Blockchain gas fees, simply, are the transaction costs users pay to network validators for the computational energy required to process and validate data on a decentralized network. Whether you are swapping tokens, minting an NFT, or executing a smart contract, these fees are the “fuel” that powers the global computer. While they safeguard the network against spam and incentivize security, understanding their mechanics is critical for anyone looking to preserve their capital in the Web3 economy.
The days of paying $80 just to buy a $20 digital collectible are largely behind us. As we navigate the landscape of 2026, the ecosystem has shifted toward Layer 2 scaling solutions and Chain Abstraction, making high fees on the main network less of a daily hurdle. However, the underlying economics remain the same, and knowing how to navigate them separates the novices from the power users.
In this comprehensive guide, we will dissect the mechanics of gas fees in the modern era. We will explore why they exist, how upgrades like EIP-1559 and EIP-4844 revolutionized the cost structure, and provide actionable strategies to keep your transaction costs near zero.
What Are Gas Fees and Why Do They Exist?
To understand gas, you must first understand the nature of a blockchain. Ethereum and similar networks are not just databases; they are decentralized world computers. Every time you send a token, mint an NFT, or interact with a DeFi protocol, you are asking this computer to perform work.
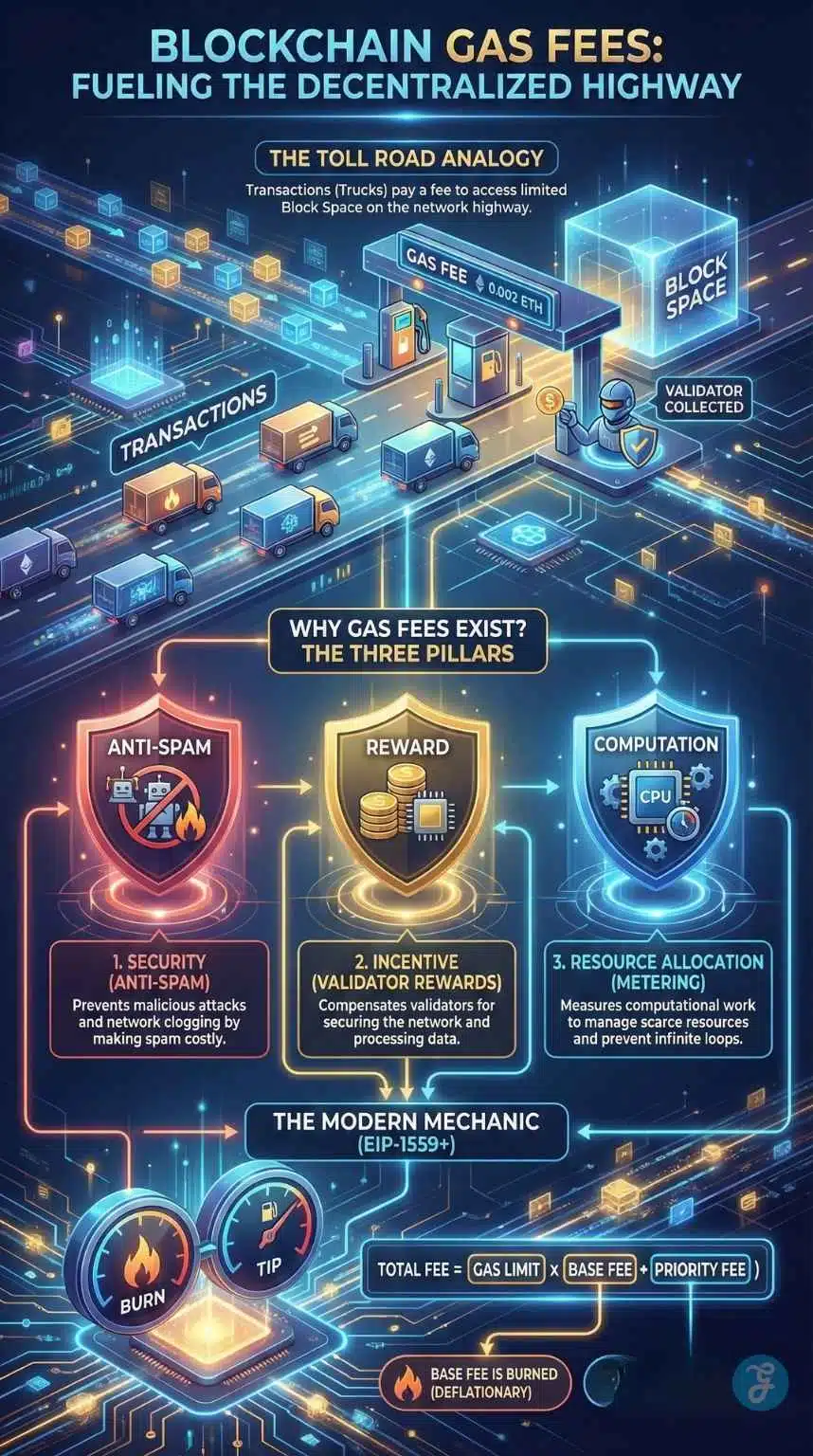
The “Toll Road” Analogy
Think of the blockchain as a secure, digital highway.
- The Blocks: These are the trucks that carry data (transactions) from Point A to Point B.
- Block Space: Each truck has limited cargo space. It can only carry so many transactions at once.
- Gas Fee: This is the toll you pay to the truck driver (validator) to load your package onto the truck.
When the highway is empty (low congestion), the toll is cheap. But during rush hour, say, when a major market event is happening, everyone wants their package on the next truck. The toll price skyrockets as users bid against each other for that scarce space.
The Three Pillars of Gas
Gas fees are not arbitrary; they serve three critical functions that keep the network alive:
- Security (Anti-Spam): If transactions were free, a malicious actor could send millions of useless transactions per second, clogging the network and crashing the nodes. By attaching a financial cost to every action, the network makes spam attacks economically unfeasible.
- Incentive Structure: Validators (formerly miners) spend millions on hardware and electricity to secure the ledger. Gas fees, along with block rewards, compensate them for their service. Without fees, there would be no validators, and thus, no blockchain.
- Resource Allocation: Code execution requires computational resources (CPU and RAM). Gas measures exactly how much “work” a specific task requires. A simple transfer requires little fuel; executing a complex yield-farming smart contract requires a full tank.
The Concept of “Gwei”
In the Ethereum ecosystem, gas is priced in Gwei (giga-wei).
- 1 ETH = 1,000,000,000 Gwei (1 Billion Gwei).
- 1 Gwei = 0.000000001 ETH.
We use Gwei because saying “the gas cost is 0.000000035 ETH” is cumbersome. Instead, we say “Gas is 35 Gwei.”
The Mechanics: How Gas is Calculated
The way we calculate gas has shifted dramatically over the last five years. In the early days, it was a blind auction. Today, thanks to the EIP-1559 upgrade (implemented in 2021) and the recent EIP-4844 (Blobs), the model is far more predictable.
The Modern Formula
The standard formula for calculating the transaction fee on Ethereum and EVM-compatible chains is:
“$$Total Fee = Gas Limit \times (Base Fee + Priority Fee)$$”
Let’s break down these variables.
1. Gas Limit [The Fuel Tank Size]
The Gas Limit is the maximum amount of gas units you are willing to spend on a transaction. This is determined by the complexity of the code you are interacting with.
- Standard Transfer: 21,000 Gas Units (Fixed).
- Token Swap (Uniswap): ~150,000 – 200,000 Gas Units.
- NFT Mint: ~250,000+ Gas Units.
Crucial Note: You cannot lower the Gas Limit to save money. If a trip requires 10 gallons of fuel and you only provide 5, the car stops in the middle of the road. In crypto terms, your transaction fails (“Out of Gas”), but you still pay the fee because the network did the work up to that point.
2. Base Fee [The Mandatory Toll]
The Base Fee is the minimum price per unit of gas required to be included in a block. This is set algorithmically by the network based on the demand of the previous block.
- The Base Fee is burned (destroyed), permanently removing ETH from circulation.
- If the previous block was full, the Base Fee increases by up to 12.5%.
- If the previous block was empty, the Base Fee decreases.
3. Priority Fee [The Tip]
This is the optional “tip” you pay to the validator. While the Base Fee gets burned, the Priority Fee goes directly into the validator’s pocket.
- Low Congestion: A small tip (0.01 – 1 Gwei) is sufficient.
- High Congestion: You must tip higher to incentivize a validator to pick your transaction over others.
The “Why”: Factors That Spike Gas Fees
Even in 2026, you will occasionally see gas spikes. Understanding what triggers these events allows you to avoid them.
1. Network Congestion & Block Space Scarcity
This is simple supply and demand. Ethereum blocks have a target size of 15 million gas and a hard cap of 30 million gas. When thousands of users try to fit into a block that can only hold hundreds, the algorithm hikes the Base Fee to discourage usage.
2. Smart Contract Complexity
Not all transactions are created equal.
- Sending ETH: Requires simple balance updates. Cheap.
- DeFi Interaction: Involves checking liquidity pools, calculating slippage, routing through multiple tokens, and updating oracle prices. Expensive.
Developers optimize their contracts to use less gas, but complex logic will always cost more.
3. Market Volatility [The Panic Factor]
When the price of ETH or Bitcoin crashes by 10% in an hour, users rush to exchanges to sell or top up collateral on lending platforms to avoid liquidation. This panic creates a massive surge in transactions, clogging the network and driving fees to the moon.
4. The “NFT Mint” Effect [PGA]
Though less chaotic than in 2021, popular NFT launches can still cause Priority Gas Auctions (PGA). This is when thousands of bots and users set astronomical Priority Fees (Tips) to ensure they are the first to mint a limited asset.
Network Comparison: The 2026 Landscape
The biggest change in the last few years is the migration from Layer 1 (L1) to Layer 2 (L2). In 2026, the Ethereum Mainnet is primarily a settlement layer for large institutions and L2s, while regular users transact on L2s.
Below is a comparison of the average costs and speeds across the dominant networks in 2026.
| Network | Type | Avg. Transfer Cost | Avg. Swap Cost | Speed (TPS) | Best For… |
| Ethereum (Mainnet) | L1 | $1.50 – $4.00 | $5.00 – $15.00 | 15 – 30 | Whales, High-Security Settlement |
| Arbitrum One | L2 (Optimistic) | $0.01 – $0.05 | $0.10 – $0.20 | 40,000+ | DeFi, General Usage |
| Base (Coinbase) | L2 (Optimistic) | < $0.01 | < $0.05 | 40,000+ | Social Apps, Retail Users |
| zkSync Era | L2 (ZK-Rollup) | $0.01 – $0.03 | $0.05 – $0.10 | 100,000+ | Payments, Privacy |
| Solana | Alt-L1 | < $0.001 | < $0.001 | 65,000+ | High-Freq Trading, Gaming |
| Bitcoin | L1 | $2.00 – $10.00 | N/A | 7 | Store of Value |
Key Takeaway: If you are still paying $5 to swap tokens on Ethereum Mainnet for small trades, you are doing it wrong. The ecosystem has moved to L2s.
How to Lower Transaction Costs: The Strategic Guide
You don’t need to be a technical expert to save money. By following these five strategic pillars, you can reduce your annual gas expenditure by over 90%.
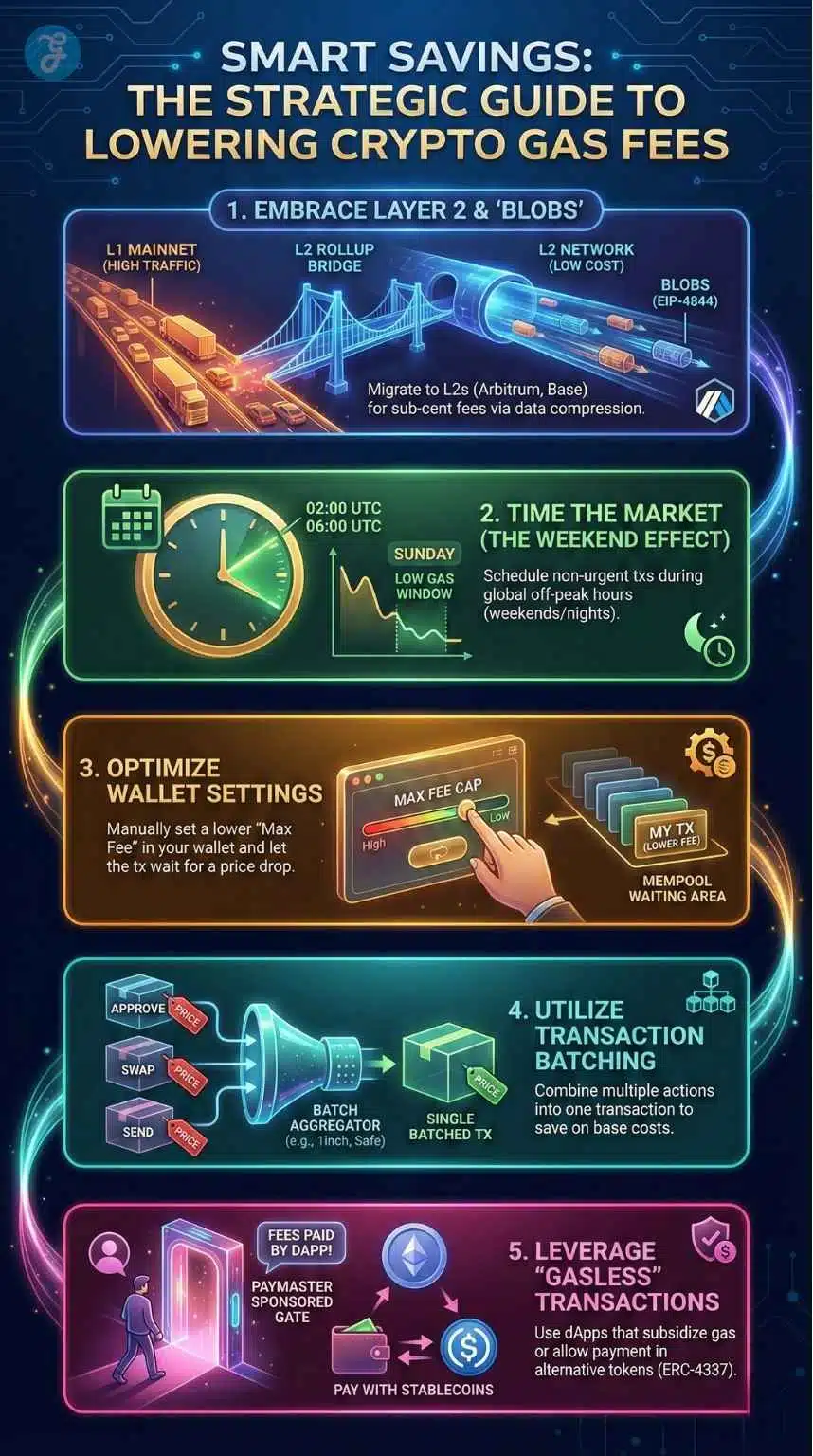
Strategy 1: Embrace Layer 2 and “Blobs”
The most effective way to lower fees is to stop using the mainnet for daily tasks.
- The Tech: L2s like Optimism and Arbitrum use Rollup technology. They bundle thousands of transactions off-chain and submit them to Ethereum in a single “Blob” (thanks to EIP-4844). This splits the L1 gas fee among thousands of users.
- The Move: Bridge your assets to an L2 once, and stay there. Most major exchanges (Binance, Coinbase, Kraken) now allow direct withdrawals to Arbitrum, Base, or Polygon, letting you bypass the Ethereum L1 entirely.
Strategy 2: Timing the Market [The Weekend Effect]
Blockchain traffic follows human schedules.
- The Golden Window: The network is historically quietest on Sundays and between 02:00 AM and 06:00 AM UTC (when the US is asleep, and Asia is just starting).
- Tools: Use gas trackers like Etherscan, GasNow, or browser extensions like Blocknative to monitor real-time prices. If you see the Base Fee is 50 Gwei, wait. If it drops to 15 Gwei, execute.
Strategy 3: Wallet Optimization & Custom Settings
Modern wallets (MetaMask, Rabby, Phantom) are your best friends if configured correctly.
- Max Fee Cap: If a transaction isn’t urgent, you can manually lower the “Max Fee.” For example, if the current fee is 20 Gwei, set your max to 15 Gwei. Your transaction will sit in the “Mempool” (waiting area) and will automatically pick up once the network price drops to your target.
- Safety Note: Never lower the Gas Limit, only the Gas Price/Max Fee.
Strategy 4: Transaction Batching
Why pay five tolls when you can pay one?
- Aggregators: Use DEX aggregators like 1inch or CowSwap. These platforms often combine the “Approve Token” and “Swap Token” steps or bundle your trade with others (Coincidence of Wants) to minimize gas usage.
- Manual Batching: If you need to send ETH to five people, use tools like Disperse.app or Safe (formerly Gnosis Safe) to send all five transfers in a single transaction, saving roughly 40% on gas.
Strategy 5: Utilize “Gasless” Transactions
We are entering the era of Account Abstraction (ERC-4337).
- Paymasters: Many modern dApps now sponsor gas fees for their users to improve the onboarding experience. Look for apps that advertise “Gasless Swaps” or “Sponsored Transactions.”
- Token Payments: Some wallets now allow you to pay gas fees in USDC or DAI instead of ETH. While this doesn’t strictly lower the cost, it saves you the hassle and cost of swapping assets just to get ETH for gas.
Troubleshooting: How to “Unstick” a Pending Transaction
Even in 2026, transactions can get stuck if you set the gas fee too low during a sudden market spike. Your wallet might just say “Pending” for hours, blocking you from doing anything else.
The Fix: The “Nonce” Replacement Method. Every transaction you send has a serial number called a Nonce (e.g., Transaction #45). The blockchain must process #45 before it can process #46. If #45 is stuck, everything waits.
To force it through without waiting days:
- Find the Nonce: Look at your stuck transaction on Etherscan or your wallet details to find its “Nonce” number.
- Send a New Transaction: Send 0 ETH to yourself (your own wallet address).
- Edit the Settings: In your wallet’s “Advanced” settings, manually set the Nonce to the same number as the stuck transaction (e.g., 45).
- Boost the Gas: Set the gas fee to “High” or “Aggressive” (current market rate + 10%).
- The Result: The network sees two transactions with Nonce #45. It picks the one with the higher fee (your new 0 ETH transfer) and drops the old stuck one. Your queue is now clear.
The Power User’s Frontier: Advanced Gas Dynamics and Future Trends
For the power users, understanding the deeper layers of the fee market offers even more advantages.
MEV: The Hidden Tax
Maximal Extractable Value (MEV) is an invisible cost. Sophisticated bots scan the Mempool for large pending trades. If they see you buying a large amount of a token, they will bribe validators with high gas fees to insert their own “buy” transaction before yours and a “sell” transaction after yours.
- The Result: You pay a higher price for your token (slippage), and the bot pockets the difference.
- The Solution: Use MEV-Protection RPC endpoints (like Flashbots Protect) in your wallet settings. This routes your transaction directly to validators, bypassing the public Mempool where the bots lurk.
Chain Abstraction: The 2026 Paradigm
We are moving toward a future where “chains” are invisible. In the past, you had to worry about having ETH on Ethereum, ARB on Arbitrum, and MATIC on Polygon. With Chain Abstraction, new protocols allow you to hold a balance of USDC, and the wallet automatically handles the bridging and gas payments in the background across any chain. The “Gas Fee” becomes just a tiny service fee, abstracted away from the user experience entirely.
Security Warning: The “Address Poisoning” Scam
Cheap gas fees on Layer 2 networks have an unintended side effect: they make scams cheaper to execute. Attackers now use Address Poisoning. They monitor your wallet activity and generate a “vanity address” that looks 95% identical to an address you frequently use (matching the first and last 4 characters). They then send you a transaction of $0 or a worthless token using this fake address.
- The Trap: Their goal is to get their fake address into your wallet’s transaction history. The next time you go to copy-paste that address to send money, you might accidentally copy the scammer’s address from your history instead of the legitimate one.
- The Defense: Never copy addresses from your transaction history. Always copy from the original source or use an Address Book (Whitelist).
The Impact of EIP-4844 [Proto-Danksharding]
It is impossible to discuss 2026 gas fees without acknowledging the pivotal moment of EIP-4844. Before this upgrade, L2s had to store their data permanently on Ethereum, which was expensive. EIP-4844 introduced “Blobs”—temporary data packets that are attached to blocks but deleted after ~18 days.
Why it matters: This turned Ethereum from a “storage” layer into a high-bandwidth “data availability” layer, permanently crashing the cost of L2 transactions by over 90%.
The Tax Reality: Are Gas Fees Deductible?
Disclaimer: This is for informational purposes only. Always consult a CPA.
In many jurisdictions (including the US), gas fees are not deductible as a personal expense, but they do reduce your capital gains tax. The IRS and other tax bodies generally view gas fees as part of the Cost Basis.
- Buying: If you buy 1 ETH for $3,000 and pay $10 in gas, your “Cost Basis” is $3,010.
- Selling: If you later sell that ETH for $4,000 and pay $10 in gas, your “Proceeds” are $3,990.
- The Benefit: You are taxed on the profit ($3,990 – $3,010 = $980) rather than the raw difference ($1,000).
Pro Tip: Keep your transaction hashes exportable. 2026 tax software (like CoinLedger or Koinly) automatically pulls these fees to lower your tax bill, but only if you track them.
Final Thoughts: The Cost of Freedom
The evolution of blockchain gas fees from the crisis levels of 2021 to the micro-pennies of 2026 is a testament to the industry’s resilience. While no one likes paying fees, it is important to remember what you are buying: censorship resistance and finality.
When you pay a gas fee, you aren’t just paying for a database update. You are paying for the assurance that your transaction cannot be reversed by a bank, blocked by a government, or altered by a corporation. You are paying for true ownership.
However, freedom shouldn’t cost a fortune. By leveraging Layer 2 networks, timing your activity, and utilizing modern wallet features, you can interact with the decentralized web freely and affordably. The era of the $100 transaction is over; the era of the global, frictionless economy has arrived.