Cybersecurity threats are constantly changing, forcing financial institutions to stay ahead with stronger defenses. As more customers rely on digital banking, the risks associated with cyberattacks, identity theft, and fraud continue to grow.
It is imperative that banks and other financial service providers adjust by implementing cutting-edge security measures. These measures should safeguard private data while preserving a flawless customer experience.
This article discusses how financial institutions are adapting to evolving cybersecurity threats.
Strengthening Authentication Methods
One primary way financial institutions address security concerns is by improving authentication methods. Conventional password and username combinations are no longer adequate to stop unwanted access. With 98% of firms using multi-factor authentication [MFA] globally, it has become the norm.
According to Statista, SMS time-based one-time passwords [TOTPs] were the most commonly used MFA, implemented by nearly 56% of the companies. There are many other MFA methods used by organizations, including:
- Email TOTPs
- Push notifications on personal mobile devices
- SMS OTPs
- Email OTPs
- QR codes scanning from a mobile device, etc.
The Need to Go Beyond MFA
Many threat actors can overcome MFA security measures through means like hacking into a mobile device. Therefore, financial institutions are integrating advanced verification technologies, including biometric authentication and facial recognition, to further enhance security. However, cybercriminals are using technology like AI deepfake to counter these measures.
An article from The Register also states that cyberattackers steal IOS users’ face scans to access their mobile banking accounts. To cope with such threats, banks need to go beyond simple biometric verification, and a liveness detection solution is the right answer. Active liveness detection is becoming a significant component of financial institutions, helping to ensure that a real person is attempting to access an account.
As AU10TIX states, this technology analyzes subtle facial movements, blinking patterns, and other indicators to confirm the presence of a live user. It also ensures that financial institutions adhere to the most stringent compliance postures.
Beyond authentication, fraud detection systems are becoming more sophisticated. Artificial intelligence and machine learning models analyze transaction patterns in real time, flagging any unusual activity. These automated systems help prevent fraud by identifying suspicious behavior before it leads to financial loss. In order to reduce risks and maintain client trust, institutions are making significant investments in these technologies.
Addressing Emerging Cyber Threats
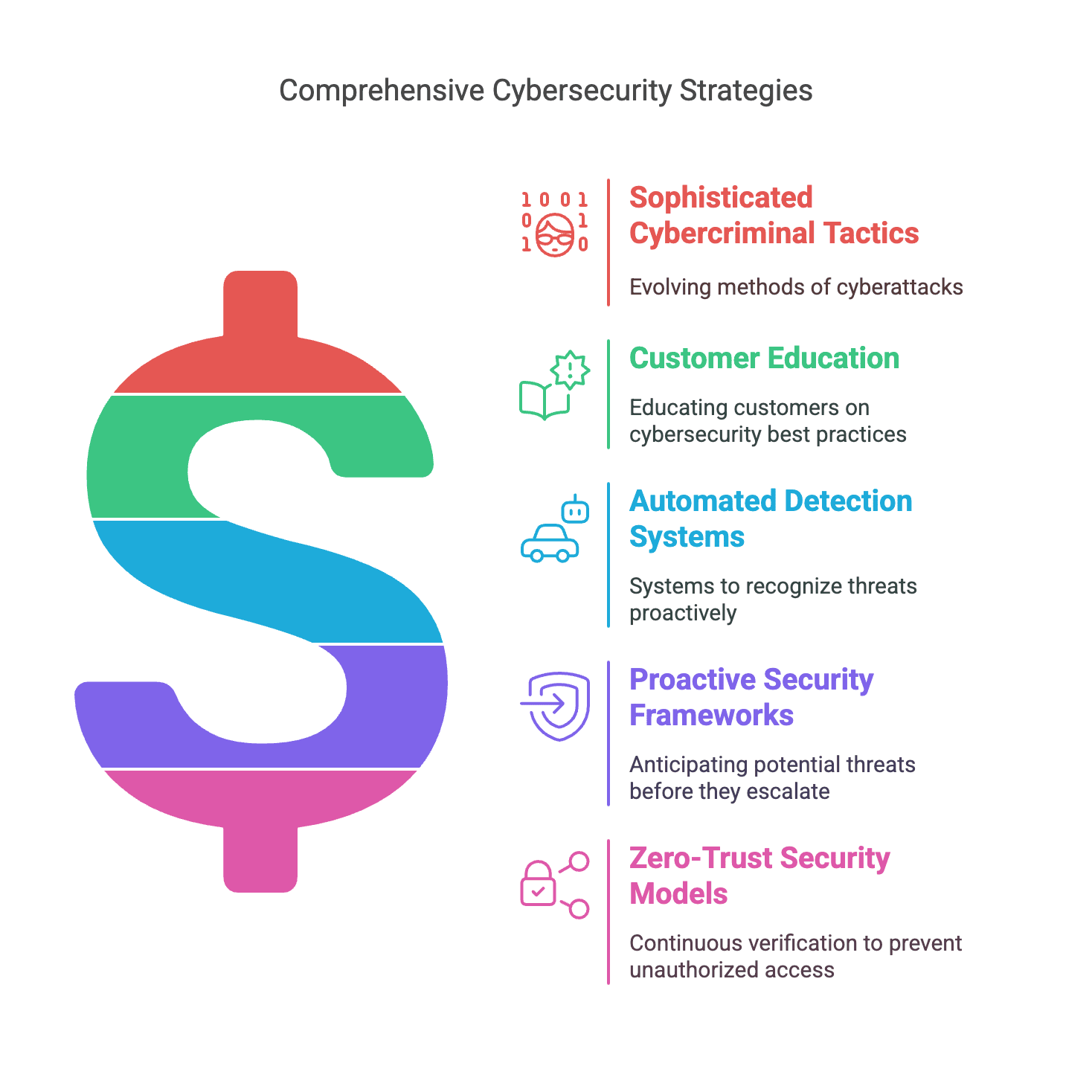
As technology advances, so do cybercriminals’ tactics. Phishing attacks, ransomware, and social engineering schemes are becoming more sophisticated. As noted in a CNBC article, these attacks are now spreading beyond emails. Cyberattackers also target people via SMS and other forms of personal communication. The number of cyberattacks is also on the rise, with phishing rates increasing by 61% in 2022 compared to the previous year.
As a result, customers and institutions find it more difficult to discern between authentic and fraudulent transactions. Banks are responding by educating customers on cybersecurity best practices and deploying automated detection systems that recognize threats before they escalate.
Financial organizations are also improving their incident response strategies. Rather than relying on reactive measures, they are shifting toward proactive security frameworks that anticipate potential threats. Real-time monitoring and rapid response teams play a key role in mitigating cyber risks.
Additionally, many institutions are adopting zero-trust security models. Data shows that over 66% of companies had implemented zero trust policies in 2024. According to this policy, no user or device should be trusted by default. This approach requires continuous verification, reducing the likelihood of unauthorized access.
Regulatory Compliance and Industry Collaboration
Regulatory bodies continue to introduce new cybersecurity standards, requiring financial institutions to implement stronger security protocols.
Adhering to these laws may preserve a high degree of security while safeguarding customer data for banks and other financial institutions. Updating encryption techniques, performing frequent security audits, and ensuring third-party providers adhere to stringent security procedures are all necessary to meet these criteria.
Collaboration across the financial sector is also crucial in combating cyber threats. Banks and fintech companies are sharing threat intelligence to identify new attack patterns and strengthen collective defenses. Industry-wide initiatives help institutions respond more effectively to large-scale cyber incidents and prevent breaches that could impact the entire financial ecosystem.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How do financial institutions protect customer data from insider threats?
While external cyberattacks are a major concern, insider threats—whether intentional or accidental—can also put customer data at risk. Financial institutions use strict access controls, employee monitoring systems, and data encryption to minimize these risks. Regular cybersecurity training ensures that employees understand security protocols and recognize potential threats.
2. How can cloud security contribute to the safety of financial data?
As more financial institutions migrate to cloud-based infrastructure, cloud security has become a priority. Banks use secure cloud environments with encryption, multi-layer authentication, and continuous monitoring to prevent unauthorized access. Compliance with industry regulations ensures that cloud providers follow best practices in data protection.
3. How do financial institutions handle cybersecurity threats related to mobile banking?
Mobile banking introduces unique security risks, including app-based malware and unauthorized access from stolen devices. Banks implement features such as encrypted connections, biometric authentication, and device fingerprinting to enhance security. Customers are also encouraged to enable security features like two-factor authentication and keep their apps updated.
Financial institutions need to continue to be flexible in their approach as the cybersecurity landscape changes. Developments in quantum encryption, blockchain security, and artificial intelligence are anticipated to shape the future of financial cybersecurity. As new threats emerge, these institutions must stay ahead by adopting innovative solutions while ensuring that customer convenience is not compromised.
Financial institutions can build a more secure digital environment by integrating advanced authentication technologies, strengthening fraud detection systems, and fostering industry collaboration. Although cybersecurity is a constant problem, the financial industry can continue to adapt and safeguard customers and companies by implementing the correct procedures.