In the fast-moving digital arena of today, businesses use software and IT systems to manage day-to-day operations, store sensitive information and keep communication lines open. But not updating these systems amounts to huge security threats. Such vulnerabilities are exploited by hackers to attack, steal, or disrupt. Software patch management is a subset of cybersecurity that ensures that timely updates, bug fixes, and security patches for vulnerabilities are applied to the IT infrastructure. An organization that lacks the efficacy of patching can willingly be attacked by malware, suffer ransomware attacks, and suffer failures of the systems. The establishment of a well-structured patching approach helps in drastically decreasing security risks, boosting operational efficiency, and enforcing regulatory compliance. For a company to reap these rewards, it needs to create a complete patch management program that encompasses the entire patching life cycle with security as a priority.
Assessing Your Patch Management Needs
Before one implements a patch management program, one needs to evaluate the environment that is currently in place in order to identify specific needs and challenges. This would involve identifying the software, operating systems, and network devices that require routine updates. Organizations also need to consider the potential risk caused by any unpatched vulnerabilities and the possible impact that delays in patching may have on their respective businesses. An inventory of all IT assets will serve as a baseline for the monitoring and management of updates. By analyzing past security incidents concerning outdated software, businesses can understand their patching priorities and develop a proper risk-based approach to vulnerability management.
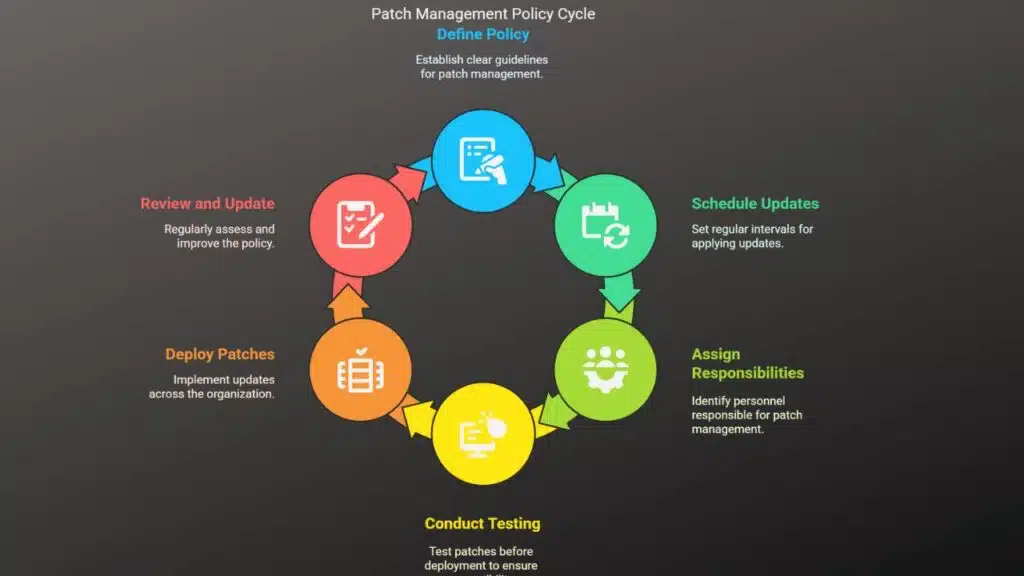
Framework for Constructing a Patch Management Policy
An organized patch management program starts with a clearly defined policy that lays down the processes and best practices of applying security updates. This policy should indicate the frequency with which updates will be installed, the responsible personnel with regards to patch management, as well as testing procedures before deploying patches. It will also include the emergency security patching guidelines when certain severe vulnerabilities come to light. A well-structured patching policy guarantees its uniformity across the entire organization thereby reducing instances of missed updates or configuration errors that may render systems vulnerable to an attack by cyber criminals.
Testing and Validation of Patches Before Deployment
Testing the patch set before deployment into the entire patch management system is one of the prime steps under the patch management systems. Although security patches remedy vulnerabilities, they will bring compatibility problems in the application of already established workflows, and sometimes they may even crash the system. To avoid unintentional disruption, it is advised for an organization to have an environment created where all patches will first be applied to that environment. This environment should mimic real-world conditions such that the impact of the patch can be tested and any interferences on pertinent applications noted. Once the patch status is verified for stability, the fix can then be scheduled for deployment throughout the system.
Conclusion
A well-structured patch management program should be one of the strongest linkers of the cyber defense circuitry. Undoubtedly, the patch management program of any organization is probably the most cost-effective process in all cost-effective aspects of risk assessment, avoidance, and transfer. Automation, then, is a major healthy factor to efficiency, while reducing the time among IT teams to strategize on greater security initiatives, without losing the key patch.