Do you want to know why and how to pop your ears? The air pressure on both sides of your eardrum is usually kept equal by your body. When the pressure changes between the middle ear and the outside, it will feel like your ears are plugged. If the pressure changes a lot, it might even hurt.
Sometimes, the air in your middle ear can’t adjust to the pressure. This can happen when you are driving or flying. Even when driving up or down a steep mountain, it could happen.
Your middle ear usually gets used to the difference in pressure over time. When it happens, your ears will pop. Sometimes you may need to yawn or swallow to help equalize the pressure. Depending on your health, you may be unable to pop your ears. You might need to see a doctor or nurse if this happens to you.
This article will explain why and how to pop your ears when they feel stuffed. It will also talk about a few things that might make it hard to pop your ears.
Is It Safe to Pop Your Ears?
Having stuffed ears can be painful and make it hard to hear. Popping your ears may help when this happens, and you need to know how to pop Your ears.
Most of the time, it’s safe to pop your ears. Most of the time, all you have to do is move your mouth muscles. No matter what method you use, you need to be gentle. You should stop trying to clear your ears and see a doctor if your symptoms worsen.
If you try to unclog your ears with an over-the-counter (OTC) or prescription medicine, don’t use it for longer than it says on the package. Talk to your doctor if your symptoms keep coming back.
How to Pop Your Ears: The Complete Process
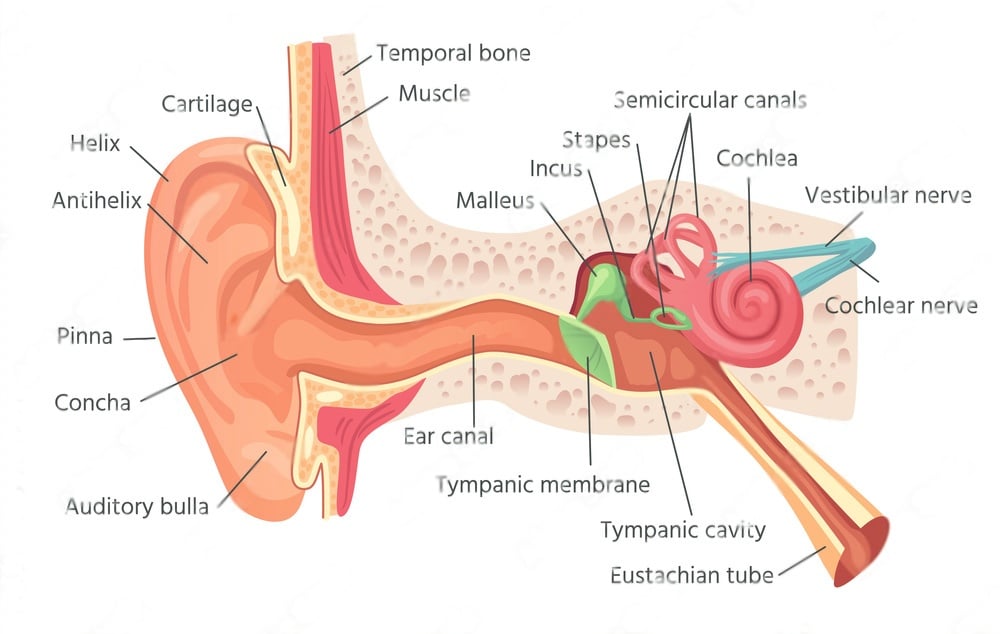
Your Eustachian tube is the part of your ear that pops. This tube is made to protect and let air into your middle ear. The Eustachian tube ensures that the air pressure on both sides of your eardrum stays the same.
Your Eustachian tubes will open when pressure builds up in your middle ear. When the tubes open, the pressure in your ear evens out. This is why your ears pop, which can help relieve pressure and pain.
Pop Your Ears by Holding Your Nose
One of the best ways to pop Your ears is to hold your nose and blow it out through your mouth. First, calm down. Then put your fingers in your mouth and nose to close them. Blow out lightly against the pressure. Your ears should pop when you hear this.
When you blow against pressure, your Eustachian tubes open up slightly. This lets pressure and fluid drain out of your ear. People often think this method is dangerous, but that’s not true. As long as you don’t put too much pressure on your eardrum or sneeze in this way, you won’t risk bursting it.
Pop Your Ears by Blowing Up a Balloon
Blowing up a balloon is another unique way how to pop Your ears. Putting pressure on the balloon to make it bigger helps push air up your Eustachian tube. You can use this method whenever your ear feels full or pressured.
You can buy balloons that are made to help you pop your ears. If you have this problem often, you could try these. You can use your nose to blow up these balloons and block off one nostril at a time. Most of the time, these balloons are for kids who keep getting wax in their ears.
You shouldn’t use this method with a cold or stuffy nose. This could cause infected mucus to get into your middle ear and give you an ear infection.
Pop Your Ears by Flexing Your Jaw
Some people can make their ears pop by flexing the muscles behind their jaw. By bending in this way, the Eustachian tube can open, and the pressure can be released.
This might be easier how to pop Your ears than pop them with your nose. If you’re on a plane or in an elevator and feel a change in pressure, you can work your jaw to keep pressure from building up.
Pop Your Ears by Yawning
When you yawn, you swallow air when you open your mouth. You can pop your ears by swallowing and moving your mouth. This brings the pressure inside and outside of your ears to the same level.
Pop Your Ears by Swallowing Often
If you drink water or something else, your ears will pop, and the pressure will even out. Pinching your nose shut is a more robust way to pop your ears by swallowing. This makes your nose empty, which helps your Eustachian tubes open.
Another common way to pop your ears is to chew gum when the pressure changes. Chewing gum or sucking on a mint makes you swallow more often and makes your mouth produce more saliva. The pressure can also be evened out by moving your jaw to chew.
How Does Ear Popping Work?
The middle ear gets air from the eustachian tube. This helps keep the pressure on both sides of the eardrum at the same level.
When there is a pressure difference, your eardrum may move in or out. The pressure difference can make the ear feel full, which is a feeling most people are used to.
When you pop your ears, you open both eustachian tubes to relieve the uneven pressure, which stops or lessens your pain.
Most of the time, the eustachian tubes open independently when you swallow, chew, or yawn. You’ll often hear something click or pop when you do these things. The noise comes from the eustachian tubes in each ear, letting air into the middle ear.
If the tubes are hard to open, there may be something in how to pop Your ears. Most of the time, they are caused by fluid, mucus, or inflammation.
Why Do Your Ears Get Plugged Up
The Eustachian tube connects the area behind your eardrum to the back of your nose and throat. You have one behind each ear, so you have two.
Dr. Goldman says, “This tube helps keep the air pressure in the space behind the eardrum and the space outside the eardrum even.” “Sometimes, when the pressure inside the Eustachian tube is different from the pressure outside the eardrum, we may feel like our ears are plugged up.”
This is called dysfunction of the Eustachian tubes, and it can also cause the following:
- Pain inside of your ear.
- Changes in your hearing.
- Feeling dizzy.
- Ringing in your ears (tinnitus).
Dr. Goldman explains some of the most common causes of ear congestion.
Changes in Air Pressure
When people fly, their ears often get stuffed up. This is so common that it has a name: “airplane ear.” But it can also happen because of other things in the environment.
“This feeling can also be caused by sudden changes in pressure, like when you drive up into the mountains or go scuba diving,” says Dr. Goldman. As the air pressure around you changes, the pressure in your inner ears tries to do the same.
Ear Infections
When the infected fluid gets stuck behind your eardrum, it can swell and bulge, causing pain and the feeling that your ear is plugged. Otitis media can happen to anyone, but kids under 8 will likely get it. Kids’ Eustachian tubes are also narrower than adults, making them more likely to get clogged.
Swimmer’s Ear
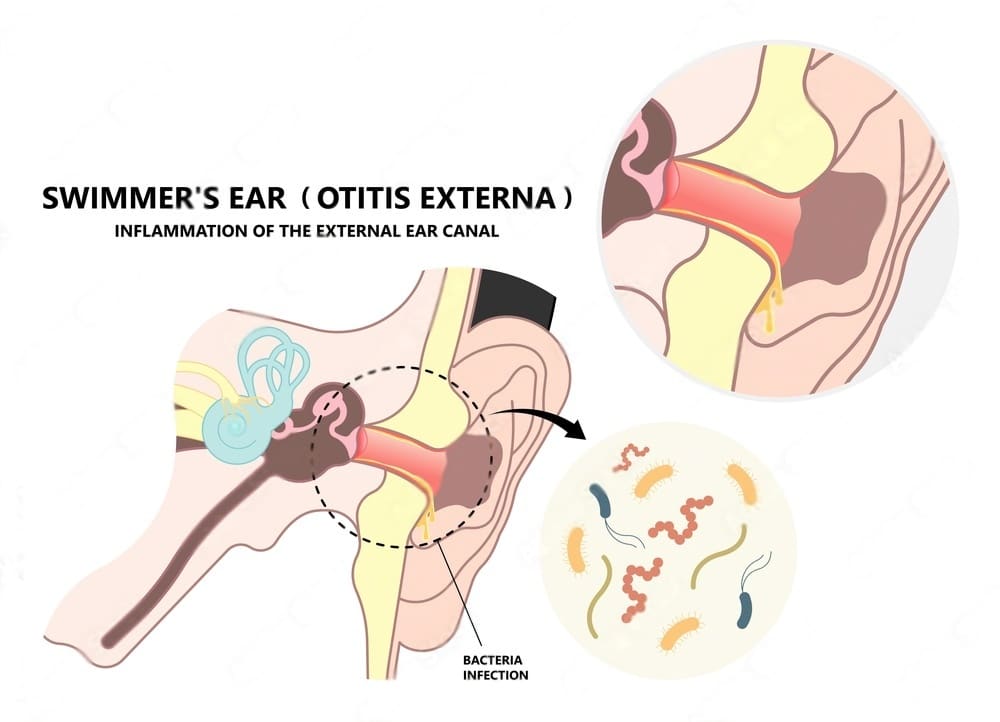
A swimmer’s ear, or otitis externa, is an infection in the lining of your ear canal. This can also cause your ears to feel blocked. This is an infection outside your ear, not in the middle ear.
“The ear canal that leads to the eardrum gets irritated and swollen, which makes the ear feel like it’s plugged up,” says Dr. Goldman. In addition to pain, itching, and pus, the swimmer’s ear is often accompanied by other symptoms.
Sinus Infections
Your Eustachian tube connects your ears to your sinuses. If you have a problem with your sinuses, blocked ears could be a sign of it. Dr. Goldman says a sinus infection can change the pressure behind your eardrum.
Allergies
Achoo! You can add stuffy ears to the list of annoying things that happen when you have allergies. They can also worsen your sinuses by inflaming your Eustachian tubes and making mucus build up.
Eustachian Tube Problems
Sometimes, you may have a health problem that affects your Eustachian tubes directly. “Growths can sometimes affect the Eustachian tubes, which can cause problems,” says Dr. Goldman. “Being born with Eustachian tubes that aren’t the right shape can also be a cause.”
Why Your Ears Won’t Pop?
If you feel pressure, pain, or like your ears are full but won’t pop, you may have a problem with your ears. This problem can be caused by problems with the way your auditory tube works.
Related Read: Tinnitus 911 Reviews
Fluid in the Ear
If there is fluid in the ear, the ear may not pop. The fluid that has thickened blocks the ear tube. So fluid doesn’t drain into the back of the throat. An infection in the ear can sometimes cause this.
This problem goes by a few different names, such as:
- Serous otitis media
- Glue ear
- Otitis media with effusion
The adenoids are small lumps of tissue high in the back of your throat. When they get bigger, they can block the hearing tubes, which can cause fluid to get stuck in the ear. When the tissues in your nose get swollen, this can also happen.
If the tissue around the auditory tube blocks it, the tissue may need to be taken out.
Surgery to put in artificial ear tubes can help with ear fluid problems that come up often. They let the ear drain and even out the pressure in the ear. Having ear tubes means that your ears won’t pop. This is because the pressure in the tube will automatically even out.
Excessive Earwax
Too much earwax can also make it hard for your auditory tube to do its job. Your doctor or nurse can clean out your ears in a few different ways. Most of the time, it can be done in their office.
Ear drops that dissolve wax can be used to remove the wax. You can also use water to flush it out. The doctor or nurse can also remove the wax with a unique tool called a cerumen spoon.
Congestion
When there is too much mucus in the middle ear space, it can be hard to keep the pressure steady. If you have allergies, try taking a decongestant before you fly or drive to a higher elevation.
Cold viruses can also cause congestion, but you should see a doctor if it lasts over three weeks. Your stuffy nose could be caused by allergies or something else.
Patulous Eustachian Tube
When a person has a patulous eustachian tube, the tube is always open. It doesn’t happen very often. Some of the signs are:
- The sensation of plugged ears
- Tinnitus, which is a ringing sound in the ear
- Autophony is when your voice seems abnormally loud to you
- Hearing your breathing
Other Causes of Poping Ears
When you are trying how to pop Your ears. Some other health problems that can affect your auditory tube are:
- Sinusitis is an infection of your nasal passages
- Nasal polyps, which are growths in your nasal passages
- Enlarged turbinates. Turbinates are structures in your nasal passages that help warm and humidify the air you breathe.
- Tonsillitis is an inflammation of the tonsils.
An ENT doctor can usually help treat or deal with the above problems. Your ENT may tell you to take medicine. In some cases, you may need to have surgery on your ears.
Because of these things, it might be hard or uncomfortable to travel. See a doctor before you leave so you can fix these problems before you leave.
When to Call Your Doctor?
Your ears may get better on their own, but you should see a doctor if any of the following happen:
- pus or discharge draining from your ear
- hearing loss
- fever
- ear pain
- ringing in your ears
Your doctor can rule out any underlying conditions causing clogged ears and other symptoms. These things could make your ears feel full:
- enlarged adenoids, also known as swollen tissue at the back of the throat
- sinus or ear infection
- allergies
- earwax buildup
- common cold
- temporomandibular joint disorders
When the eardrum is clogged, it can sometimes get so big that it bursts. This is called a perforated eardrum. This could happen because:
- an ear infection
- activities involving rapid pressure changes, such as air travel
- head trauma
A perforated eardrum requires a doctor’s care. Most people get better on their own within a few weeks. In some cases, you might need surgery.
Medical Treatment for Blocked Ears
If you have trouble with how to pop Your ears, it could be a sign of a bigger problem. If this problem keeps happening and hurts, you should make an appointment with an ENT to find out what’s wrong and how to fix it. Some common treatments are:
- To thin the mucus and help the ears drain, decongestants are used.
- Surgical removal of the surrounding tissue, such as the tonsils or adenoids, blocks drainages.
- Putting tubes in the ears to help them drain and even out.
- Earwax removal at the doctor’s office with irrigation or special eardrops
When other conditions affect how the ears equalize, an ENT can recommend medication or surgery to control the symptoms.
Final Words
When your eustachian (auditory) tubes are blocked, your body can’t even out the pressure in your ears, so you feel clogged. Try yawning, swallowing, or chewing to pop your ears. Taking a decongestant could also be helpful.
Several things, like fluid in the ear, too much earwax, and congestion, can make it feel like your ears are full. Some health issues, like sinusitis and tonsillitis, may need to be treated by a doctor or nurse.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Check out some commonly asked questions about How to Pop Your Ears.
How can I prevent airplane ears?
To avoid the feeling of clogged ears, especially during takeoff or landing, you can try a few things:
- Take a decongestant 30 minutes to an hour before traveling
- Use earplugs
- Chew gum or repeatedly yawn as the plane takes off and lands
Could COVID-19 cause ears to feel clogged?
COVID-19 has been linked to ear infections, making your ears feel plugged up. But ear pressure is more likely to be caused by other illnesses, like a sinus infection or another type of ear infection. Tell your doctor about how you feel.
Is it normal for children to feel like their ears are blocked?
Yes, because a child’s Eustachian tubes, which connect the back of the throat to the middle ear, are small and can easily get clogged by mucus or changes in air pressure. This is also why children are more likely than adults to get ear infections.
How can I pop my ears myself?
Try forcing yourself to yawn a few times until your ears pop. Swallowing helps to move the muscles that open the eustachian tube. Taking small sips of water or sucking on hard candy can help make you want to swallow more. If neither yawning nor swallowing helps, take a deep breath and pinch your nose shut.
How do you relieve ear pressure?
To get rid of ear pain or discomfort, you can do things to open the eustachian tube and relieve the pressure, such as:
- Chew gum.
- Inhale, then gently exhale, holding the nostrils closed and mouth shut.
- Suck on candy.
- Yawn.
Can you manually pop your ears?
Most of the time, your Eustachian tubes are closed. They open when you swallow or yawn. So doing these things on purpose might help clear your ears, especially if no allergy or infection is at the root of the problem.
How do you open a blocked ear?
If your ears are clogged, you can open your eustachian tubes by swallowing, yawning, or chewing sugar-free gum. If this doesn’t work, take a deep breath and try to blow gently out of your nose while closing your mouth and pinching your nose. Then If you hear a pop, you know you’ve done it right.
Why is my ear blocked?
There are a few things that can lead to plugged ears. Fluid in the ear, changes in air pressure, too much earwax, or even small objects that block the eardrum are all possible causes. There are different ways to treat each cause, so it’s important to talk to a professional.
Why does my ear feel full?
Fluid in the middle ear, hay fever, allergies, or blowing your nose too much are common causes. Ear pain can be caused by ear congestion from an infection or by sudden changes in barometric pressure, which usually happen when an airplane is going down.
How long does a blocked ear last?
If your blocked ears are caused by air pressure, they will probably be fine after a day. If you have a blocked ear because of an ear infection, you may have to wait until your body gets rid of the virus or bacteria that caused it (you might need an antibiotic to speed things up). And it could take a week or two to do that.
Disclaimer: This content is for informational purposes only and does not replace professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. This information is not comprehensive and should not be used to make health or well-being decisions. Consult a qualified healthcare professional with questions about a medical condition, treatment options, or health regimen. This website or the content should never replace professional medical advice.