Meta, the parent company of Facebook, Instagram, and WhatsApp, has announced a groundbreaking initiative to build the world’s longest undersea cable, named Project Waterworth. This massive infrastructure project, spanning more than 50,000 kilometers (31,000 miles) across five continents, is designed to significantly enhance global digital connectivity and support the rapidly growing demands of artificial intelligence (AI).
This new cable will provide high-speed data transmission between key regions, including the United States, India, South Africa, Brazil, and other strategic locations. Meta says the project represents a multi-billion-dollar, multi-year investment, reflecting the increasing importance of undersea fiber-optic networks in today’s data-driven economy.
The Importance of Undersea Cables in Global Digital Infrastructure
Global communication and the internet rely heavily on an extensive network of subsea cables, which transport over 95% of intercontinental internet traffic. According to the Centre for Strategic and International Studies (CSIS), more than 1.2 million kilometers of undersea cables are already installed worldwide, forming the backbone of international data exchange.
These cables connect continents, allowing businesses, governments, and individuals to access fast and reliable internet services. From streaming high-definition videos and social media interactions to global banking transactions and AI computations, these deep-sea conduits power the modern digital economy.
With Project Waterworth, Meta aims to expand and reinforce this crucial infrastructure, ensuring more efficient data transfer, better resilience against disruptions, and improved internet access in underserved regions.
What is Project Waterworth?
Meta’s new Project Waterworth cable is expected to become the longest undersea cable in history, surpassing the current record-holder, 2Africa, which stretches around 45,000 kilometers (28,000 miles).
The name “Waterworth” pays tribute to Gary Waterworth, a former Meta employee who played a crucial role in global connectivity projects before his passing. He had previously worked at Alcatel Submarine Networks (ASN), one of the leading companies specializing in undersea cable installation.
This new system will incorporate the latest fiber-optic technology, ensuring that it can meet the growing demands of AI applications, cloud computing, and future advancements in digital communication.
Technical Specifications and Cutting-Edge Features
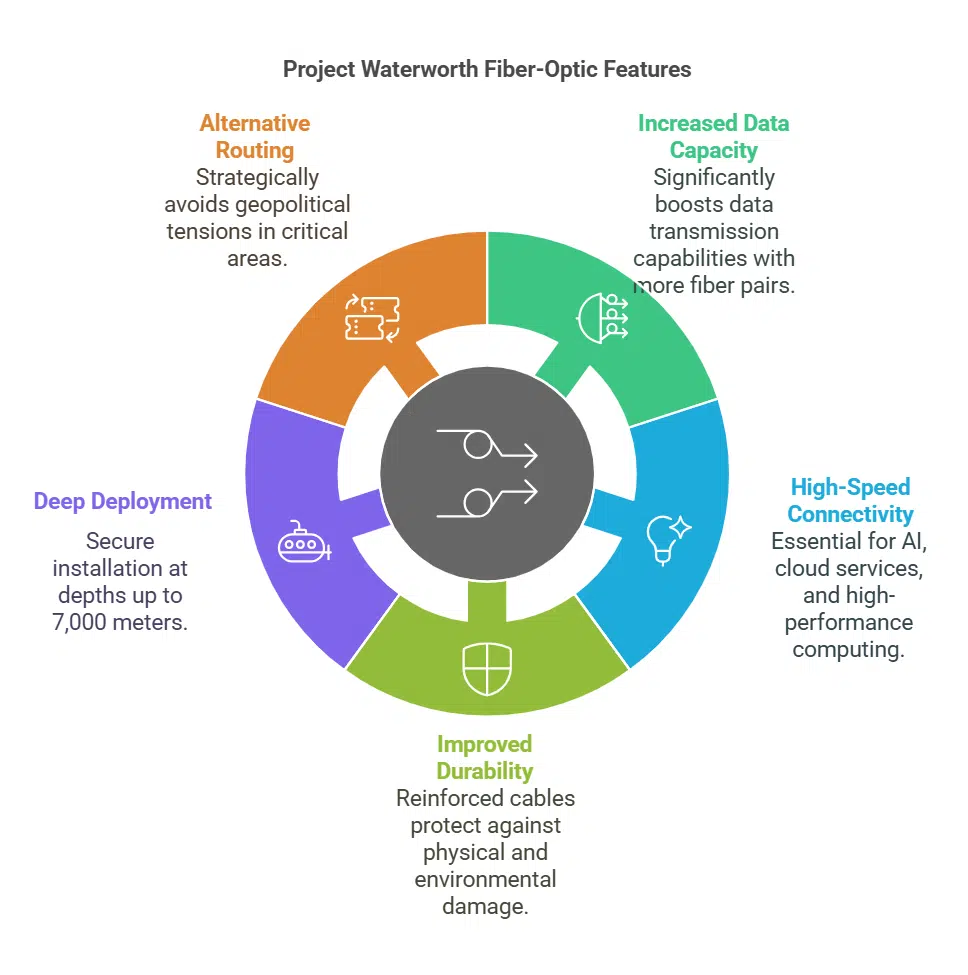
Project Waterworth will utilize advanced fiber-optic technology to provide:
- 24 fiber pairs—significantly increasing data capacity compared to standard cables, which typically have 8 to 16 pairs.
- High-speed connectivity—essential for AI-driven applications, cloud services, and high-performance computing.
- Improved durability—cables will be reinforced with armored sheaths and buried under the seabed in shallow areas to protect against damage.
- Depth deployment of up to 7,000 meters (4.3 miles)—ensuring security against external threats like ship anchors, fishing activity, and environmental shifts.
- Alternative routing to avoid geopolitical tensions, such as the South China Sea and the Red Sea, where disruptions are more likely.
According to Telegeography, Meta has two other privately owned subsea cable systems, but Project Waterworth will be its largest and most ambitious to date.
Why Is Meta Investing in Undersea Cables?
Traditionally, undersea cable networks were developed and operated by telecom giants. However, in recent years, tech companies like Meta, Google, Microsoft, and Amazon have taken a more direct role in building these infrastructures.
Key Reasons Behind Meta’s Investment:
-
AI and Data-Intensive Services
- AI applications require huge amounts of real-time data processing.
- High-speed, low-latency connections are crucial for AI model training, machine learning algorithms, and cloud-based AI tools.
-
Reducing Reliance on Third-Party Infrastructure
- Meta, Google, and Microsoft are building their own subsea cables to reduce dependency on traditional telecom providers and cut costs in the long run.
- This allows greater control over data flow, security, and performance.
-
Strengthening Network Resilience
- Undersea cables face around 200 incidents of damage each year due to natural disasters, human activity, and potential sabotage.
- Having multiple independent cable systems ensures business continuity and disaster recovery.
-
Expanding Connectivity in Emerging Markets
- Many regions, particularly in Africa, South America, and parts of Asia, still suffer from slow and expensive internet.
- Meta aims to improve global access, ensuring faster connections to its platforms, including Facebook, Instagram, WhatsApp, and the Metaverse.
Security and Geopolitical Considerations
Subsea cables are not just technological marvels—they are also geopolitical assets. These vast digital highways carry sensitive government, financial, and corporate data.
In recent years, concerns over cyber threats and potential sabotage have risen sharply. In January 2025, NATO launched patrols in the Baltic Sea after suspected sabotage attacks on telecom and power cables. Numerous experts have implicated Russia as a potential culprit.
To minimize security risks, Project Waterworth has been strategically routed to avoid politically sensitive areas, reducing the likelihood of interception, spying, or disruptions.
Meta vs. Google: The Race for Undersea Dominance
Meta’s Project Waterworth is a direct challenge to Google, which currently leads in undersea cable investments.
- Google owns 16 undersea cable projects, while Meta is still catching up.
- Google’s “Equiano” cable system links Europe to Africa, and its “Dunant” cable connects the U.S. and France.
- Meta’s previous cables, including “Anjana,” have been smaller in scale compared to Google’s massive investments.
However, Project Waterworth could shift the balance, giving Meta a powerful foothold in global data infrastructure.
Economic and Social Impact
Meta claims that this massive infrastructure project will generate significant economic benefits:
- Boosting digital economies—Countries connected to the cable will see lower data costs, better connectivity, and improved opportunities for businesses and startups.
- Creating jobs— The construction and maintenance of the cable will support thousands of direct and indirect jobs worldwide.
- Enhancing AI capabilities—AI-driven industries, including healthcare, education, and finance, will benefit from faster data processing.
In particular, India stands to gain substantial advantages, as the cable will strengthen the country’s position as a global leader in AI, IT, and software development.
When Will Project Waterworth Be Completed?
While Meta has not provided an exact launch date, the project is expected to be operational by the end of this decade. Given its sheer scale, the construction process will take several years, requiring coordination between multiple global partners.
A Historic Leap for Global Connectivity
Meta’s Project Waterworth represents one of the most ambitious digital infrastructure projects of the 21st century.
By investing billions into this record-breaking subsea cable, Meta is not only strengthening its own network but also shaping the future of global internet access.
With AI becoming a driving force of the digital economy, high-speed data transmission is more critical than ever. If successfully executed, Project Waterworth could redefine global connectivity, making digital services more accessible, efficient, and resilient for billions worldwide.