Singapore’s robust economy, world-class infrastructure, and high quality of life make it a top destination for individuals seeking permanent residency (PR). But do you know how to get PR in Singapore?
Becoming a Singapore PR allows you to enjoy benefits such as subsidized healthcare, education privileges, and the ability to live and work in Singapore without visa restrictions.
This guide provides a step-by-step roadmap for obtaining PR in Singapore, with detailed information and actionable insights.
What Is Permanent Residency in Singapore?
Permanent Residency (PR) in Singapore allows non-citizens to reside in the country indefinitely. While PRs do not have voting rights or access to some social benefits available to citizens, they enjoy privileges such as the ability to change jobs without a new work visa and priority access to housing and education.
Benefits of Becoming a Singapore Permanent Resident
- Job Flexibility: You can change employers without needing a new work pass.
- Healthcare Access: Eligibility for subsidized public healthcare services under the Central Provident Fund (CPF).
- Educational Privileges: Children of PRs have access to local schools with subsidized tuition fees.
- Business Opportunities: Freedom to start a business in Singapore with fewer restrictions.
- Pathway to Citizenship: After several years as a PR, you can apply for Singaporean citizenship.
- Retirement Benefits: Participation in the CPF allows you to save for retirement and access housing grants.
Eligibility Criteria for Singapore PR
1. Professional, Technical Personnel, and Skilled Workers (PTS) Scheme
- Who Can Apply: Individuals working in Singapore under an Employment Pass or S Pass.
- Requirements:
- Stable employment in Singapore.
- Regular CPF contributions.
- Employment in sectors that contribute to the economy.
2. Family Ties Scheme
- Who Can Apply:
- Spouses of Singapore citizens or PRs.
- Unmarried children below 21 years old of Singapore citizens or PRs.
- Aged parents of Singapore citizens.
3. Global Investor Programme (GIP)
- Who Can Apply: High-net-worth individuals who invest significantly in Singapore’s economy.
- Requirements:
- Minimum investment of SGD 2.5 million in a new or existing business or approved fund.
4. Foreign Artistic Talent Scheme (ForArts)
- Who Can Apply: Artists, performers, and other creative professionals with a strong track record.
- Requirements:
- Significant contribution to Singapore’s arts and culture scene.
5. Student Scheme
- Who Can Apply: Foreign students studying in Singapore.
- Requirements:
- Outstanding academic performance.
- Active participation in co-curricular activities.
Step-by-Step Guide to Applying for Singapore PR
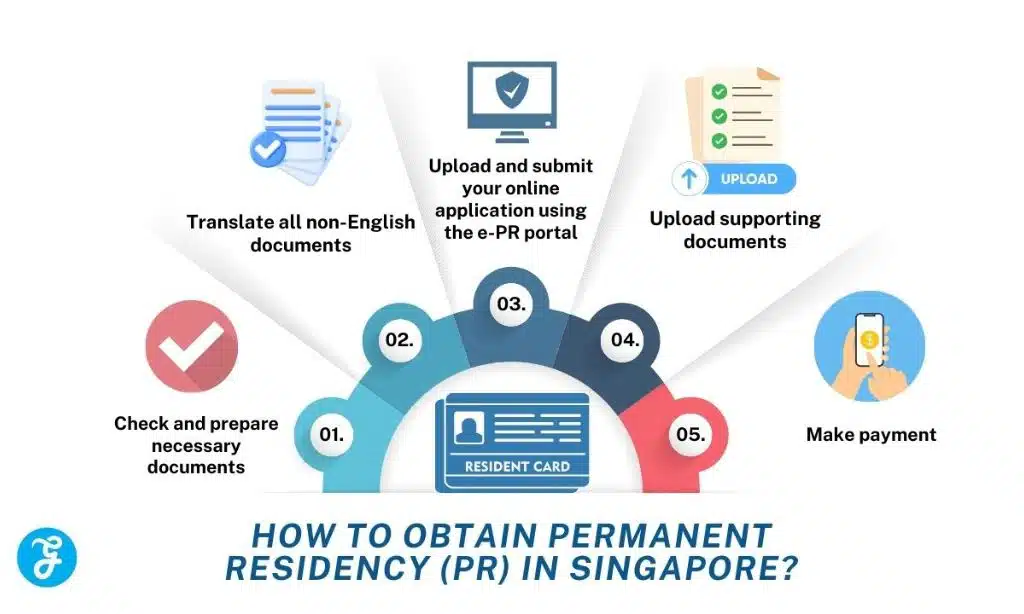
1. Assess Your Eligibility
- Determine the scheme that best applies to your situation.
- Review the specific requirements for your chosen scheme.
2. Gather the Required Documents
| Document Type | Examples |
| Personal Identification | Passport, birth certificate, marriage certificate (if applicable). |
| Employment Records | Employment pass, payslips (6 months), CPF contribution records, tax returns (last 3 years). |
| Educational Certificates | Academic transcripts, diplomas, or degrees. |
| Financial Documents | Bank statements, CPF statements, proof of investments (for GIP applicants). |
| Family Documents | Birth certificates of children, spouse’s documents, proof of relationship to a Singapore citizen or PR. |
Important: Translate all non-English documents into English and have them certified.
3. Submit Your Application via the ICA e-PR Portal
- Visit the ICA e-PR Portal.
- Create an account and log in.
- Complete the application form and upload required documents.
- Pay the non-refundable application fee (SGD 100).
- Review and submit your application.
4. Track Your Application
- Processing typically takes 4–6 months.
- Use the ICA portal to monitor the status of your application.
- Be responsive if ICA requests additional documents.
5. Await the Outcome
- Approval: You’ll receive an In-Principle Approval (IPA) letter with instructions for completing PR formalities.
- Rejection: ICA does not provide specific reasons for rejection. Consider improving your profile (e.g., career stability, community contributions) and reapply after 6 months.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Incomplete Documentation: Missing or incorrect documents can delay processing or lead to rejection.
- Inaccurate Information: Ensure all details match official records.
- Weak Integration Evidence: Lack of community involvement or poor employment history can weaken your application.
- Delays in Submission: Missing deadlines for additional documents can harm your chances.
Tips to Strengthen Your Application
- Contribute to the Community: Volunteer in local events or join community organizations to show commitment to Singaporean society.
- Demonstrate Financial Stability: Maintain regular CPF contributions and showcase stable earnings.
- Highlight Long-Term Plans: Include a personal statement explaining your intent to build a life in Singapore.
- Seek Professional Help: Immigration consultants can help optimize your application.
Singapore PR Schemes at a Glance
| Scheme | Eligibility | Key Requirements | Processing Time | Application Fee (SGD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Professionals/Technical Personnel & Skilled Workers (PTS) Scheme | Holders of Employment Pass or S Pass. | Stable employment in Singapore; contributions to the Central Provident Fund (CPF). | Approximately 6 months | $100 per applicant |
| Family Ties Scheme | Spouses, unmarried children (under 21), or aged parents of Singapore citizens or PRs. | Proof of relationship (e.g., birth or marriage certificates). | Approximately 6 months | $100 per applicant |
| Global Investor Programme (GIP) | High-net-worth investors. | Minimum investment of SGD 2.5 million in a qualifying business or fund; submission of comprehensive business documents. | Varies; subject to individual assessment | $7,000 per applicant |
| Foreign Artistic Talent (ForArts) Scheme | Artists and professionals in the arts and culture sector. | Significant contributions to Singapore’s arts and cultural scene; strong track record in relevant fields. | Approximately 6 months | $100 per applicant |
| Student Scheme | Foreign students studying in Singapore. | Outstanding academic performance; completion of at least one national examination (e.g., PSLE, GCE ‘N’/’O’/’A’ levels) or enrollment in the Integrated Programme (IP). | Approximately 6 months | $100 per applicant |
Additional Notes:
- Submission: All applications must be submitted online through the Immigration & Checkpoints Authority (ICA) e-Service platform.
- Payment: Fees are non-refundable and payable online.
- Other Fees: Additional fees apply for the entry permit, re-entry permit, and Singapore Identity Card after approval.
- National Service: Male applicants may have National Service obligations under the Enlistment Act.
This table is based on data verified from official sources like the ICA website.
Tax Information for Each PR Scheme in Singapore
Learn how Singapore’s tax policies align with its reputation as a global financial hub. Here’s what each PR scheme means for your tax commitments.
Professionals/Technical Personnel & Skilled Workers (PTS) Scheme
As a PR under the PTS scheme, you are considered a tax resident if you stay or work in Singapore for at least 183 days in a calendar year. Key tax details include:
- Income Tax:
- Income up to SGD 20,000: 0%
- SGD 20,001 to SGD 30,000: 2%
- SGD 30,001 to SGD 40,000: 3.5%
- SGD 40,001 to SGD 80,000: 7%
- SGD 80,001 to SGD 120,000: 11.5%
- SGD 120,001 to SGD 160,000: 15%
- SGD 160,001 to SGD 200,000: 18%
- SGD 200,001 to SGD 320,000: 19%
- Above SGD 320,000: 24%
- CPF Contributions: Both employer and employee must contribute based on monthly wages:
- Total CPF contribution rate: Up to 37% (split between employer and employee).
- Contributions reduce as the individual ages.
- Tax Reliefs: Eligibility for CPF relief, earned income relief, and family-related reliefs such as spouse and child relief.
Family Ties Scheme
PRs under the Family Ties Scheme are taxed similarly to those in the PTS scheme if they meet the 183-day residency requirement. Additional considerations include:
- Income Tax: Progressive tax rates as outlined above.
- Property Tax:
- Owner-occupied residential properties: 0% to 23%, depending on annual value.
- Non-owner-occupied properties: 12% to 36%.
- CPF Contributions: Employed family members contribute similarly to the PTS scheme.
Global Investor Programme (GIP)
High-net-worth individuals under the GIP may face specific tax implications:
- Corporate Tax: Flat 17% on business profits, with partial exemptions for smaller firms:
- First SGD 10,000 of taxable income: 75% exemption.
- Next SGD 190,000 of taxable income: 50% exemption.
- Income Tax: Follows the progressive tax rates outlined above.
- Investment Taxation:
- Capital gains and foreign-sourced income (not remitted to Singapore) are tax-exempt.
- Dividend income from qualifying companies may be exempt.
- Stamp Duties on Property Purchases:
- Additional Buyer’s Stamp Duty (ABSD) of up to 30% for high-value property acquisitions.
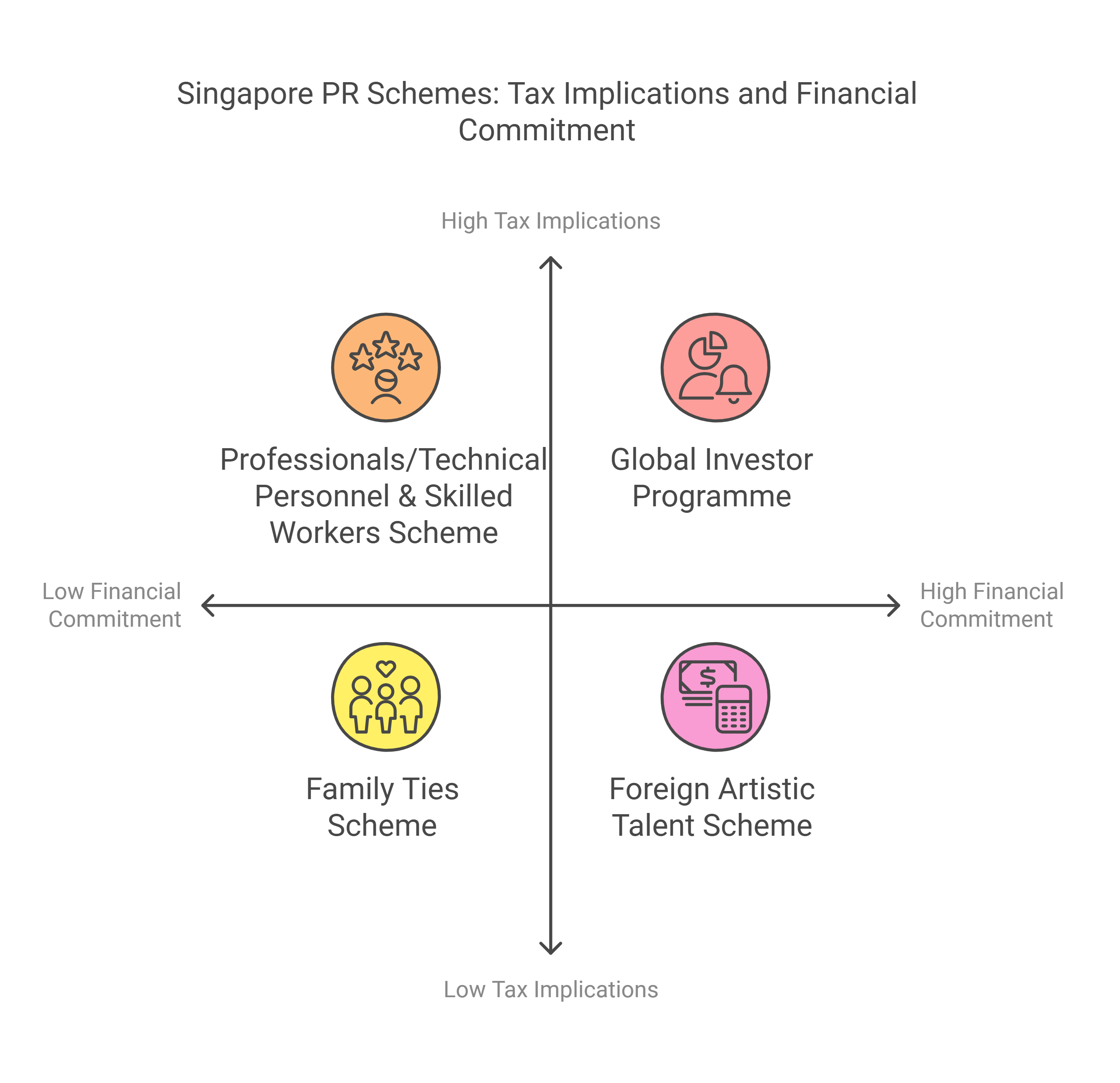
Foreign Artistic Talent (ForArts) Scheme
PRs under the ForArts Scheme are often self-employed or freelance professionals. Tax obligations include:
- Income Tax: Progressive tax rates as outlined above.
- Self-Employed Contributions:
- MediSave contributions required based on annual net trade income:
- Up to 10.5% for annual incomes exceeding SGD 50,000.
- MediSave contributions required based on annual net trade income:
- GST Registration: Mandatory if annual revenue exceeds SGD 1 million. GST rate is 8% (increasing to 9% from 2024).
- Tax Deductions: Includes expenses related to creative work, such as studio rental, materials, or travel costs.
Student Scheme
Foreign students who gain PR status and engage in employment must adhere to these tax requirements:
- Income Tax: Progressive tax rates as outlined above, applicable if income exceeds SGD 22,000 annually.
- CPF Contributions:
- First and second year of PR status: Lower transitional rates (employer: 7.5%, employee: 5%).
- Full contribution rates apply from the third year.
- Tax Reliefs: Generally limited, unless the student becomes financially independent and meets criteria for earned income relief.
Can Singapore PR Be Available for Foreign Source Income Criteria?
Singapore Permanent Residency (PR) is generally not granted directly based on foreign-sourced income. Instead, PR eligibility is assessed under specific schemes, each with defined requirements. While foreign-sourced income alone doesn’t qualify someone for PR, it may indirectly support an application, especially under the Global Investor Programme (GIP) or similar criteria.
Taxation on Foreign-Sourced Income
Foreign-sourced income that is not remitted to Singapore is exempt from taxation. However, remitted income may be subject to Singapore tax laws unless exempt under specific provisions. For example:
- Certain exemptions apply to foreign-sourced dividends, branch profits, and service income if remitted under qualifying conditions.
- This favorable tax environment can make Singapore appealing for high-net-worth individuals, but it is not a standalone PR eligibility factor.
Takeaways
Obtaining permanent residency in Singapore is a multi-step process that requires careful preparation, comprehensive documentation, and a clear understanding of the eligibility criteria. Whether you’re a skilled professional, an investor, a student, or a family member, there is a pathway suited to your background.
By following this guide, presenting a strong case, and demonstrating your commitment to contributing to Singaporean society, you can significantly enhance your chances of approval. Obtaining PR status not only guarantees your residency in Singapore but also provides access to a multitude of opportunities for a more promising future.