An advanced interrelation of science, philosophy, and morality has often sparked debates on the relevance and effects of biocentrism. As a theory, it values all living organisms equally regardless of their size or form while attributing a unique value to human life in particular. However, these ideas have faced strong questioning and criticism. This is clear from the heated debate about ‘Biocentrism Debunked.’
In this blog post, we will explore the history and development of biocentrism while uncovering its flaws through analysis from both supporters and critics alike. With an understanding of how well-founded this controversial perspective is, you can join in on the debate with an educated opinion that considers multiple angles.
Let’s find out if biocentrism is truly debunked – no matter your standpoint!
- Biological guidelines suggested by biocentrism cannot be certified as true at the current level of scientific reasoning.
- Humans are part of a greater interconnected ecosystem and have an ethical responsibility to protect all life forms equally.
- Biocentrism advocates for sustainable practices such as reducing consumption levels, restoring ecosystems, and taking into account consequences that affect future generations.
- Critiques against biocentrism question its practicality and complexity in terms of understanding consciousness and life itself.
Defining Biocentrism: An Overview of the Theory
Biocentrism is a groundbreaking scientific theory that claims consciousness is the fundamental force driving the universe. Proposed by Robert Lanza in 2007, it suggests that our physical bodies can be used to create bridges between this world and other realms of existence.
The core idea behind biocentrism is that life exists as an interconnected network with all its individual parts rejoined into one big entity. It further states that human beings have an inherent responsibility to protect not only their environment but also every single living thing on Earth regardless of any notion of superiority or inferiority.
This implies animals, plants, and microbes should receive equal moral consideration when making decisions about them and their habitats because they are all part of the planetwide web of coexistence.
Additionally, biocentrism challenges traditional views on ethics and value since it stresses the importance for individuals to take action rather than sitting around waiting for somebody else to act first before taking the burden themselves intimately linked with something bigger such as the Universe itself unlike older theories separated from cosmic factors.
A Brief History of Biocentrism
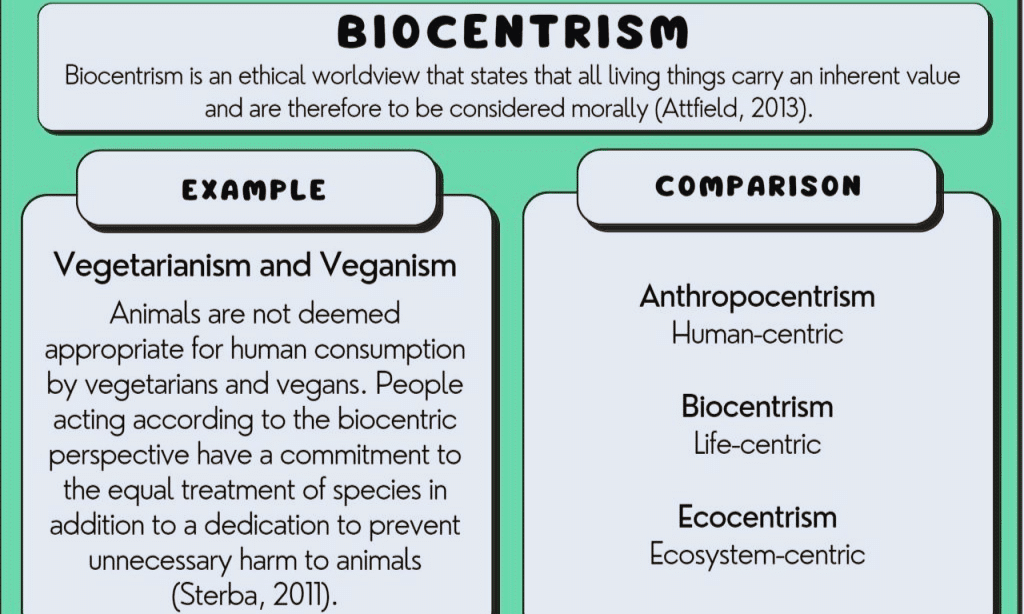
Biocentrism is the philosophical perspective that all life has inherent value, and as such should be treated with moral consideration. The concept of biocentrism was introduced in 2007 by American biologist Robert Lanza and has since been a present discourse throughout the academic community.
Prior to this introduction, much of the existing discourse on life revolved around its objectification life becoming subordinate to scientific inquiry or external ethical frameworks like Anthropocentrism.
The formal discussion surrounding biocentrism entered public dialogue around 2009 when Lanza published his book Biocentrism: How Life Created the Universe which contained detailed arguments for why life should take precedence over more traditional ideals about our relationship with nature.
According to this line of thinking, human beings are stewards rather than superiors who must bear responsibility for their actions taken in regard to protecting natural habitats and ecosystems from degradation and destruction due to industrialization or rising population numbers.
Today both academics and political activists alike discuss this perspective frequently, allowing us glimpses into how stakeholders across disciplines view these issues differently yet strive for similar outcomes—sustainable habits that go beyond economic efficiency models but also consider wider ecological impacts holistically while engaging indigenous communities in discussions which directly affect them (inclusive engagement).
From serving as an alternative framework for understanding what meaningfully constitutes conservation efforts today onwards there is a general consensus happening where people can agree on core rules without marginalizing any individual’s experiences related to ecology or sustainability concepts entirely.
Supporting Arguments for Biocentrism
Biocentrism emphasizes the value of all life forms and how they can contribute to fairness, moral justice, and other principles. Keep reading to learn more!
All Life Has Inherent Value
According to the theory of biocentrism, all living beings possess inherent value and should be treated with fairness, morality, justice, respect, and dignity. Inherent worth means that there is a significant moral worth ascribed to life itself regardless of one’s race or species.
It implies an ethical obligation towards other living things as they are autonomous entities entitled to basic rights such as freedom from harm or destruction based on their lack of human cognition or practical purpose.
This concept encompasses political, ecological, and literary stances that emphasize the importance of protecting natural habitats while striving for social equality amongst all life forms plant, animal, and Human alike.
Human Beings Are Stewards, Not Superiors
While traditional Western philosophy has placed man at the top of hierarchical order, biocentrism rejects this notion and instead proposes that all parts of nature should be seen as equal.
Biocentrists suggest humans should view themselves as stewards rather than superiors. This requires a shift in thinking, from viewing human beings as the only valuable actors on Earth to recognizing the intrinsic value of every organism regardless of its size or significance.
Doing so requires reducing consumption levels, restoring ecosystems, and minimizing the exploitation of natural resources for development purposes. It also means accepting different positions on current issues such as animal rights; with biocentrism comes a duty to respect living creatures in their own right and not only when it serves humankind’s interests.
Need to Protect the Natural World
Protection and conservation of the natural environment is essential for human well-being and ethical considerations must be taken into account when making decisions. Biocentrism challenges traditional anthropocentric views that prioritize human interests over environmental concerns by teaching that all life forms, including humans, have inherent moral standing.
Therefore, biocentrism advocates for the protection of all living beings in order to maintain a balanced and healthy ecosystem – not just humans. Humans’ actions should reflect our responsibility as stewards of nature rather than owners with absolute power over resources within it.
We need to consider both short-term solutions that will benefit us in the immediate future as well as long-term consequences impacting future generations, animals, and ecosystems on Earth – this is an important aspect of biocentrism which has been embraced by many environmental activists over time.
Critiques and Counterarguments to Biocentrism
Analyzing the weaknesses of biocentrism, from its practicality to the complex nature of life and consciousness, is essential for a full understanding of this controversial theory.
Loopholes and Flaws in the Theory
- Biocentrism’s radical shift away from traditional, anthropocentric views has caused confusion and contradictions in its scientific ideas.
- Some argue that certain fundamental biological guidelines within the theory could not be certified or justified as true under current reasoning capabilities; thus questioning its accuracy in the overall discussion of life and consciousness.
- Biocentrism faces challenges due to its difficulty in articulating its fundamental concepts and a dearth of additional empirical evidence. This inadvertently places it in conflict with other academic disciplines like physics, mathematics, and chemistry, as it introduces interpretations that surpass the boundaries of what these specialized fields can currently support or logically justify. Consequently, this raises questions about the contemporary validity of biocentrist theories when contrasted with past decades when we had less comprehensive knowledge across all scientific domains pertaining to this matter and fewer field studies that could test and potentially disprove its hypotheses.
- Furthermore, aside from its disputes with established principles in other scientific domains such as natural philosophy, which serves as a precursor to contemporary environmental science, certain criticisms leveled against biocentrism imply that it might overlook the intricate aspects of human behavior.
The Practicality of Biocentric Rules
It is widely accepted that biocentrism promotes a holistic approach to ethical decision-making regarding nature and the natural environment. But what does this mean in terms of the practical implementation of biocentric rules in everyday life? There are potential implications for how decisions should be made when it comes to protecting the earth’s resources.
Complexity of Life and Consciousness
This is a major topic of discussion in the biocentrism debate. Biocentrists believe that consciousness should be fundamental, defining our reality and life itself as opposed to merely an emergent property produced by complex physical processes.
In their view, life and consciousness cannot be reduced to material elements like particles or waves but are rather intimately connected with the fabric of space-time itself. The complexity of this theory has proven difficult for some critics to accept; they criticize its lack of clear definitions both about what exactly constitutes consciousness and how it functions within physical laws.
Moreover, skeptics argue over whether there is solid evidence backing such claims or if it relies on often vague correlations between observation and data. While supporters counter with arguments regarding quantum physics which may suggest links between phenomena such as wave-particle duality and conscious choice-making in human behavior, this controversy continues unresolved in many circles today due to its seemingly unsolvable complications.
6 Alternative Theories of Biocentrism Debunked

This section examines alternative theories such as anthropocentrism, ecocentrism, and others that offer an alternate perspective to biocentrism.
Anthropocentrism
Anthropocentrism is an ethical belief that prioritizes human interests above all other beings. This alternative theory to biocentrism predicts moral obligations only towards other human beings, with the potential to significantly influence how humans view and interact with the environment.
Pollution, animal hunting, and efficient energy use – are all issues that can be framed in a uniquely human-centric or anthropocentric manner. An understanding of our biological interconnectivity can also lead us to consider more broadly how actions today might impact future generations – whether through direct environmental degradation or effects on health and well-being that arise from its consequences.
Anthropocentrism has been seen as both a misunderstood problem responsible for damaging global relations between species as well as potentially providing solutions for advancing sustainability initiatives in keeping within certain boundaries of ethics and morality while prioritizing needed changes.
Ecocentrism
Ecocentrism is a holistic ethical perspective that views Earth as an interconnected organism and highlights the need to value, respect, and protect the natural world. It prioritizes the well-being of ecosystems and species over individual living beings in order to sustain their mutual interdependence.
Ecocentrists believe that humans are deeply connected with nature, and have an obligation to act as stewards for non-human life forms. As such, ecocentric believers call for environmental conservation practices that prioritize biodiversity, sustainability, ecosystem services, and natural resources – all while recognizing our obligation to ‘give back’ what has been taken from Mother Nature.
By protecting individual organisms together rather than focusing solely on their economic value or human use potentials we can strive towards achieving a more balanced ecological system – one where air cycles freely among plants, animals benefit from clean water sources perpetually stocked with nutrient-rich food sources will be supported by organic soil structures containing abundant microflora.
Animal Rights and Liberation Ethics
This ethical framework extends moral consideration beyond human beings and ecosystems to encompass individual animals. It vehemently argues for the rights and liberation of animals, placing a spotlight on their intrinsic worth and the moral imperative to minimize their suffering and exploitation.
In direct contrast to biocentrism’s treatment of different species as having equal value, Animal Rights and Liberation Ethics prioritize the individual experiences and rights of animals. This theory advocates for a significant shift in our ethical perspective, emphasizing that animals deserve to live free from unnecessary harm and pain, asserting their autonomy, and compelling society to recognize and respect their interests and well-being.
In essence, it challenges the notion of a uniform ethical value for all species and instead champions the unique moral status of animals.
Pragmatic Environmentalism
Pragmatic environmentalism, as an alternative approach to environmental ethics, emphasizes a decidedly practical perspective in navigating our relationship with the natural world. It contends that ethical decisions concerning the environment should be firmly grounded in practical considerations, including human well-being, social advantages, and economic factors.
This ethical perspective arises out of a concern for the real-world feasibility and utility of some biocentric principles, which it questions. At its core, pragmatic environmentalism posits that practicality should serve as the guiding principle behind environmental decision-making. A fundamental aspect of pragmatic environmentalism is the pursuit of a delicate equilibrium between the imperative of environmental protection and the necessity of addressing human needs and societal benefits.
This approach asserts that the most effective environmental policies and actions are those that not only safeguard the natural world but also deliver tangible benefits for society. In essence, it advocates for solutions that are both ecologically responsible and beneficial to human welfare.
Posthumanism
Posthumanism represents a philosophical and ethical paradigm that challenges the long-held anthropocentric view of humans as distinct from and superior to nature. It urges a comprehensive reevaluation of human-nature relationships, especially in light of recent advances in technology and evolving understandings of consciousness. This perspective takes the position that our traditional concepts of humanity and nature are outdated and need to be rethought.
Posthumanism calls for a more holistic and interconnected relationship with the environment. It envisions a future in which technology is not merely a tool but an integral part of our existence, where human consciousness and nature are viewed as intricately intertwined. This shift in perspective prompts us to acknowledge the profound impact of technology on our understanding of the environment and our place within it.
In essence, posthumanism challenges us to think beyond conventional ethical boundaries and embrace a more nuanced and interconnected worldview that accounts for the evolving dynamics of our relationship with nature in the age of technological advancement. It encourages us to navigate this intricate web of interactions with thoughtfulness and responsibility.
Sentience-Centered Ethics
Sentience-centered ethics is a moral framework that places a significant emphasis on the capacity for sentience or consciousness as the fundamental criterion for moral consideration. This ethical perspective contends that beings with the ability to experience pleasure and pain, to feel, and to be aware, inherently deserve special ethical attention. The central premise of this theory is that the presence of sentience creates a distinct moral status that demands recognition and protection.
This theory underscores the moral obligation to prioritize the well-being and protection of sentient beings. It steers the ethical conversation toward a more concentrated concern for the welfare of conscious entities within the broader context of biocentrism. In essence, sentience-centered ethics directs attention to the inner experiences and emotions of living beings, emphasizing the importance of preventing suffering and promoting positive experiences.
By focusing on sentience, this ethical framework aims to ensure that moral considerations encompass the capacity to experience the world in subjective ways. It highlights the ethical responsibility to safeguard the interests and welfare of sentient creatures, offering a unique perspective within the broader discourse of biocentrism and environmental ethics
Biocentrism and Environmentalism: Does it Promote Action?
Biocentrism, an ethical philosophy that centers on the intrinsic values of living organisms, has been adopted more and more in environmental discourse. The idea that all life forms possess moral value is key to biocentrism since it questions our (often anthropocentric) Thinking which suggests non-human interests are disposable.
As a result of this perspective, biocentrists argue for policies that protect the natural world from human interference; using biodiversity as a means to measure conservation progress and emphasizing sustainability in policy creation.
Biocentrist action also encourages individuals to reduce their ecological footprints through activities such as swapping out single-use plastic or choosing less energy-intensive lifestyles.
Through its push for greater appreciation of nature’s inherent worth biocentrism provides tangible ways in which people can live more harmoniously with the planet. In other scenarios, biocentric philosophies demand companies who engage in extraction practices do so with responsibility and conference rights and safety standards that prioritize human health over company profit margins.
Beyond promoting sustainable behaviors, biocentrism offers a much-needed alternative take on traditional anthropocentric views better known as speciesism: believing certain populations deserve preferential treatment solely because they belong to a particular group (i.e. humans).
Bicentrist principles also challenge ideas about consumption often equated with development or modernity by putting forward societal shifts away from valuing material gain above all else towards appreciating people’s relationship with their environment holistically.
Biocentrism in Scientific and Philosophical Contexts
Explore the debates, arguments, and evidence that demonstrate its validity in modern science and philosophy.
Notable Figures in the Biocentrism Debate
- Rupert Sheldrake is an English author and biologist who coined the term “morphic resonance,” arguing that memory can be stored in a collective unconsciousness within nature. He has proposed that morphic fields may explain certain quantum effects, including psychokinesis and telepathy, and supports Francis Crick’s views on consciousness being fundamental to reality.
- Robert Lanza is an American biocentrist who proposes ideas regarding biocentrism, which he believes could revolutionize our understanding of life, death, time, space, and consciousness by explaining how biological organisms interact with energy more closely than previously understood through modern science.
- Thomas Nagel is an American philosopher best known for his critique of reductionist accounts of causation in biology in his book Mind & Cosmos: Why the Materialist Neo-Darwinian Conception Of Nature is Almost Certainly False (2012). Through this work, he posits criticisms against religious explanations for human experience as well as evolutionary theories such as neo-Darwinian synthesis by pointing out gaps in both interpretations ultimately advocating for alternative approaches to philosophy like biocentrism.
- Brian Morris is a British sociobiologist from the University College London whose research focuses mainly on animal behavior from an ethological perspective which challenges much of the politically based concerns surrounding biocentrism and defends its scientific standing where applicable while suggesting areas that may need further development or consideration.
Arguments in Favor of Biocentrism’s Validity
- Biocentrism is built around the belief that all life forms have inherent value and should be respected regardless of species, individual, culture, race, or class status.
- Its ethical framework places a strong emphasis on equality among living beings and unambiguous fairness towards those vulnerable to exploitation and harm.
- It encourages humanity to observe moral justice in everyday life and foster positive relationships with nature by preserving ecosystems, advocating environmental conservation, minimizing resource use, and preventing unnecessary interference with delicate natural patterns.
- Biocentrism also seeks to create a mindset where humans accept their place as stewards rather than superiors of the environment – all investments made towards sustainability must be for the benefit of communities in harmony with Earth’s vital forces rather than its destruction or manipulation for short-term profits alone
Criticisms of Biocentrism
- Biocentrism has been criticized for its unreasonably demanding rules, which have proven to be difficult to implement in practical terms.
- The theory is largely based on philosophical and theoretical arguments rather than concrete scientific proof, drawing criticism from many mainstream physicists.
- Without offering any evidenced-based solutions, biocentrism relies on the human responsibility factor alone as a source of coercion towards protecting nature – something that can prove too vague or simplistic depending on varying contexts.
- Critics view biocentrism’s disregard for traditional empiricism and scientific methodology as unreliable and unconvincing when compared to other established theories with tangible evidence backing them up such as evolutionary biology or quantum mechanics.
- Biocentric views propose an entirely different relationship between humans and nature that steers away from established ethical considerations based on anthropocentric principles; some argue this lack of balance creates further environmental issues caused by morality being incompatible with what is needed practically to protect Earth’s resources responsibly over time
Scientific Evidence and Biocentrism
The concept of biocentrism remains controversial in the scientific and philosophical community. Although there is no empirical evidence available to prove its validity, physicists such as Robert Lanza believe that reality exists within consciousness rather than external objects or events.
According to him, all energy, forces, and matter are “conjured up” with awareness alone. There have been studies conducted that suggest an inherent connection between humans and the natural world; one example is a study involving fruit flies by JX Kao et al., indicating a link between nature’s biodiversity and human health.
Yet overall, the idea of biocentrism does not match traditional Western concepts from physics and religion concerning materialism and dualism – rendering it contentious among academic circles even today.
Biocentrism in Religious and Philosophical Contexts
Biocentrism is an ethical theory that puts living organisms at the center of moral consideration, based on the idea that all life forms have intrinsic value. From a philosophical perspective, biocentrism challenges human-centric philosophies by suggesting that we are not superior to other species but rather stewards and trustees of nature.
This view has wide-reaching implications for religious and spiritual systems in which reverence for the natural world and its creatures is enshrined as a pivotal tenet. Biocentric ideologies assert principles such as nonviolence towards animals, care for ecosystems, respect for diversity among species, reducing wastage in farming practices, and protecting habitats from destruction or extermination caused by human activities.
Therefore, biocentric views promote sustainability with regard to harvesting resources judiciously while preserving environmental wealth in general – a fact which many faith communities across both Eastern and Western religions agree upon universally today.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Now, let’s find out answers to some questions many people ask about Biocentrism.
1. What is biocentrism?
Biocentrism is the idea that life and consciousness are fundamental to reality, and not merely arising from physical or material forces.
2. Who proposed biocentrism?
The concept of biocentrism was proposed in 2007 by American biologist Robert Lanza and astrophysicist Bob Berman.
3. How has biocentrism been debunked?
Biocentrism has been widely contested with new research showing that our experience is a product of underlying physical processes, meaning consciousness does not drive reality as suggested by this theory.
4. How does biocentrism challenge other academic disciplines?
Biocentrism can be perceived as challenging other academic disciplines like physics, mathematics, and chemistry by introducing interpretations that may go beyond what these fields can currently support or justify. This raises questions about the compatibility of biocentrism with established scientific principles.
5. What are some common criticisms of biocentrism?
Common criticisms of biocentrism include its potential oversights of human behavior, such as greed, leading to ecologically damaging decisions in pursuit of financial gain. It is often accused of ignoring the material benefits that society can achieve by exploiting natural resources, without considering the long-term environmental consequences.
Takeaway
The debate over biocentrism is ongoing, and there are strong counterarguments from both scientific and philosophical standpoints. Critics have pointed out flaws in the theory as well as its lack of practical applications, debating how best to improve our stewardship of life on earth while also navigating complex questions surrounding consciousness.
While not accepted as a widely valid perspective, biocentrism retains value for some individuals in providing moral guidance and understanding the interconnectedness of all living things.
Ultimately, it appears that a more rigorous evaluation of the validity of this concept will be needed to determine its merit within scientific inquiry moving forward into 2024.