Suffering a personal injury can be a life-altering experience, affecting not only physical health but also mental well-being. Whether caused by a car accident, workplace incident, medical negligence, or public liability case, the psychological toll of such injuries can be severe and long-lasting.
Many Australians find themselves struggling with emotional distress, anxiety, depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder [PTSD] following an injury, yet mental health aspects are often overlooked in the recovery process.
This article delves into the 5 psychological impacts of personal injury in Australia and how to address them, offering practical solutions, expert insights, and available support systems to help individuals regain emotional stability and improve their quality of life.
1. Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder [PTSD]
PTSD is one of the most prevalent and debilitating psychological impacts of personal injury, often leaving victims in a prolonged state of distress. Those who have endured a traumatic event, such as a severe accident, physical assault, or medical malpractice, may develop PTSD symptoms that can persist for months or even years without appropriate intervention.
This mental health condition affects not only an individual’s emotional state but also their physical health, relationships, and ability to work or perform daily tasks. Symptoms such as flashbacks, emotional numbness, and hypervigilance can severely disrupt one’s life, making it crucial to seek timely psychological support.
Without professional treatment, PTSD can lead to further complications, including depression, anxiety disorders, and substance abuse, exacerbating the overall impact of personal injury on a person’s well-being.
Symptoms of PTSD:
- Flashbacks or intrusive memories of the traumatic event
- Nightmares and sleep disturbances
- Severe anxiety and heightened startle response
- Avoidance of places, people, or activities associated with the trauma
- Emotional numbness or detachment from others
Addressing PTSD in Australia
In Australia, several treatment options and support networks are available for individuals struggling with PTSD due to personal injury:
- Professional Therapy: Cognitive-behavioral therapy [CBT] and Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing [EMDR] are proven effective in treating PTSD.
- Medication: Antidepressants and anti-anxiety medications can help alleviate severe symptoms.
- Support Groups: Organizations like Phoenix Australia and Beyond Blue offer support networks for trauma survivors.
- Legal Compensation: Victims of personal injury may be entitled to compensation through WorkCover, TAC, or other insurance schemes, which can fund psychological treatment.
Key Statistics
| PTSD Prevalence in Australia | Details |
| 12% of Australians | Experience PTSD at some point in their lives |
| 25% of severe injury victims | Develop PTSD symptoms |
| 2-4 times more likely | PTSD sufferers have higher rates of depression and anxiety |
2. Depression and Emotional Distress
Personal injury frequently results in profound emotional distress, with many individuals facing depression due to abrupt lifestyle changes, mounting financial pressures, and the overwhelming struggle to regain autonomy in their everyday activities.
The inability to perform routine tasks, participate in social interactions, or return to work can intensify feelings of frustration, helplessness, and isolation. Many individuals experience anxiety about their future, worrying about long-term recovery, medical expenses, and financial stability.
The emotional toll can also strain personal relationships, leading to additional stress and a diminished support system. Seeking professional mental health support, along with medical treatment and rehabilitation, is crucial in managing these challenges and fostering emotional resilience.
Common Signs of Depression:
- Persistent feelings of sadness or hopelessness
- Loss of interest in activities once enjoyed
- Fatigue, low energy, and lack of motivation
- Difficulty concentrating and making decisions
- Suicidal thoughts in severe cases
Addressing Depression in Australia
Depression following a personal injury requires a multifaceted approach:
- Psychological Counseling: Psychologists and psychiatrists provide structured therapy, such as CBT and interpersonal therapy.
- Mental Health Helplines: Lifeline [13 11 14] and Beyond Blue offer 24/7 crisis support.
- Financial Assistance: Personal injury claims can cover mental health treatment costs.
- Workplace Adjustments: Employees returning to work after injury may require flexible hours or modified duties.
Mental Health Coverage in Australia
| Support System | Coverage Details |
| Medicare | Covers 10 subsidized therapy sessions per year |
| Private Health Insurance | Provides additional therapy coverage |
| WorkCover & TAC | Funds psychological treatments for injury victims |
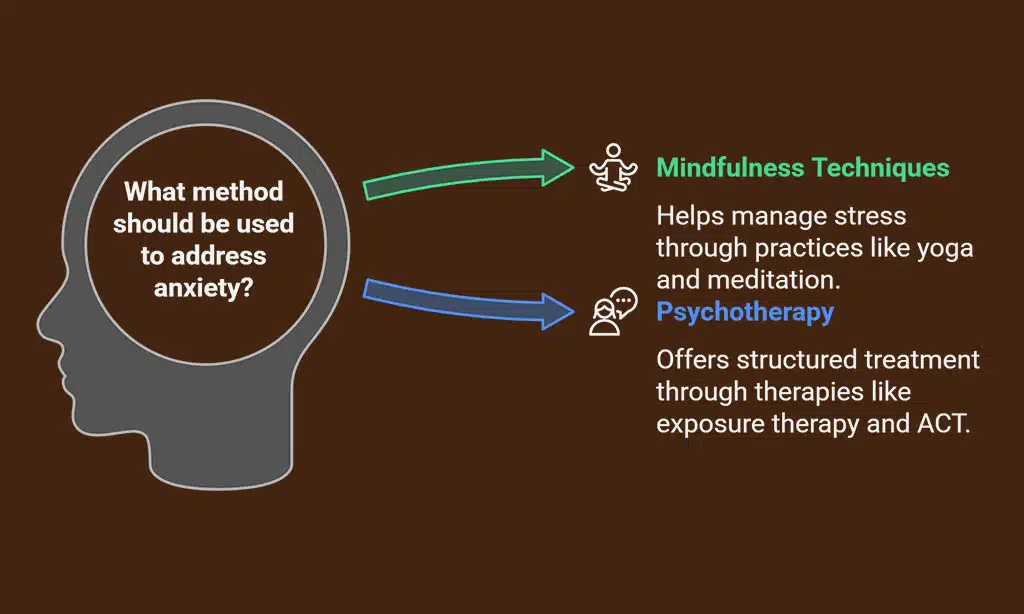
3. Anxiety Disorders
Anxiety disorders are a major psychological impact of personal injury, affecting an individual’s daily functioning and overall mental health. Victims often develop generalized anxiety disorder [GAD], panic disorder, or social anxiety, which can manifest as persistent worry, intrusive thoughts, or sudden episodes of intense fear.
The trauma of the injury, coupled with financial stress and lifestyle changes, can heighten anxiety levels, making it difficult to focus, sleep, or engage in normal activities.
Some individuals may develop post-traumatic stress disorder [PTSD], experiencing flashbacks or heightened sensitivity to triggers related to the accident. Without proper treatment, anxiety disorders can severely impact a person’s quality of life, making professional counseling, therapy, and support systems essential for recovery.
Symptoms of Anxiety:
- Excessive worry and fear
- Heart palpitations and shortness of breath
- Restlessness and irritability
- Avoidance of social interactions
Addressing Anxiety in Australia
- Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques: Yoga, meditation, and breathing exercises help manage stress.
- Psychotherapy: Exposure therapy and acceptance and commitment therapy [ACT] are effective treatments.
- Lifestyle Changes: Regular exercise and a balanced diet improve mental resilience.
4. Loss of Self-Esteem and Identity
Personal injury can alter a person’s self-perception, leading to diminished confidence and a loss of identity, especially if they can no longer perform tasks they once excelled at. This can be particularly devastating for individuals whose careers, hobbies, or daily routines were central to their sense of self-worth.
Feelings of inadequacy, frustration, and helplessness may arise as they struggle with physical limitations or dependence on others.
The inability to participate in social or professional activities as before can lead to isolation and a deep sense of loss. Rebuilding self-esteem often requires emotional support, therapy, and finding new ways to engage in meaningful activities that foster a renewed sense of purpose.
Ways to Regain Confidence:
- Counseling and Career Coaching: Helps individuals adapt to new roles and find purpose.
- Community Engagement: Support groups and volunteering aid social reintegration.
- Rehabilitation Programs: Occupational therapy assists in regaining independence.
5. Social Isolation and Relationship Struggles
Many injury victims experience social withdrawal due to mobility limitations, emotional distress, or stigma. The inability to participate in social activities, attend work, or engage in hobbies can lead to feelings of loneliness and detachment from friends and family.
Emotional distress, including anxiety and depression, may further hinder communication and strain relationships, making it difficult to seek or accept support. Additionally, caregivers and loved ones may struggle to understand the victim’s emotional and physical challenges, leading to misunderstandings or feelings of frustration on both sides.
Over time, this isolation can deepen, impacting mental well-being and overall quality of life. Seeking counseling, support groups, and maintaining open communication with loved ones can help rebuild connections and foster emotional healing.
Strategies for Rebuilding Social Life:
- Joining Support Groups: Connecting with others facing similar challenges reduces loneliness.
- Maintaining Open Communication: Expressing needs to loved ones fosters understanding.
- Seeking Professional Help: Therapists can provide guidance on rebuilding relationships.
Takeaways
The psychological impacts of personal injury can be profound, affecting emotional well-being, relationships, and daily life. However, recovery is possible with the right support, coping strategies, and professional assistance. Understanding the five psychological impacts of personal injury and how to address them in Australia is essential for both victims and their families.
By seeking therapy, joining support groups, and accessing legal and medical resources, individuals can navigate these challenges more effectively. Building resilience, maintaining open communication with loved ones, and engaging in adaptive strategies can foster emotional healing.
For more guidance, consult local mental health professionals, legal advisors, and government support programs in Australia to ensure a smoother path to recovery.