricing power can fade quickly.
The Case For “This Is Structural”
AI changes the baseline.
Even if growth slows, the “floor” for compute and memory demand may be higher because AI is becoming embedded across enterprise workflows, consumer devices, and cloud services.
Memory content per system is rising.
AI shifts the architecture of servers, pushing more memory and storage into each deployed unit. That can keep bit demand strong even with modest unit shipment growth.
Infrastructure lock-in creates momentum.
Data-center preleasing, long-term power contracts, and multi-year build schedules reduce the ability to reverse course quickly. That can extend demand visibility for hardware suppliers.
The most credible synthesis is this: the cycle still exists, but it is now shaped by more variables. In the past, the main drivers were consumer electronics and generic cloud expansion. In this era, the drivers include packaging capacity, grid constraints, and geopolitics. That makes the cycle harder to forecast, but it also makes extreme swings more likely.
Key Statistics To Watch In 2026
-
Semiconductor market size projected to approach $1T in 2026, driven by strong logic and memory growth.
-
Semiconductor equipment spending projected to remain elevated through 2026, including increasing importance of packaging and test.
-
Data-center electricity demand projected to rise sharply through 2030, with AI-optimized facilities growing faster than traditional data centers.
-
Data-center vacancy and preleasing indicators remain tight in major North American markets, implying demand is being booked ahead of delivery.
What Happens Next: 2026 Milestones That Will Confirm Or Break The Thesis
Samsung AI Chip Profit Jump And The Memory Price Path
The first and simplest milestone is whether memory pricing remains durable beyond the initial surge. If contract pricing continues to reset upward or remains firm through multiple negotiation cycles, it suggests tightness is structural. If pricing spikes and then rolls over quickly, it suggests a classic shortage spike.
Watch for three signals:
-
HBM qualification expansion: More customers and broader qualification can reduce single-supplier dependence and stabilize supply.
-
DDR5 vs. older-gen substitution: If buyers shift more aggressively to alternative configurations, pricing pressure could ease.
-
Inventory discipline: The cycle turns when customers quietly rebuild inventories and then stop ordering.
Packaging Capacity And Yield Ramps
If advanced packaging capacity expands smoothly and yields improve, AI deployments can accelerate. If packaging remains constrained, it can keep the market tight even if wafer output grows.
The practical indicators are lead times for packaging-related tools and materials, and whether AI accelerator vendors report fewer supply bottlenecks over successive quarters.
Foundry Competition And Ecosystem Control
The chip race is also about who controls the most reliable production pipeline. Leading foundries that deliver consistent yields at advanced nodes will maintain pricing power. Firms that struggle to ramp new process nodes can lose share even in a booming market.
For Samsung specifically, the question is whether it can convert its scale into a stable “full-stack” AI hardware story, from memory to logic to packaging, and whether customers reward that integration with long-term commitments.
Power And Site Constraints: The Silent Governor
Even if demand is strong, deployment can be throttled by power. If grid buildouts and interconnection timelines improve, AI capacity can scale faster and pull through more chip demand. If delays worsen, chip orders may become lumpier, with bursts followed by pauses.
This is why the “AI chip boom” increasingly tracks utility decisions and construction pipelines.
Final Thoughts: Why This Profit Jump Is A Market Readout, Not Just A Samsung Story
Samsung’s projected operating-profit surge is a financial signal that AI has shifted hardware back into the strategic center of the global economy. It validates that the AI boom is not merely a software trend, but an industrial cycle spanning fabs, packaging lines, and data-center construction.
The $1 trillion chip race framing is useful because it captures what is really happening: semiconductors are becoming foundational infrastructure at a scale that rivals historic industrial expansions. In that world, memory is no longer an afterthought. It is a gating resource, and its pricing power can reshape margins across the entire tech stack.
What comes next depends on whether constraints ease gradually or suddenly. A gradual easing supports a long, investable buildout where manufacturers, equipment suppliers, and infrastructure developers all share the upside. A sudden easing raises the risk of oversupply and another sharp correction. The evidence as of January 2026 leans toward continued tightness, but the cycle will ultimately be decided by capacity ramps, efficiency gains, and the pace of data-center power expansion.