Are you looking to learn about the history of the Gaza Strip? This blog post will be your ultimate guide. The Gaza Strip is a small landlocked territory located along the Mediterranean Sea, just northeast of Egypt’s Sinai Peninsula.
It has been at the heart of many conflicts between Israel and Palestine for decades. Here we will discuss its past, geography, demography, conflict, economy, and more in detail. So get ready to explore this controversial region’s turbulent history!
Content Highlights
- The Gaza Strip is a small landlocked territory located along the Mediterranean Sea, northeast of Egypt’s Sinai Peninsula. It has been at the center of tension and conflict between Israel and Palestine for decades.
- Throughout its history, it has changed its control several times between countries, including Britain, Egypt, Israel, the All-Palestine government & Palestinian Authority/Hamas, once declaring independence in 1994.
- Under ‘Israeli Occupation’ from 1967 to present-day Palestinians living inside this region have faced various tensions in their everyday lives due to restrictions on access to natural resources or work opportunities; moreover, they’ve experienced high casualties during armed wars such as 2008-2009 Operation Cast Lead & 2014 – Gaza War which caused large scale destruction throughout parts of the area often leading them into greater humanitarian crisis in Gaza despite riches economic potentials accessible within the region itself.
Latest Updates:
Background and Location of The Gaza Strip
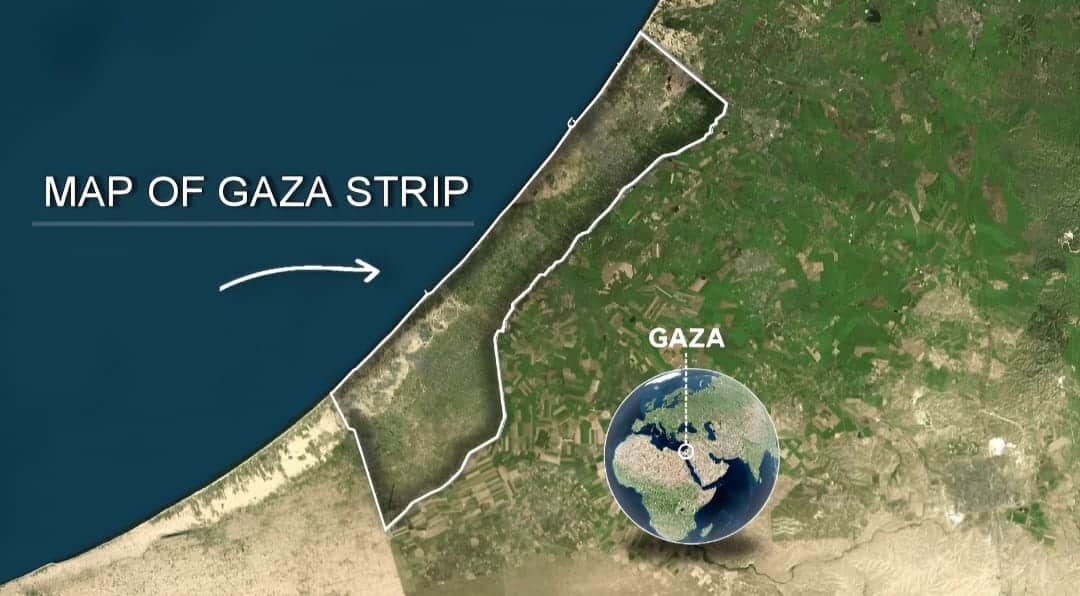
The Gaza Strip is located on the southeastern coast of the Mediterranean Sea in the Middle East with geographic coordinates of 31.3547° N and 34.3088° E.
Geographic Coordinates
The Gaza Strip is located at 31.3547° N and 34.3088° E in the Middle East. It borders the Mediterranean Sea to its West and is bordered by Egypt to its south and Israel to its east and north.
These geographic coordinates help us better understand both the physical boundaries of this region as well as historically how this region has been positioned geopolitically.
Its proximity to key political players such as Israel, Egypt, and Turkey makes it a particularly contentious arena for global powers vying for strategic gains in their respective agendas.
This small territory has become an internationally contested space where interests conflict over regional power dynamics sustained through complex negotiations of political identity that hold significant implications for understanding the Middle Eastern geopolitical landscape at large.
Map References
The Gaza Strip is located between the Mediterranean Sea and Israel, adjacent to the Sinai Peninsula. The precise geographic coordinates of the region are 31.3547° N and 34.3088° E. It is divided into five governorates: North Gaza, Deir al-Balah, Khan Yunis, Rafah, and Gaza City Area.
Maps highlighting these areas and other regional political boundaries can provide insight into further understanding of its geography and its renowned history as a conflict zone spanning multiple countries.
Additionally, maps showing economic activity, including education centers and healthcare locations, can provide valuable information on life in Gaza today.
Furthermore, ethnic maps featuring different groups living within much smaller sub-districts demonstrate how vibrant communities have developed and still exist despite ongoing tensions.
Area
The Gaza Strip is a small, densely populated area located on the east Mediterranean coast between Egypt and Israel. Spanning 365 km² (140.9 square miles), it is an enclave bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the west and south, Israel to the north and east, and Egypt’s Sinai Peninsula to its southwest.
Geographically speaking, The Gaza Strip has coordinates of 31.3547° North latitude and 34.3088° East longitude.
The narrow strip of land serves as the home for 2.3 million Palestinians (as of September 2023) who have been subject to indefinite occupation by Israeli forces since 1967.
As part of this conflictual relationship dating back to 1948 when Israel declared statehood within historic Palestine, both sides are subjected to regularly destructive warfare along with social tensions, including restrictions over movement due to its ethnically concentrated population situation leading them into great humanitarian crisis despite the rich economic potential of fisheries, agricultural fields, and vast resources available inside the region itself.
History of the Gaza Strip
The modern history of the Gaza Strip can be traced back to 1923, when it came under the control of the British Mandate.
Prior to 1923
Prior to 1923, the Gaza Strip was not an independent territory and instead formed part of the Palestine Mandate administered by Great Britain from 1923 to 1948. This period saw movement on both sides of the political divide in terms of British actions towards Zionism and Palestinian resistance efforts.
These struggles set in motion a pattern that would remain essential for many decades until today – namely, British administration over Palestinian territories as part of a broader imperial project manifesting itself through agreements such as the famous McMahon–Hussein Correspondence, where proposals on Jewish self-determination were discussed.
The area became known officially as “Palestine” under this agreement, and this name ultimately came to define what is now Israel while also hovering over what are now Israeli-occupied Palestinian territories, including the Gaza Strip, prior to its independence.
British Mandate (1923-1948)
The British Mandate in Palestine was established in 1923 and lasted until 1948. The British tried to manage the growing demand for Jewish immigration. However, they faced many challenges from both the Jewish Yishuv and Palestinian Arab communities.
During this period, there were protests, riots, uprisings, civil disobedience, and more due to the tensions between these groups over land rights. The result of this conflict fueled what we now know as the ongoing Israeli-Palestinian conflict with Gaza at the center of attention today.
As a testament to how volatile things were during that period, control shifted between different governments every year leading up to 1948, with some regions having no formal government control at all.
All-Palestine Government (1948)
The All-Palestine government was created in 1948 during the Arab-Israeli War as a result of UN General Assembly Resolution 181. The resolution recommended partitioning Palestine into separate Jewish and Arab states, leading to the formation of the All-Palestine government with limited jurisdiction over areas not under Israeli control, including the Gaza Strip.
The Mufti of Jerusalem, Haj Amin al-Husseini, was appointed its leader due to his strong nationalism and influence over Palestinian politics. He became president in late 1948 but his government could never exercise effective control because it lacked authority over large parts of land occupied by Jewish forces who prevented their independence hopes for an all-Palestian state from materializing.
Egyptian Occupation (1959-1967)
The Gaza Strip was occupied by Egypt from 1959 to 1967 after the dissolution of the All-Palestine Government. During this time, Egypt justified its occupation under the pretext of pan-Arabism as its military forces had full control over the region.
For 8 years, Gaza citizens were forced to live under Egyptian rule; Palestinian political parties and civil society organizations continued to be repressed while Israel maintained an increasing level of influence in other parts of Palestine.
In 1967, there was a significant event called the Israeli Six-Day War. During this war, Israel gained control of East Jerusalem, the entire West Bank, and the Gaza Strip. This changed the borders and created new opportunities for resolving conflicts between Zionists and the Palestinians.
Israeli Occupation (1967)
In 1967, Israel launched what is now known as the Six-Day War against Arab states Egypt (which controlled the Gaza Strip), Syria, and Jordan. On June 5th, the Israeli Defense Forces captured the Gaza Strip in just two days of battle.
This marked the beginning of a long period of military occupation by Israel that continues to this day. The UN Security Council confirmed that it should be treated as “an occupied territory,” its inhabitants continuously subjected to restrictions imposed by foreign powers on their everyday lives.
These changes included reducing access to natural resources, work opportunities, infrastructure development, and livelihoods such as fishing and agriculture; moreover, they led to an increase in Palestinian displacement due to conflict with Jewish settlers who were previously forcefully moved into settlements across the area.
Palestinian Authority (1994)
The Palestinian Authority (PA) was established as part of the landmark “1993 Oslo Accords peace agreement” between Israel and the Palestinians. Its establishment aimed to give autonomous governing control over identified Palestinian-majority regions in parts of Gaza, Jerusalem, and the West Bank.
The PA also sought to create a peaceful framework for negotiations on final status issues between Israeli and Palestinian leaders, including border demarcations and settlement withdrawals.
To this end, the PA has largely governed Palestine since 1994 through direct council elections among its citizens in areas that were defined under Israeli-Palestinian agreements. It is responsible for providing economic initiatives such as infrastructure projects in municipal services, transportation networks, healthcare services, and education systems while upholding civil rights laws that protect Palestinians from any form of discrimination based on race or religion.
Hamas Takeover (2007)
In 2007, Hamas (an acronym for Islamic Resistance Movement) took effective control of the Gaza Strip from its rival, Fatah, after winning a majority in Palestinian parliamentary elections.
In response to this defensive move, Israel declared it an “enemy entity” and authorized a series of actions against the Strip, including cutting off fuel and electricity supplies as well as banning movement into and out of Gaza with limited exceptions.
The takeover by Hamas led to significant changes in the governance of the Strip; these included restrictions on freedom of speech, severe restrictions on press freedom, increased militarization in border areas, and other controversial measures that have drawn criticism from around the world.
Gaza Wars (2008-2009, 2012, 2014, 2021, 2023)
From December 2008 to January 2009, the Middle East witnessed a 22-day military offensive in Gaza as Israel responded to rocket attacks on the town of Sderot. The conflict resulted in a tragic toll, with approximately 1,400 Palestinians and 13 Israelis losing their lives before a ceasefire was reached.
Moving forward to November 2012, tensions flared again as Israel targeted Hamas’s military chief of staff, Ahmad Jabari, leading to eight days of intense Israeli air raids on Palestinian territories. The consequences were dire, with the loss of nearly 180 lives, mostly civilians.
July to August 2014 marked a tragic episode when the kidnapping and killing of three Israeli teenagers by Hamas triggered a seven-week war. Over 2,100 Palestinians in Gaza and 73 Israelis, including 67 soldiers, tragically lost their lives during the conflict.
Fast-forwarding to May 2021, a period of heightened tension during the Muslim holy month of Ramadan escalated into violence. Hundreds of Palestinians were injured at the Al-Aqsa Mosque compound in Jerusalem by Israeli security forces. Hamas demanded the withdrawal of Israeli security forces from the compound and the Sheikh Jarrah neighborhood in East Jerusalem, leading to rocket attacks on Israel and Israeli airstrikes on Gaza. The 11-day conflict resulted in at least 260 deaths in Gaza and 13 in Israel.
Regrettably, in October 2023, the conflict took a deadly turn when Hamas launched a devastating attack on Israel, causing the loss of more than 1,400 lives and the capture of nearly 200 people. Israel responded with an intense counteroffensive and a “complete siege” of Gaza, hinting at a potential ground assault. The situation remains fluid, and the exact death toll is yet to be determined.
|
Time Period |
Event Description |
Casualties |
|
Dec 2008 – Jan 2009 |
Israel’s 22-day military offensive in Gaza following rocket attacks; 1,400 Palestinians, 13 Israelis |
1,400 Palestinians, 13 Israelis |
|
Nov 2012 |
Israel’s targeting of Hamas’s military chief; 8 days of air raids; ~180 casualties |
~180 casualties |
|
Jul – Aug 2014 |
Kidnapping of 3 Israeli teenagers by Hamas; 7-week war; 2,100+ Palestinians, 73 Israelis |
2,100+ Palestinians, 73 Israelis |
|
May 2021 |
Tensions during Ramadan clashes at Al-Aqsa Mosque, rockets, airstrikes; 260 deaths in Gaza, 13 in Israel |
260 deaths in Gaza, 13 in Israel |
|
Oct 2023 |
Hamas launches deadly attack on Israel; ongoing conflict with casualties |
casualties ongoing |
Table: Summary of Key Gaza Strip Conflicts: 2008-2023
Geography, Geology, and Climate of The Gaza Strip
The Gaza Strip is a small region of land located between Israel and Egypt, with the Mediterranean Sea to the west. Its terrain is composed mostly of low dunes and stony hills bordering sandy beaches.
Its climate is hot and arid, with very little rainfall in summer.
Natural Resources
The Gaza Strip is a region on the eastern shore of the Mediterranean that is surrounded by Egypt’s Sinai Peninsula to the south and Israel’s Negev Desert to the east. Rich in natural resources, this region has some arable land for agricultural production as well as underground deposits of oil.
Despite these opportunities for economic growth, conflict with neighboring nations has hampered development in many areas.
The primary mineral resource in Gaza comes from beneath its waters: natural gas reserves situated along its coast, estimated at over three and half trillion cubic feet by 2009. At one time, there was also potential gold mining activity near Nega’im Mountain, but unfortunately, it could not be realized due to political factors.
Elevation and Terrain
The Gaza Strip is a flat to rolling, sand and dune-covered coastal plain in the easternmost part of the Mediterranean Sea. The average elevation throughout this 140.9 mi² territory is quite low at just 141 feet above sea level.
The Gaza Strip boasts its highest elevation at Abu ‘Awdah, also known as Joz Abu ‘Auda, standing at 105 meters (344 feet) above sea level. Notably, Gaza City, the region’s largest urban center, is located on a relatively low, rounded hill with an elevation of 14 meters (46 feet) above sea level.
As such, there are no significant mountain ranges present in the Gaza Strip as they would normally be found at much higher elevations than what characterizes this region. The battled-scarred terrain is typically composed of a combination of flat land as well as waves of sand dunes with occasional patches of scrub vegetation and farmland scattered about this harsh environment.
Climate
The Gaza Strip has a temperate climate, with mild winters and dry, hot summers. Characterized by Mediterranean climates of warm to hot and dry conditions during the summer, cool wetter weather comes in winter.
According to the World Bank projections on climate change in the region, there is an expected increase in days over 35 degrees Celsius due to global increases in temperature – making life difficult for many local inhabitants who depend on outdoor work or natural resources like farming.
With no easy access to cooling technology or air conditioning units (which are banned from importation into Gaza by Israel), these changes create further hardship for people living daily lives in this area.
Natural Hazards
The Gaza Strip is prone to frequent drought due to the lack of a perennial source of surface water. It can have an immense impact on the already impoverished and densely populated area, leading to food shortages, loss of livelihoods, and drastic declines in economic conditions.
Water scarcity also poses a risk for households and businesses, making it more difficult to access clean drinking water without significant investment in infrastructure development or other expensive solutions to mitigate environmental risks associated with insufficient resources.
The geography of the region includes diverse terrain and environmental conditions that can pose natural hazards such as flooding from high rainfall levels, dust storms, sandstorms, landslides, or soil erosion on steep slopes along riverbanks.
Demographics and Religious Influence in the Gaza Strip
As of September 2023, around 2.3 million people populate the Gaza Strip, with almost 99% of them being Muslim and 1% being other religions, including Christianity.
Population and Ethnic Groups
The Gaza Strip is home to a population of approximately 2.3 million people, predominantly made up of Sunni Muslim Palestinians. This makes the area one of the most densely populated in the world, with 99% Muslims and 1% Christians.
Due to this religious split, sectarian tensions have been known to escalate into further violence on both sides. The population has fluctuated over time due to wars and other events that affected movement within and outside the region. However, it is estimated there are currently around 2.3 million resident Palestinians living in the Strip as of September 2023.
Despite some conflict between religions, Christianity remains an increasing presence among locals; many churches also freely exist across Gaza, which actively serve its congregations despite some restrictive factors posed by Hamas authorities.
Languages and Religions
In the Gaza Strip, Arabic is the official and predominant spoken language. Among other languages spoken is Hebrew by many Palestinians in addition to their native Arabic and English, which is widely understood.
The majority of people living in the Gaza Strip identify as Sunni Muslims, while there is a small minority of Palestinian Christians making up 1-2% of its population. Jews are rarer, but some have been known to live in or near cities with large Arab populations due to certain exemptions from Israel’s military occupation about movement within those areas toward Israel.
Interfaith dynamics between religions remain tense given the historical context leading up to Palestinian statehood and ongoing conflict with Israel over access rights into parts of Palestine such as Jerusalem for religious pilgrimages, both Christian and Muslim alike, leaving no room for much interfaith dialogue as yet.
Religious Compliance With Islam
Sunni Muslims predominantly inhabit the Gaza Strip, and Islamic religious courts handle legal matters related to personal status in the region. Religious compliance with Islam plays a significant role in daily life as well as within the legal system, owing largely to the overwhelming majority of Muslim residents.
There are different opinions on this subject among the people living in Gaza, including those who embrace Islam and its various interpretations entirely and those more secular-minded individuals or groups who seek ways to reconcile both national identity with faith identity without fully embracing an all-encompassing form of religiosity.
Laws applied by Sharia courts can include marriage regulations such as age requirements for grooms, divorce proceedings, and settlement disputes over land ownership.
In spite of debates regarding doctrinal differences between sects within Islam or debates about how much religion should interfere with political governance issues that come up again from time to time, there is no denying that religious compliance remains an important factor when talking about life in Gaza’s society today.
Violence Against Christians
There have been recent reports of violent incidents against the Christian community in the Gaza Strip. This includes physical violence, vandalism of churches and other religious places, as well as threats from militant groups.
According to annual reports by groups such as Human Rights Watch and International Christian Concern, these harassments are often motivated partly on religious grounds. Despite totaling only a few hundred individuals, Christians in the region face frequent hostility and persecution due to their faith and shared beliefs with Western nations.
Religion plays a big role in this region, often leading to conflicts, especially among groups with different beliefs. This makes it tough for minorities like Christians to live peacefully in areas where most people are very religious and strict about certain aspects of their faith, like prayer rituals in their families.
Governance and Control of the Gaza Strip
The political structure of the Gaza Strip is heavily influenced by Israel’s presence in the region, providing insight into how and why day-to-day life in Gaza often faces significant challenges.
Learn more about who governs the Gaza Strip and how they do it.
Hamas Government
The Palestinian Islamic organization Hamas is the governing authority in the Gaza Strip. Established in late 1987, its declared goal was to end Israel’s occupation of the territory and put forward a platform of armed struggle and social welfare.
After training their members with help from adjacent countries such as Lebanon, Jordan, Egypt, and Saudi Arabia, they participated in national elections held by Palestinian pavers in 2006.
Subsequently winning a majority vote within that region, they have since been deemed responsible for rhetorical attacks against both Israeli citizens as well as attempts at launching rockets into parts of Israeli territories.
Their victory has allowed them to become a de facto ruling power over two million Palestinians living within the region’s borders with autocratic decisions regarding political topics ranging from childcare to restrictions upon media outlets inside Palestine itself.
Parties outside present-day Gaza view their activity with apprehension as the United States has licensed them terrorists, while Russia sees the opportunity for dialogue towards resolution between themselves and Israelis suzerainship over areas thus far individually claimed file or another.
Security and Legality of Rule
The control of the Gaza Strip is a contentious issue involving competing groups and interests. Since its establishment in 1994, the Palestinian Authority has been largely left out of decision-making regarding security and governance issues within the Strip by Israel.
Israeli authorities have implemented numerous restrictions on Palestinians living in the Gaza Strip with significant influence over their movement, resources, access to water, electricity, etc as well as imposing rapid and illegal settlement expansions, which are violations of international law.
In turn, this impacts economic development (including employment opportunities) for those living in Gaza, limiting it even further since events following the 2007 Hamas takeover, where there was reported to be military hostility between Israel and Hamas forces, among other organizations present in Gaza today.
Occupation and Statehood
The occupation and statehood of the Gaza Strip have been shaped over much of the last century by various political and military dynamics. Prior to 1957, the Gaza Strip was mainly undeveloped farmland with a population of approximately 80,000 Palestinian Arabs living in several disconnected villages.
In 1967 during the Six Day War, Israeli forces occupied the Gaza Strip taking control from Egypt, which had taken it 17 years prior. Since then, Israel has held varying levels of military and/or civilian control until its unilateral disengagement beginning in 2005, which sought to restore some self-governance to Palestinians within the region.
In 2007 Hamas secured formal governance by assuming complete administrative control after winning parliamentary elections as well as a subsequent battle for power with Fatah, another major Palestinian entity vying for influence in this region.
Since this conflict erupted 16 years ago, no other entity has effectively controlled or completely cleared out any group designated as posing an imminent threat by one entity or another.
Control Over Airspace and Other Restrictions
Israel and Egypt exercise control over the airspace, territorial waters, and movement of people into and out of the Gaza Strip. Israel has imposed a strict land, sea, and air blockade on Gaza since its disengagement plan in 2005.
This has made it difficult to import goods from abroad or export anything beyond the reduced limits set by Israel. The closure also means that many Gazans are unable to leave their own country as well as get medical assistance outside of borders due to restrictions put in place by both nations.
Additionally, these measures have caused population density in the strip itself leading to impoverishment in the area through a lack of resources and economic activity further exacerbated by armed conflict between Israeli forces and Palestinian militants occurring periodically throughout recent years.
Economy and Education
The Gaza Strip has been heavily affected by the numerous conflicts it has suffered, devaluing its economy and restricting access to education.
Impact of Conflicts on the Economy
The Israeli blockade on the Gaza Strip since 2007 has had devastating effects on the region’s economy, including severe restrictions on the flow of goods and materials. This has resulted in unprecedented levels of poverty and unemployment throughout Gaza- with approximately 53% of its population living below the poverty line.
The ongoing conflicts between Israel and Hamas have only further exacerbated these economic challenges due to destruction caused by violent clashes over time. This conflict especially impacts schools as their infrastructure is often damaged or destroyed during periods of violence which hinders efforts to rebuild them as needed.
In addition, political instability created by ongoing fighting makes it much more difficult for attempts to promote economic development in the area through new investments and projects that would otherwise benefit those living there materially and financially.
Education Availability
Around 50 schools in Gaza were damaged by the Israeli Airstrike on 19 May 2021. This number is increasing day by day. For instance, here are some of the schools that have been damaged or destroyed in the recent wars:
- Jabalia Elementary Girls School in northern Gaza
- UNRWA school in al-Maghazi refugee camp, in central Gaza
The availability of education in the Gaza Strip is severely hindered by the numerous obstacles that can affect educational access. Due to the unstable political and social environment, violence, economic hardships, poverty, and social situations, accessing quality education has become increasingly challenging for students living in the area.
The United Nations Relief Works Agency (UNRWA) provides services across camps and communities in Gaza with a focus on creating an educational system accessible to all youth. However, this program still faces various challenges due to its limited resources due to financial constraints and dangers posed by conflict-related instability.
In order to ensure educational accessibility for children in the Gaza Strip, UNRWA works hard towards initiating programs such as aiding student mobility within Gamma through free school transportation service, which allows kids safe access to schools without having to worry about threats outside of the home environment or misplacement resulting from frequent Israeli airstrikes or ground clashes between opposing forces.
Health and Healthcare Statistics
The Gaza Strip has suffered from health and healthcare challenges due to the conflict and lack of resources. Infectious and communicable diseases are frequent occurrences, as well malnutrition is a significant problem.
According to medical sources, 232 Palestinians were killed in Israeli air attacks on the area in 2021 alone. The ongoing conflicts have resulted in damaging or destruction of tens of thousands of homes, including countless healthcare facilities, such as hospitals and primary care centers.
This severely strains the existing healthcare system due to limited available resources for treatment options outside severe emergencies. These resource limitations create an atmosphere where preventable health issues remain widespread due to limited access to preventive measures such as vaccinations and regular check-ups being unavailable for many people in the region.
Role of Unrwa
The UNRWA has been providing assistance to Palestine refugees in the Near East for almost 70 years. In the Gaza Strip, it operates in 8 recognized refugee camps, where many people are dependent on their services.
The UNRWA plays a crucial role in providing education and other facilities like health care to refugees living there. With insecurity and conflicts rampant in daily life, school closures happen frequently, disrupting educational services regularly.
Yet despite these obstacles, the UNRWA strives to provide quality education opportunities as well as promote values such as tolerance, cultural identity, and gender equality among young Palestine Refugees.
Culture and Sports in the Gaza Strip
Palestinian culture and sports are an important part of life in the Gaza Strip, with many demonstrations of fine art, performances, festivals, as well as recreational athletic activities.
Fine Arts
Fine arts are an integral part of life in the Gaza Strip and have played an important role in reflecting its people’s cultural heritage. From paintings to photography, literature to theatre, music, dance, and more, the vibrant artistic community within the territory has contributed to culture and identity for decades.
Despite conflicts facing Palestinians living in this highly-populated area–GC Fine Arts initiatives continue highlighting their unique voice with educational programs that encourage creative expression, collaboration, and cross-cultural learning opportunities.
With various galleries from across the city showcasing works of art created by talented local artists; diverse performance venues promoting independent musicians; films or plays illustrating Palestinian narratives; as well as other forms like dance & poetry competitions – there is no shortage of fine arts activity throughout Gaza Strip that reflect its distinct cultural values.
Moreover, these pursuits bring locals together, whether through a shared love for a particular artist or topic discussed, while also giving rise to opportunities for peaceful dialogues and negotiations between Palestinian factions within society.
Athletics
The role of athletics and sports in the culture of the Gaza Strip cannot be underestimated. Athletics have long been used as a way for Palestinians to express their identity, ambition, and pride.
The region has produced some colorful and talented athletes who have gone on to reach national and international acclaim in various sports, such as basketball, martial arts, karate, swimming, table tennis, and football.
Notable athletes from the Gaza Strip include Haneen Al-Halabiya (karate), Jamal Abu Owais (javelin throwing), and Mohammad Akram Zayed (basketball).
These exceptional accomplishments show that despite intense challenges posed by living under Israeli military occupation – lack of resources, travel restrictions, etc., Gazans can triumph against all odds with dedication, hard work, and strong willpower.
Cultural Events and Festivals
The Gaza Strip is home to a vibrant cultural scene, featuring diverse music festivals, art exhibitions, theater performances, and traditional dances. These events allow the people of the Gaza Strip to showcase their rich cultural heritage as they celebrate cultural diversity and promote peace.
Music festivals feature Palestinian musical styles such as Dabke (folklore dance) and oud (traditional string instrument). Art exhibitions allow local artists to display their artwork while giving visitors insight into Palestinian culture through visual arts.
Theater performances highlight social issues in the region and offer an alternative perspective on reality from that shown in mainstream media outlets. Traditional dances preserve long-standing traditions by showcasing ancient practices that have been passed down over generations.
Notable People and Places in the Gaza Strip
Notable figures from the area include early 20th-century Palestinian poet Ibrahim Touqan, Nobel Peace Prize Laureate Shimon Peres, Palestinian leaders such as Yasser Arafat and Mahmoud Abbas, and many more.
Significant architectural and archaeological sites located in the Gaza Strip are the Tell Rafah fortress, Khan Yunis Mosque, Al Balad House Museum in Deir el-Balah, and Sayed Dawoud Palace, ruined fortresses of Nuseirat camp, among others.
Notable Figures From History
Gaza Strip’s history is rich with influential figures from different backgrounds, all of whom have helped to shape its culture and politics. The early period was greatly impacted by the Amarna Letters, which were written in 1360 BC by local rulers seeking support from the Egyptian Pharaoh.
Sheikh Izz ad-Din al-Qassam fought against British mandatory rule alongside Arab forces during the 1920s. In 1948 he led an armed resistance to Zionism that has since become symbolically important for Palestinian nationalists; his name has been adopted by Hamas’ military wing (‘Izz ad-Din Qassam Brigades’) as a tribute to his legacy.
Furthermore, Dr Hanan Ashrawi became widely known for her involvement in the peace process between Israel and Palestine after being appointed Minister of Higher Education in July 1991 in Yasser Arafat’s government.
Current Prominent Individuals
The Gaza Strip is home to a number of prominent individuals working to bring change and progress to the beleaguered enclave.
One such example is Ismail Abdel Salam Ahmed Haniyeh, who has held several positions in the leadership of Hamas since being elected as Prime Minister of the Gaza Strip government in 2006.
He has been heavily involved with negotiations for Palestinian statehood and promoting closer Islamic unity via his regional tours.
Another individual deserving of mention is Dr. Mona El-Farra, an activist and physician from Gaza City who serves on numerous boards promoting healthcare initiatives within Palestine. She founded the “Middle East Children’s Alliance – Gaza Emergency Campaign,” which works to improve medical infrastructure through donations, and was recently named one of Forbes Magazine’s “100 Most Powerful Women” list for 2020.
Significant Landmarks and Archaeological Sites
The Gaza Strip is home to a wide range of significant landmarks and archaeological sites. These sites trace their history back thousands of years, often representing remnants from an ancient trading culture found in the region.
In 2008, the Al-Outul site located within the overhead densely populated Shati refugee camp was excavated by archaeologists, and numerous artifacts were discovered that are believed to date back 2,000 years.
Many other remarkable places have been uncovered here over the decades and yet they remain somewhat unexplored due to conflict or present living conditions in the area. Despite these challenges, some monuments like Deir al Balah Mosque are still standing strong and hold great historical significance for many.
Recent Developments and Current Situation in the Gaza Strip
Unceasing violence between Israel and the Palestinians in the Gaza Strip affects almost all aspects of daily life, painting a grim picture that can only be broken through political initiatives.
Read on to learn more about this complex region.
Ongoing Conflicts With Israel
The ongoing conflict between Israel and Palestine dates back to the Middle East War of 1967. During this war, Israel gained control over much of the area, including the Gaza Strip, from Egypt.
The Gaza Strip is a small, densely populated coastal enclave in western Asia controlled by Palestinian rulers on behalf of Hamas. Since then, disputes over borders and resources have led to periodic conflicts within this region.
There has been an increase in bilateral tension since May 2021 when armed clashes broke out between Israeli security forces and Palestinians inside the Al-Aqsa Mosque compound in Jerusalem, which resulted in widespread protests, violence, air strikes conducted by Israeli Forces across Gaza as well as launches of rockets from militants based in Gaza into Israeli territory.
Attempts at Reconciliation With Fatah
Over the past few years, a number of attempts have been made to reconcile the two Palestinian factions, Fatah and Hamas. These efforts were sparked by an agreement between them in October 2017 and supported by Egypt-leading talks in Cairo in 2018.
Algiers sponsored reconciliation talks that same year, resulting in further tentative agreements. Despite these steps forward, however, the unification of Hamas and Fatah administrations remains unfinalized due to longstanding disagreements over several issues, such as shared security control and financial obligations for Gaza’s civil servants.
As such, the situation within Palestine is deemed a frozen conflict with no clear resolution on the horizon yet.
The complexity of attempting to achieve peace or stability between two conflicting entities cannot be underestimated especially when it comes to brokering an agreement between Hamas and Fatah – charged elements who represent opposing visions regarding how Palestinians should proceed politically going forward.
Impact of Conflicts on Daily Life in Gaza
The recent developments in the long-running conflict between Israel and Gaza have had a wide-reaching impact on the daily lives of people in Gaza. At least 4,651 Palestinians have been killed and 14,245 wounded as a result of Israeli attacks.
These attacks have led to significant destruction and damage to infrastructure and civilian amenities such as schools and hospital blasts in Gaza. The ongoing violence has also exacerbated pre-existing issues caused by population density which is among the highest anywhere in the world due to restrictions placed on imports or exports from Gaza that cause severe poverty among many of its residents.
This led to UN Secretary-General Antonio Guterres’ office warning that an all-out war could erupt unless urgent steps are taken towards reconciliation. Thus it is clear to see that these Palestinian civilians suffer immensely due to this deteriorating situation.
Latest News and Updates
The Israel-Hamas conflict in the Gaza Strip is an ongoing situation with frequent updates. In May 2021, Hamas launched a broad invasion of Israeli territory, triggering air raid sirens in multiple cities and towns across Israel, warning of attacks.
Since then, at least 232 Palestinians have been killed as a result of Israeli air strikes targeting the Gaza Strip. The attack made by Hamas is considered to be one of the broadest invasions in 50 years between both sides, while there have been continuous attempts for reconciliation between Fatah’s Palestinian Authority and Hamas’ government to reach peace.
Currently, international organizations are also providing assistance to mitigate any potential long-term damage arising from this tragic situation as many innocent civilians continue to suffer from the impact of violence due to daily life disruptions under occupation and constant shelling.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Read the most frequently asked questions regarding the Gaza Strip below.
1. Where Is the Gaza Strip?
The Gaza Strip is located along Israel’s southwestern coast in the eastern part of the Mediterranean Sea. It is bordered by Egypt to its southwest and Israel to its east and north.
2. What Are Some Facts About the Gaza Strip?
The Gaza Strip has a population of approximately 2.3 million people living over an area of 365 square kilometers. It has been occupied since 1967, when Israel gained control over it from Egypt following the Six-Day War.
3. How Did Israel Gain Control Over The Gaza Strip?
Israel took control of Palestine, including The West Bank, during the Six Day War in 1967 with help from America providing weapons for both air and sea assistance and support for military personnel involved in taking control of territories within Palestine as well as other bordering countries around it like Syria, Jordan, etc.
4. Is There Still Conflict Between Israelis & Palestinians Now That They Share Authority Over The West Bank & Gaza Strip?
Yes, although Israelis have taken control over both locations, recent conflicts such as wars that occurred between them and Hamas forces led to several disputes regarding their shared resources like land rights or refugee policies, which creates tension and many sustained factors contributed towards violence today in those two areas.
Final Words
Despite years of conflict and instability, the people of the Gaza Strip continue to retain a strong sense of hope for their future. Despite frequent bouts of violence that have at times reached levels unseen in recent years, the residents of Gaza remain resilient in their pursuit of opportunities for peace and stability.
International organizations like UNRWA are critical players in helping to provide aid and support to those in need in this region on what is often referred to as the world’s largest prison.
Recent attempts at reconciliation between Hamas and Fatah have been met with some success, yet protests, violence, and border closures by Israel still plague everyday life within its borders while new challenges arise daily, given heightened tensions with neighboring countries.
Despite these issues, which loom large over Israeli-Palestinian relations, there remains optimism that both sides can reach an agreement allowing Palestinians living not only inside but also outside of the Gaza Strip more freedom over their lives and communities.