In 2026, the corporate “skills gap” is no longer a distant warning—it is an $8.5 trillion global economic hemorrhage. As AI automates routine tasks, the desperate race to reskill 1 billion workers has forced a radical evolution in EdTech: moving beyond trivial “leaderboards” to high-stakes, AI-driven simulations that mimic real-world crises. Gamified learning has matured into a behavioral engine, using risk, rewards, and consequence-based progression to hardwire decision-making under pressure rather than passive content consumption. This is not just about making learning fun; it is about making workforce survival scalable.
The Structural Shift: From “Chocolate-Covered Broccoli” to AI-Driven Ecosystems

To understand the current surge in high-fidelity gamified learning, we must acknowledge the failures of the past decade. In the early 2020s, “gamification” in the corporate sector was often derisively termed “chocolate-covered broccoli.” Organizations slapped badges, points, and generic leaderboards onto dry, click-through compliance PDFs, expecting a magical boost in engagement. It worked briefly—until the novelty wore off, resulting in what industry analysts by 2024 termed “Gamification Fatigue.”
However, the landscape in 2026 has shifted dramatically due to two converging forces: the urgency of the skills crisis and the maturity of Generative AI and Spatial Computing. We are no longer talking about earning a gold star for watching a video. We are seeing the rise of “Serious Games”—complex, adaptive environments where a cybersecurity analyst defends against a live, AI-generated ransomware attack, or a sales director navigates a volatile negotiation with an emotionally responsive digital avatar.
The “why” is simple: Passive learning has failed to keep pace with the half-life of professional skills, which has shrunk to less than five years. The new ecosystem is defined by “Learning Twins”—digital counterparts to employees that track not just completion, but behavioral adaptation.
The Shift from Legacy to Next-Gen Gamification (2020 vs. 2026)
| Feature | Legacy Gamification (2015-2023) | Next-Gen Gamified Learning (2026) |
| Core Mechanic | Points, Badges, Leaderboards (PBL) | Adaptive Scenarios, AI Simulations, Role-Play |
| Technology | Static LMS, Standard Web Modules | Generative AI, VR/AR, Spatial Computing |
| Feedback | “Correct/Incorrect” after quiz | Real-time behavioral analysis & coaching |
| Personalization | Segmented by Department | Individualized by AI “Learning Twin” |
| Primary Goal | Completion Rates | Skill Application & Behavioral Change |
| Engagement | Extrinsic (Rewards) | Intrinsic (Mastery & Flow) |
The Economics of Competence: ROI, The Skills Chasm, and the $8.5 Trillion Problem
The sharpest edge of the skills gap lies in technical proficiency. With the World Economic Forum’s Future of Jobs Report highlighting that 50% of all employees need reskilling, companies are finding that traditional lectures cannot teach reaction time. The economic argument has flipped due to the high cost of attrition and incompetence.
The “Engagement Paradox” is the enemy of traditional L&D (Learning and Development). Completion rates for standard Massive Open Online Courses (MOOCs) hover around 15-20%. In contrast, well-designed gamified pathways in 2026 are seeing completion rates upwards of 85-90%. Furthermore, the data retention is superior. The “Forgetting Curve”—the theory that we lose 90% of what we learn within a week—is flattened by the “loop” mechanic of games: Try, Fail, Feedback, Retry.
Cybersecurity provides the clearest ROI case study. A lecture can define “phishing,” but it cannot train the nervous system to spot a sophisticated deep-fake CEO voice authorization. Gamified “Cyber Ranges”—virtual environments that simulate corporate networks—allow teams to battle red-team AI bots. These are not quizzes; they are war games.
Companies utilizing simulation-based training for technical roles report a 40-60% reduction in “time-to-proficiency” compared to traditional video-based modules. When the cost of a data breach averages over $4 million, the ROI of a $50,000 gamified training license becomes mathematically undeniable.
ROI Analysis of Corporate Training Modalities (2026 Data)
| Metric | Traditional Classroom/Zoom | Standard eLearning (Video) | Gamified AI Simulation |
| Avg. Cost Per Learner | High (Travel/Time) | Low | Medium (Software License) |
| Knowledge Retention (30 Days) | 10-20% | 20-30% | 75-80% |
| Avg. Engagement Time | High (Forced) | Low (Passive) | High (Active) |
| Scalability | Low | High | High |
| Time to Proficiency | Baseline | 10% Faster | 40-60% Faster |
The Psychology of Immersive Learning: Why VR and “Flow” Work Where Lectures Fail?
Perhaps the most surprising trend in 2026 is the dominance of gamification in soft skills training. Empathy, leadership, and conflict resolution were historically considered un-teachable via software. Enter VR and AI avatars. “Empathy Engines” now place managers in the shoes of a disgruntled employee or a dissatisfied customer.
In these high-fidelity VR simulations, the “game” is to de-escalate a tense situation. The system tracks voice tone, eye contact (via headset sensors), and word choice. This utilizes the psychological state of “Flow”—a zone of energized focus where learning happens fastest. Because the stakes are simulated, the fear of failure is removed, allowing for rapid experimentation.
Expert Perspective: Dr. Elena R., an Organizational Psychologist, notes, “We are seeing a 4x faster confidence improvement in soft skills when learners practice with avatars compared to role-playing with peers. The avatar doesn’t judge, allowing the learner to fail safely and try again immediately.”
This is critical because, as AI automates technical coding and data entry tasks, the human-centric skills of management and negotiation become the premium currency of the 2026 workforce. The Global Soft Skills Training Market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 34.5% through 2029, fueled entirely by these immersive technologies.
The 2026 Corporate Skills Gap Snapshot
| Skill Cluster | Shortage Severity | Gamification Suitability | Primary Training Method |
| AI & Big Data | Critical | High | Coding challenges, Sandbox environments |
| Cybersecurity | Critical | Very High | Red Team/Blue Team War Games |
| Leadership/Mgmt | High | High | VR Role-play, Branching Scenarios |
| Sustainability/Green Skills | Medium | Medium | Resource Management Sims |
| Creative Thinking | High | Low | Collaborative Workshops (Hard to gamify) |
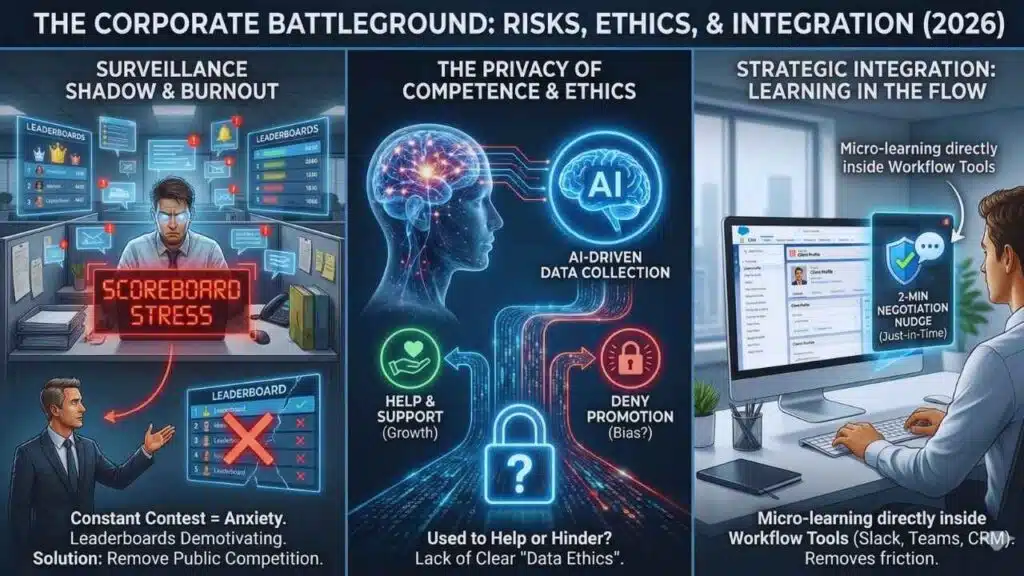
The Corporate Battleground: Winners, Losers, and the Ethics of Surveillance
No analysis is complete without examining the risks. The “gamification” of work has a dystopian shadow. As learning platforms become more integrated with daily workflow tools (Slack, Teams, Salesforce), the line between “training” and “surveillance” blurs.
Gamification Fatigue & Burnout:
There is a limit to how much “fun” an employee can handle. When every task—from logging sales calls to compliance training—is turned into a contest, it creates a state of constant, low-grade anxiety. Employees in 2026 are reporting “Scoreboard Stress,” where the public visibility of their learning progress pits them against colleagues in an unhealthy way. Mark T., CIO of a Fortune 500 Tech Firm, recently admitted, “We stripped out the leaderboards. They were demotivating our bottom 50% and creating arrogance in our top 10%. We kept the simulations but removed the public competition.”
The Privacy of Competence:
AI-driven systems collect vast amounts of data on how an employee thinks. If a manager struggles with a decision-making simulation, is that data used to help them, or is it secretly used to deny a promotion? The lack of clear “Data Ethics” in corporate L&D is a ticking time bomb.
Strategic Integration:
The final piece of the 2026 puzzle is where this learning happens. The trend is “Micro-learning in the Flow of Work.” Gamified nudges now appear directly inside the software employees use. For example, a salesperson opening a CRM record for a difficult client might get a 2-minute “mini-game” challenge on negotiation tactics specific to that client’s industry before they make the call. This “Just-in-Time” training removes the friction of scheduling workshops.
Future Outlook 2030: The Metaverse, Neural Interfaces, and Continuous Adaptation
What happens next? As we look toward 2027 and 2030, three major trends will define the next phase of EdTech.
- The Metaverse Standard: While the “consumer” Metaverse has struggled, the “corporate” Metaverse for training is solidifying. We expect a standardized protocol for training credentials where a “Level 5 Safety Certificate” earned in a VR simulation is verifiable via Blockchain and portable between employers.
- Brain-Computer Interfaces (BCI): Early pilots are already using non-invasive headbands to measure “cognitive load” during training. If a game is too easy, the system detects boredom in the brainwaves and ups the difficulty. If the user is overwhelmed, it throttles back. This is the ultimate frontier of personalization.
- The “Chief Skills Officer”: The strategic importance of closing the skills gap will elevate L&D leaders to the C-Suite. The ability to “gamify” the workforce’s evolution will be a key competitive advantage for CEOs.
Final Thoughts
Is EdTech finally bridging the corporate skills gap? Yes, but only for those who look past the buzzwords. The companies winning in 2026 are not the ones giving out digital stickers; they are the ones building sophisticated, AI-backed flight simulators for their business. They recognize that in an era of rapid disruption, the ability to learn faster than the competition is the only sustainable advantage. Gamification, when executed with depth and strategic intent, provides the acceleration engine required to keep pace.