Many people now have the option of preserving fertility. Egg freezing and embryo freezing are two of the most popular methods. Each presents its unique advantages and hurdles. In this post, we explore these options to understand their differences and implications.
Understanding Egg Freezing
Understanding the differences between egg freezing vs. embryo freezing can help select the most suitable fertility preservation method. Egg freezing, or oocyte cryopreservation, is when a woman has her eggs harvested, frozen, and stored. Through this process, women can freeze their eggs and then use them later.
Pros of Egg Freezing
Flexibility is one of the main benefits of egg freezing. This method allows women to hold onto their reproductive capacity without the immediate necessity of a partner. It controls reproduction and will enable you to wait until you are ready to give birth or have gained success in your career.
Freezing your eggs allows you to plan your family in the future. The preservation of frozen eggs at a young age may improve the possibility of a successful pregnancy or surrogacy at a later date.
Cons of Egg Freezing
Despite its benefits, egg freezing is not without its difficulties. It is expensive and may require several cycles to achieve adequate eggs. Additionally, the woman’s age when the eggs are frozen affects success rates, with younger women generally enjoying greater success.
At least it is not a promise that you will get pregnant. The eggs must then be thawed, fertilized, and implanted, each involving risks.
Exploring Embryo Freezing
Embryo Freezing Here, eggs are fertilized with sperm before freezing. This method is commonly employed by couples postponing pregnancy.
Pros of Embryo Freezing
Frozen embryos have a better chance of leading to a successful pregnancy than egg freezing. Fertilized embryos survive the freezing and thawing process better than unfertilized eggs.
This option can give individuals peace of mind, as it helps couples secure their opportunity to have a child together. This same technology also allows pre-implantation genetic testing to screen for genetic disorders.
Cons of Embryo Freezing
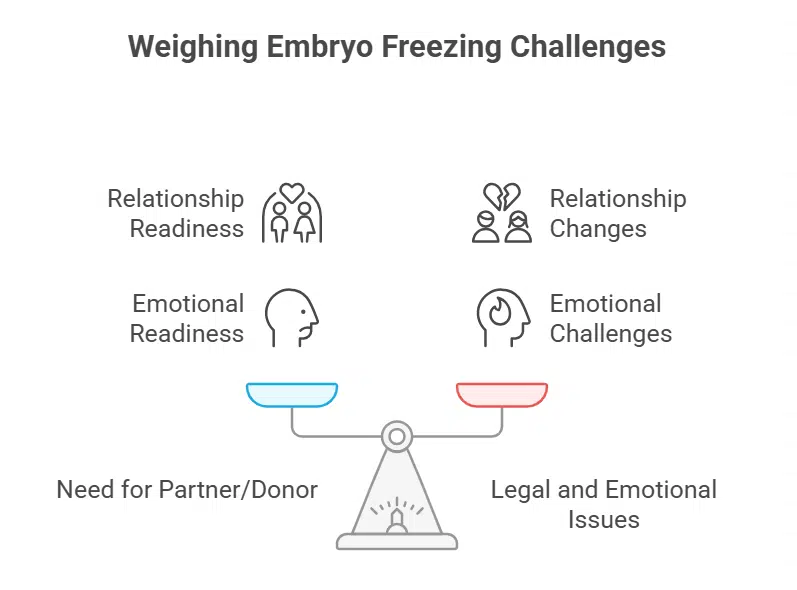
The only downside is that you need to have a partner or donor sperm when you freeze them. It can be a bit of a dealbreaker when someone is not ready to go there.
Freezing embryos can raise legal issues. If the relationship changes or ends, embryos can be the subject of a dispute. This complexity arises from the emotional challenges associated with managing frozen embryos.
Cost and Availability Comparison
Both methods require a lot of money. Costs can be high, and insurance may or may not cover services. Those price tags are for medications, procedures, and storage charges. Accessibility varies with location and infrastructure. Urban centers could provide additional facilities and choices, while rural places may lack access.
Emotional and Psychological Factors
The choice to freeze eggs or embryos is not only financial; it is also emotional and psychological. The selection can affect relationships and the longer-term building of families.
And for individuals, fertility preservation provides the ability to dictate their reproductive fate personally. But the unknown of future success can still make you somewhat anxious. It is even emotionally taxing to incorporate the waiting period and the possibility of repeating multiple cycles.
These higher success rates may give you peace of mind; hence, embryo freezing could be reassuring. But that adds a whole layer of complication to dating, even more so if life changes. Whether to discard, donate for reproductive or research purposes, or freeze embryos for future use, how do I manage all these decisions in the future?
Ethical and Legal Aspects
There are ethical and legal aspects of both egg freezing and embryo freezing. Usage and storage time also depend on legislation regarding the recycling process, which differs in every region.
Freezing embryos adds even greater legal complications. Couples, in particular, may have to set out the terms of embryonic use, if any, in advance. Changes in relationship status can complicate these agreements.
There are historically fewer legal complications with egg freezing. But you have to reckon with regulations for storing and final use.
Conclusion
Both egg and embryo freezing offer valuable options for fertility preservation. Each comes with its own set of benefits and challenges. Egg freezing provides autonomy and flexibility, while embryo freezing offers higher success rates and genetic insights. Cost, accessibility, emotional factors, and legal considerations are crucial in making an informed choice. Understanding these aspects can help individuals and couples decide which path aligns best with their personal and reproductive goals.