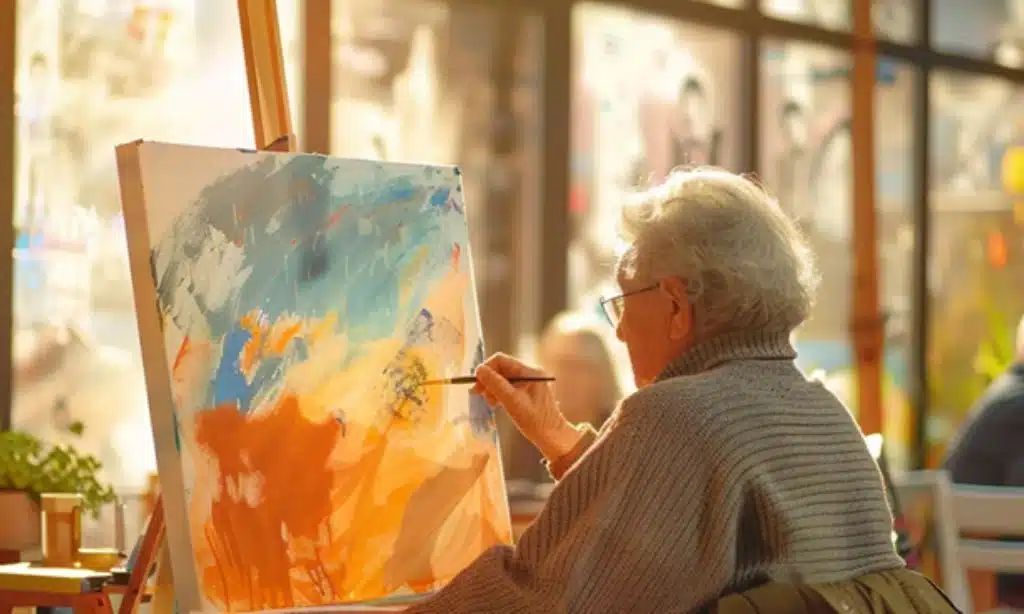Alzheimer’s disease, a degenerative brain disorder, impacts millions of individuals worldwide, altering their memory, thinking, and behavior. As the disease progresses, it can become challenging for affected individuals to maintain a semblance of normalcy in their daily lives. Nonetheless, certain interventions, such as therapeutic activities, have shown promise in managing symptoms and enhancing quality of life. Professionals and caregivers alike are recognizing the benefits of these non-pharmacological approaches to dementia care. Below, we explore the various therapeutic activities and their positive impact on individuals with Alzheimer’s.
Understanding Alzheimer’s Disease and the Importance of Therapeutic Activities
Alzheimer’s disease is more than just memory loss; it is a chronic neurodegenerative condition that gradually erodes an individual’s cognitive functions. Symptoms often begin subtly, with slight forgetfulness, but can progress to severe impairment, including speech and recognition issues. The progression varies, presenting a unique set of challenges for each patient and caregiver.
Therapeutic activities are designed to engage those with Alzheimer’s in meaningful tasks that can stimulate cognitive processes and provide a sense of accomplishment. These interventions range from mental exercises to social interactions, and they play a crucial role in disease management. Despite Alzheimer’s current incurability, such activities can slow cognitive decline and enhance patients’ well-being.
Integrating therapeutic activities into a patient’s routine requires a personalized approach, considering their interests, abilities, and disease stage. Activities that are too difficult can lead to frustration, while those too simple may not provide enough stimulation. Finding this balance is essential for maximizing benefits and ensuring patient engagement.
Physical Exercise as a Cornerstone for Alzheimer’s Management
Physical exercise is another pivotal component in managing Alzheimer’s disease, with numerous studies supporting its role in maintaining brain health. Engaging in regular physical activity helps improve cardiovascular health, which is directly linked to cognitive function. Indeed, exercise can spur the growth of new brain cells and promote the survival of existing cells, a vital aspect in the face of Alzheimer’s progression.
Exercise routines should be tailored to the individual, taking into account their physical capabilities and medical conditions. Structured activities such as walking, tai chi, and light resistance training not only help maintain muscle mass and balance but can also reduce the risk of falls and injuries. The social aspect of group exercises can further enhance the therapeutic benefits by providing socialization opportunities.
Additionally, the release of endorphins during exercise provides a natural mood boost, combating the depression and anxiety that often accompany Alzheimer’s disease. Consistency is crucial, as regularity helps foster a routine, contributing to a sense of normalcy and security for the individual with Alzheimer’s.
The Role of Creative Arts in Enhancing Quality of Life for Alzheimer’s Patients
Creative arts therapies are emerging as significant instruments in Alzheimer’s management. Art, music, and dance offer a medium through which individuals can express themselves without relying solely on verbal communication. These forms of self-expression can be particularly poignant for those who struggle with language and memory, as the creative process can awaken emotions and memories that are otherwise hard to access.
Art therapy can be especially powerful, serving as an outlet for emotions and as a means to trigger dormant memories. Crafting a painting, a sculpture, or a collage allows patients to concentrate on the colors, textures, and patterns, promoting focus and relaxation. In doing so, art therapy can decrease the occurrence of aggressive behaviors, which are sometimes a response to the overwhelming emotions associated with cognitive decline.
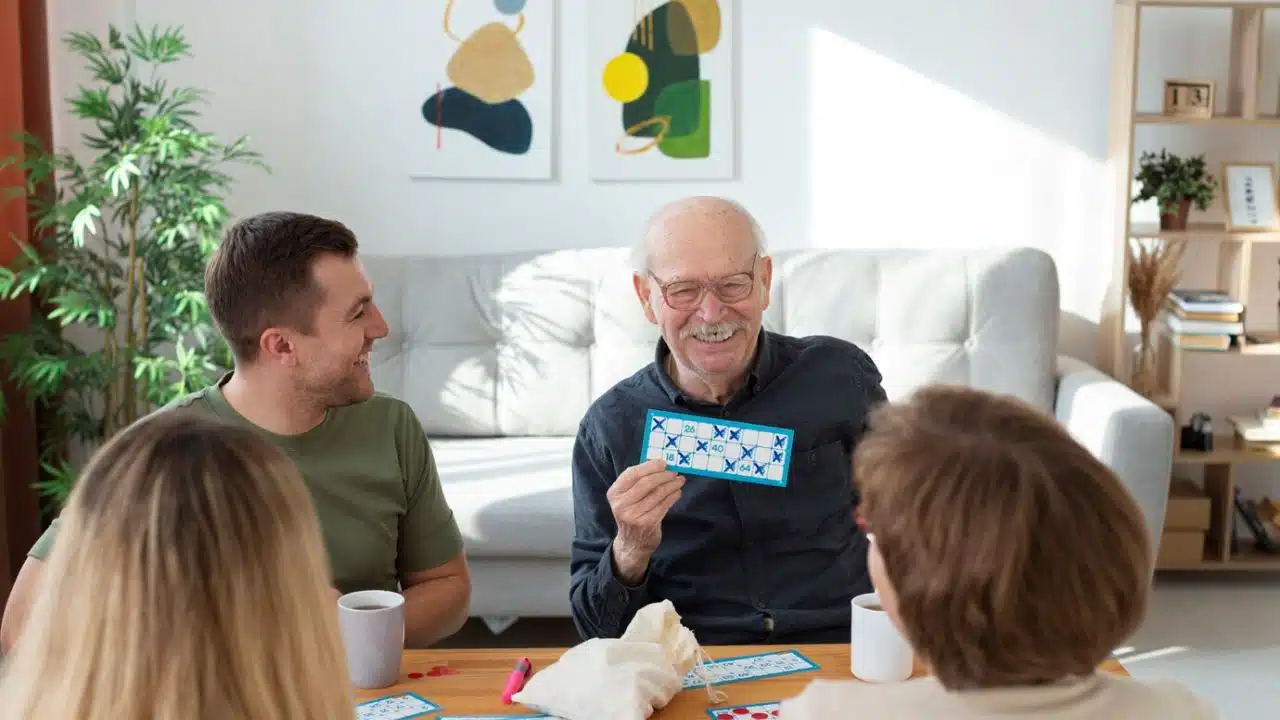
Social Engagement and Support Groups in Alleviating Alzheimer’s Isolation
Alzheimer’s disease often leads to social withdrawal and isolation as it becomes more challenging to interact with others. However, maintaining social connections is vital for mental health, and engaging in group activities or attending support groups can mitigate feelings of loneliness. Social engagement provides meaningful interactions, stimulating conversation, and an overall sense of belonging, critical to those with Alzheimer’s.
Support groups offer a platform for sharing experiences, exchanging caregiving tips, and expressing shared concerns. For people with Alzheimer’s, this means encountering peers who are in similar situations, which can alleviate the stigma and isolation they might feel. This sense of community is irreplaceable in bolstering mental health and facing the adversities of the disease.
Altogether, therapeutic activities show significant benefits in managing the symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease. They offer more than just temporary respite; they can fundamentally enhance the overall quality of life for patients and provide essential support to their caregivers. An integrative approach that includes cognitive stimulation, physical exercise, creative arts, and social engagement creates a robust defense against the ravages of Alzheimer’s, ensuring that each individual’s journey through this condition is met with compassion, dignity, and hope.