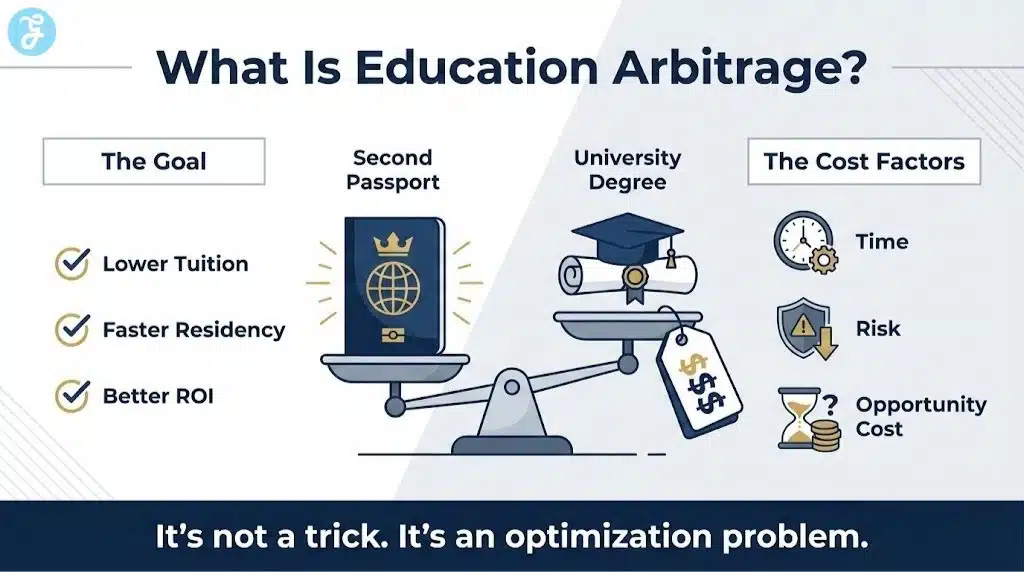
Paying international tuition can feel like getting charged twice, once for the degree and again for the passport you hold. The idea behind education arbitrage is simple: you look for legal, realistic ways to change your tuition classification, access subsidized seats, or qualify for local fee schedules. In some cases, a second passport can be one of the biggest levers because it can change how a country views you for tuition, funding, and residency pathways.
This guide explains how Cheaper International Tuition With Second Passport can work in practice, where it usually does not, and how to evaluate it without falling for misleading shortcuts. It is not about gaming systems. It is about understanding how countries set fee categories and using lawful status options to plan smarter.
How Universities Decide Your Tuition Category
Most people assume tuition is based on citizenship alone. That is sometimes true, but many systems use a mix of rules.
Common Factors Include:
-
Citizenship (nationality for fee status in some regions)
-
Residency (lawful residence, duration, and continuity)
-
Ordinary residence or domicile (where you truly live and intend to remain)
-
Immigration status (PR, long-term residence, specific visa types)
-
High school location (some countries link fees to where you completed prior study)
-
Economic area membership (for example, EU or EEA based frameworks)
A second passport can matter when the fee rules are tied to a citizenship group, or when it helps you secure a residence status faster that then leads to local fees.
Where A Second Passport Helps Most
A second passport tends to have the strongest tuition impact in four situations:
- Regional citizenship blocs
If a country charges lower tuition to citizens of a recognized bloc, a passport that places you inside that bloc can unlock local or near-local fees. -
Faster pathway to residence
Some passports make it easier to move, work, or remain legally. That can shorten the time to qualify for resident fee status where residency duration matters. -
Access to public funding and student support
Even if tuition does not drop, your net cost can fall if your new status opens access to grants, subsidized loans, or public scholarships. -
Expanded university options and admissions routes
Some programs reserve seats or have different evaluation pipelines for certain citizenship categories. That can indirectly reduce costs by enabling admission to more affordable public institutions.
Where A Second Passport Usually Does Not Help
It is just as important to know the limits.
A second passport often does not reduce tuition when:
-
Fees are set primarily by residency history, not citizenship
-
“Home fee” requires multi-year ordinary residence in the country, often before the course starts
-
Your new passport does not change your eligibility for the key category (for example, you still live outside the region that defines local fees)
-
The country has a simple split: domestic residents vs everyone else, regardless of passport
In plain terms, a second passport can open doors, but it rarely replaces the need for real residence if the system is residence-driven.
A Practical Definition Of Education Arbitrage
Education arbitrage is not a trick. It is an optimization problem.
You are balancing:
-
Total degree cost (tuition + living)
-
Time to eligibility (how long until your status changes fees)
-
Opportunity cost (income you forego while waiting)
-
Risk (rule changes, processing delays, policy shifts)
-
Fit (academic quality, language, career outcomes, migration options)
The goal is not “lowest sticker price.” The goal is the best outcome per dollar, with predictable rules.
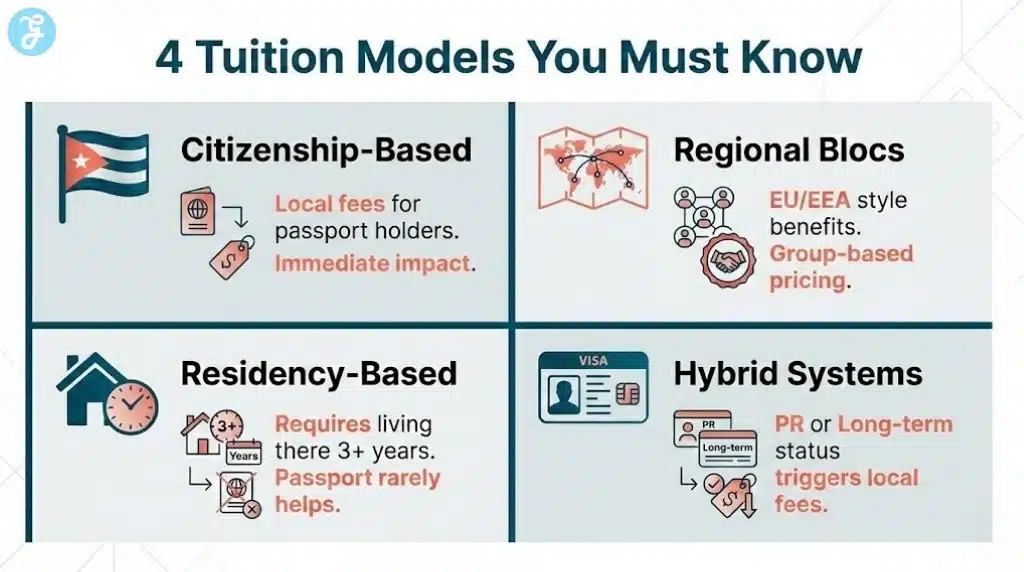
Tuition Models That Make Second Passports Valuable
Different countries use different models. Here are the most common ones you will encounter.
Model 1: Citizenship-Based Local Fees
Some systems strongly favor citizens for public university pricing. In these cases, a second passport may create an immediate or near-immediate impact.
What to look for:
-
Public universities with standardized national fees
-
Fee tables that explicitly list citizen categories
-
Government-set tuition caps for nationals
Reality check: Many countries still require residency, even for citizens, to avoid “passport-only” fee shopping.
Model 2: Regional Bloc Benefits
Regional frameworks can create large tuition differences. If the fee rules recognize a bloc, the right second passport can shift you into that favored group.
What to look for:
-
“EU, EEA, Swiss” or similar categories
-
Equal treatment provisions in the national education policy
-
Separate fee schedules by nationality group
This is one of the clearest routes where Cheaper International Tuition With Second Passport can be realistic, especially when the bloc membership is directly referenced in fee status rules.
Model 3: Residency-Based Home Fee Status
This is extremely common. The rule is often: you pay home fees only if you have lived in the country for a specific period before the start date, and your residence was not primarily for education.
What to look for:
-
“Ordinarily resident for X years”
-
“Not solely for the purpose of full-time education”
-
“Settled status, permanent residence, or equivalent”
In this model, the second passport is useful mainly because it makes lawful residence easier to obtain and maintain.
Model 4: Hybrid Systems With Immigration Status Triggers
Some countries treat permanent residents similarly to citizens for tuition, even if they are not citizens.
What to look for:
-
PR categories that qualify for domestic rates
-
Long-term residence permits that trigger local fees
-
Special rules for refugees, protected persons, or long-term permit holders
Here, a second passport can still help indirectly, by enabling a more favorable immigration path.
A Simple Decision Framework
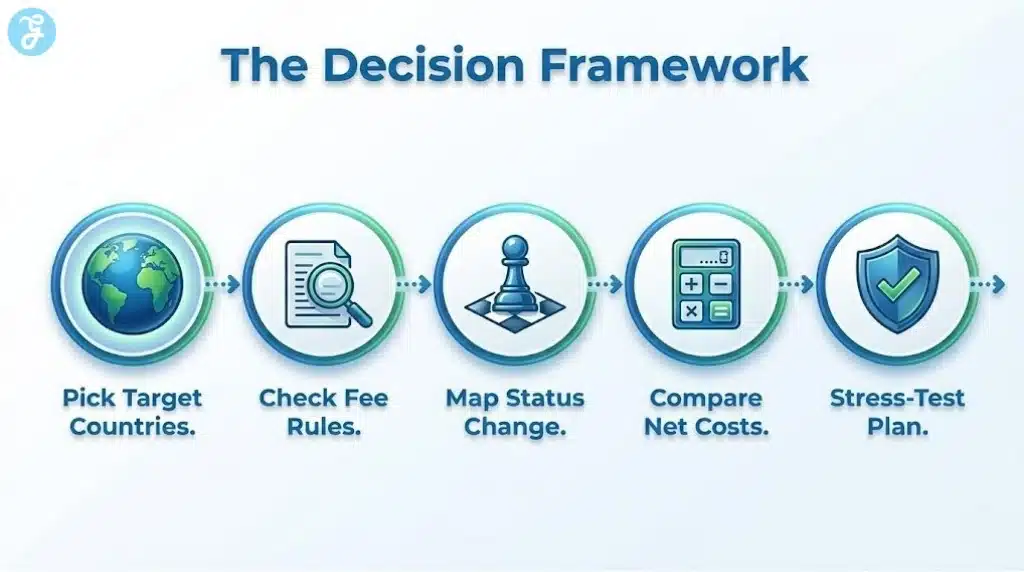
Before spending money on any citizenship plan, run the decision like a business case.
Step 1: Pick Your Target Countries And Degree Level
Fee rules can vary by:
-
Undergraduate vs postgraduate
-
Public vs private institutions
-
On-campus vs online
-
Professional degrees (medicine, law) vs standard programs
Shortlist 2 to 4 countries and 6 to 12 universities.
Step 2: Identify The Fee Status Rule That Applies
Do not rely on marketing pages. Find the university’s fee status policy, then confirm it with the admissions or fee status team.
Capture:
-
Categories and their definitions
-
Required documents
-
Cutoff dates for qualifying status
-
Appeal process
Step 3: Map Which Status Change Actually Moves The Needle
Ask a blunt question: “What would have to be true for me to pay the local fee?”
Possible answers:
-
“You must be a citizen”
-
“You must be a permanent resident”
-
“You must be ordinarily resident for 3 years”
-
“You must live in the country and meet domicile requirements”
Only then consider whether a second passport affects that answer.
Step 4: Compare Net Cost, Not Just Tuition
Add:
-
Rent, health insurance, transportation
-
Visa and legal costs
-
Lost income during any waiting period
-
Currency risk
-
Ability to work part-time
Step 5: Stress-Test For Rule Changes
Education and immigration policies change. Your plan should still work if:
-
Processing takes 6 to 12 months longer than expected
-
Fee rules tighten residency requirements
-
Work limits on student visas change
Common Pathways People Consider
This section is about patterns, not promises. Eligibility and outcomes depend on your profile, the country, and the exact program rules.
EU Citizenship And Studying In Europe
For many people, EU citizenship is the most discussed lever because it can influence:
-
Freedom of movement and residence in many European countries
-
Administrative friction for enrollment and work rights
-
Eligibility for certain public fee schedules in specific contexts
However, “EU passport equals free tuition everywhere” is an oversimplification. Some countries have low public fees for most students regardless of passport, while others have complex residency conditions.
If your plan is Europe, your key question is: does the target country price primarily by citizenship group, residency history, or both?
Ancestry-Based Citizenship Routes
Some people qualify for citizenship through descent. When it is available, it can be more straightforward than investment routes.
Potential advantages:
-
Often lower cost than other routes
-
Strong passports with broad mobility
-
Long-term family asset, not just a study tactic
Potential limitations:
-
Processing timelines can be long
-
Documentation requirements can be strict
-
Tuition benefits still depend on each country’s fee status rules
Citizenship By Investment And The Tuition Myth
Investment citizenship programs can offer mobility, but tuition outcomes are not guaranteed. In many education systems, residency and ordinary residence matter more than passport.
If you are considering this route, treat it as a mobility and long-term optionality decision first. Consider tuition reduction a possible bonus only if you can tie it to clear fee rules.
Residency First, Citizenship Later
Sometimes the better route is not a second passport at all. It is a legal residency strategy that leads to local fees.
Examples include:
-
Skilled work pathways leading to PR
-
Family-based migration
-
Long-term residence permits
-
Study-to-work routes that eventually trigger domestic fee status for a second degree
This is slower, but can be more predictable where home fee status is tied to residence.
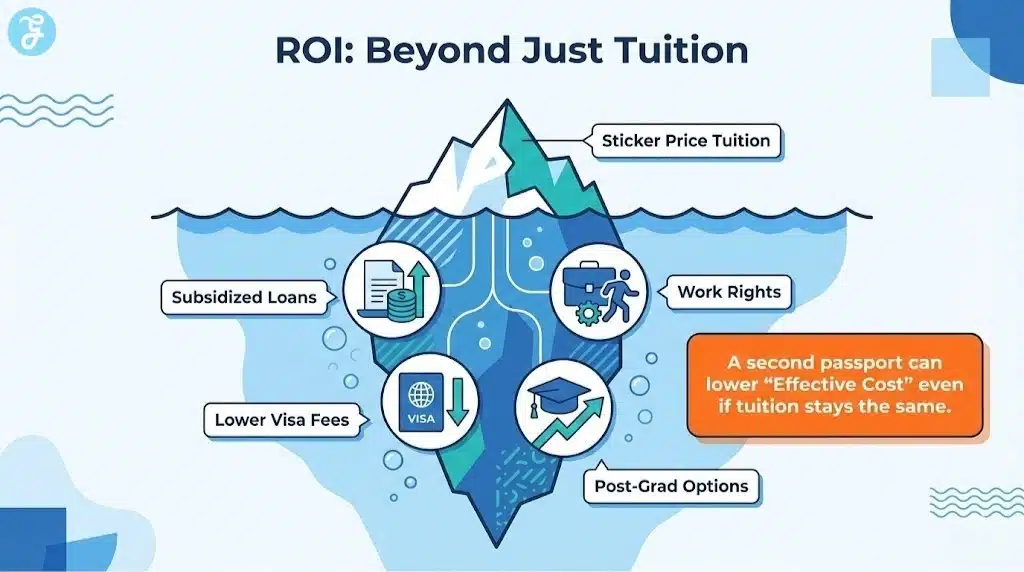
How Second Passports Reduce Costs In Real Life
Not every benefit shows up as a tuition line item. Here are the main cost channels.
1) Lower Sticker Tuition In Certain Systems
This is the most obvious scenario. It happens when the fee schedule explicitly gives locals or certain nationality blocs lower tuition.
If your second passport moves you into that category, you may see immediate savings.
2) Access To Subsidized Student Loans Or Grants
In some places, citizens and long-term residents can access public student finance. That can dramatically reduce upfront burden.
Even when tuition stays similar, funding access can lower your effective cost and improve cash flow.
3) Reduced Visa Costs And Paperwork Overhead
A “better” passport can reduce:
-
Visa application fees
-
Renewal costs
-
Required financial proof
-
Time spent navigating complex compliance
That does not sound like tuition savings, but it often adds up.
4) More Working Rights While Studying
If your status gives you stronger work rights, your net cost can fall because you can earn more without violating rules.
This benefit is meaningful only if:
-
The local job market supports student work
-
Wages are sufficient relative to living costs
-
Work rights are clearly defined and enforceable
5) Better Post-Study Options That Improve ROI
Education arbitrage is also about outcomes. If a second passport improves your ability to stay and work after graduation, your return on investment can rise, even if tuition only falls modestly.
At around this point, it is worth restating the focus: Cheaper International Tuition With Second Passport is most reliable when it is backed by a published fee status rule, not a general belief about passports.
A Comparison Table You Can Use
Use this as a planning template. Replace entries with your target countries and universities.
| Decision Factor | What To Check | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Fee Status Basis | Citizenship, residency, or both | Determines whether a second passport is decisive |
| Residency Duration | 1, 2, 3+ years ordinary residence | Many “home fee” rules are time-based |
| “Not For Education” Clause | Does residence for study count? | Some rules exclude time spent as a full-time student |
| PR Equivalence | Does PR pay domestic fees? | PR may be a faster lever than citizenship |
| Funding Eligibility | Grants, loans, subsidies | Can reduce net cost more than tuition alone |
| Work Rights | Hours allowed, wage levels | Helps offset living expenses |
| Processing Timelines | Passport or residence timeline | Impacts start dates and opportunity cost |
| Policy Volatility | Recent rule changes | Your plan should survive updates |
Hypothetical Case Studies
These are simplified examples to show how planning logic works.
Case Study A: Bloc Citizenship Unlocks Local Fees
A student targets a public university system where fee categories explicitly list a regional citizenship group with lower tuition. The student qualifies for a second passport in that group through ancestry.
Outcome pattern:
-
Tuition drops at enrollment, or after meeting a minimal residence condition
-
Visa friction decreases
-
The student gains access to more universities with similar pricing
Risk:
-
Some programs still require residence in the country, not just nationality
-
Competitive programs may still have limited seats
Case Study B: Residency Rules Override Citizenship
A student obtains a second passport that improves mobility, then applies to a country where “home fee” requires three years of ordinary residence, not primarily for study.
Outcome pattern:
-
Tuition does not drop immediately
-
The passport helps the student move earlier, work legally, and begin the residence clock
-
The student targets a later start date or a second degree for home fee eligibility
Risk:
-
Delayed payoff
-
Residence conditions can be strict and heavily documented
Case Study C: PR Strategy Beats Passport Strategy
A student chooses a pathway where permanent residence qualifies for domestic tuition. Instead of buying or pursuing a second passport, they plan a work-linked migration route first.
Outcome pattern:
-
Domestic tuition becomes available after PR
-
Funding options may improve
-
The plan is slower but can be clearer
Risk:
-
Immigration pathways can be competitive
-
PR timelines may shift
Documents And Proof You Will Likely Need
Fee status decisions are documentation-heavy. Plan for:
-
Passports, national IDs, and travel history
-
Residence permits, visas, and entry stamps
-
Lease agreements, utility bills, tax records
-
Employment contracts or payroll records
-
Proof of where you lived for specific dates
-
Prior education transcripts showing location and dates
Keep clean records. Fee status appeals often fail due to missing evidence, not because the student was truly ineligible.
Mistakes That Cause People To Overpay
-
Assuming citizenship automatically equals home fees
Many systems tie home fees to ordinary residence, not nationality. -
Ignoring cutoff dates
Eligibility is often measured on a specific date before the course starts. -
Not reading the “purpose of residence” clause
If the rule says you must not have been living there mainly for education, student residence may not count. -
Buying a passport without confirming the policy
Always confirm the exact fee status rule for your target university. -
Underestimating living costs
A cheaper tuition country can still be expensive to live in, especially in major cities.
Ethics, Compliance, And Reality Checks
Education systems are designed to subsidize residents and taxpayers. Countries try to prevent “passport-only” tuition shopping, which is why residency and ordinary residence tests exist.
Your safest approach is:
-
Be truthful in applications
-
Avoid any plan that involves misrepresenting residence
-
Treat tuition status as a compliance area, not a hack
If you are unsure, ask the university’s fee status team for a written assessment. In many cases, a short email can prevent a costly mistake.
A Step-By-Step Action Plan
1) Build A Two-Column Shortlist
Column A: countries and universities that already have low tuition for most students.
Column B: countries where your status might change the tuition category.
2) Get Written Confirmation
Send a concise message to each university:
-
Your citizenships
-
Where you have lived for the past 3 to 5 years
-
Your immigration status in the target country
-
Your planned start date
Ask what fee category applies and what would need to change for a lower category.
3) Choose The Highest Certainty Route
Prioritize:
-
Clear policy language
-
Minimal waiting periods
-
Stable immigration pathways
-
Strong academic outcomes for your field
4) Lock Your Timeline
Work backward from intake deadlines. Include buffers for:
-
Passport processing
-
Residence permits
-
Document legalization and translation
-
Fee status assessments
5) Calculate A Conservative Budget
Use worst-case assumptions for:
-
Exchange rates
-
Rent inflation
-
Processing delays
-
Additional semester costs
When This Strategy Makes Sense
Education arbitrage using a second passport makes the most sense when:
-
Your tuition savings are large and clearly rule-based
-
The passport also improves mobility, work rights, or long-term options
-
You can meet any residence conditions without derailing your career timeline
-
You have a backup plan if rules tighten
It makes less sense when the passport is expensive, the tuition benefit is uncertain, and the residency requirements are long and strict.
The Bottom Line
If you approach it carefully, Cheaper International Tuition With Second Passport can be a real strategy, but it is not a universal shortcut. The key is to start with the fee status rule, then work backward to the status change that the rule actually recognizes.
A passport can open doors. The tuition discount usually comes from what you do with that passport, where you live, and how the university defines “local” in its policy. Plan with documents, timelines, and clear written confirmations, and you will avoid the costly myths that surround international fees.