Working with databases can feel complicated for web developers, especially if you don’t know where to start. Whether it’s retrieving data, updating records, or combining tables, SQL queries are essential tools every developer needs to master.
Without them, handling real-world data efficiently becomes a challenge.
SQL is the backbone of relational databases and powers many applications we use daily. Knowing the right queries helps in managing database schemas and ensures smooth data retrieval and manipulation.
This blog will guide you through 7 essential SQL queries for every web developer should know to improve efficiency and enhance your skills.
Ready to enhance your knowledge? Keep reading!
Select Data from a Table
The SELECT statement retrieves data from one or more database tables. It is a fundamental SQL command, essential for data analysis and management in relational databases. For example, `SELECT * FROM employees;` fetches all records from the “employees” table.
You can also target specific columns like `SELECT name, age FROM employees;` to focus on particular details.
SQL queries using SELECT allow users to analyze data quickly and effectively. Structured Query Language ensures precise control over which information gets displayed by combining SELECT with conditions or filters later on.
This makes it an indispensable tool for web developers working with database management systems such as SQL Server or IBM DB2.
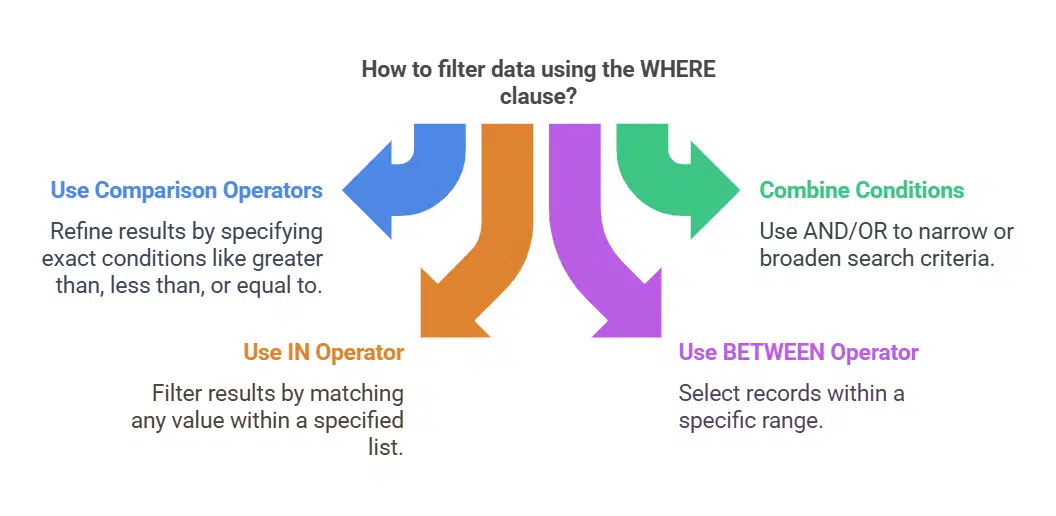
Filter Data with WHERE Clause
Use the WHERE clause to filter database queries based on specific conditions. For instance, retrieve customers born after 1990 using `SELECT * FROM Customers WHERE BirthYear > 1990;`.
Operators like `>`, `<`, and `=` refine these results. Combine multiple conditions with AND or OR for more precise filtering. To find users from both California and Texas, use `WHERE State IN (‘California’, ‘Texas’)`.
Search within a range by applying BETWEEN. Query orders placed between January 1 and March 31: `SELECT ‘FROM Orders WHERE OrderDate BETWEEN ‘2023-01-01’ AND ‘2023-03-31’;`. Exclude null values with IS NOT NULL to avoid incomplete records.
Use this feature in SELECT statements or data manipulation commands like UPDATE when refining datasets in relational databases.
Sort Data Using ORDER BY
The ORDER BY clause sorts query results in ascending or descending order. This improves readability and helps organize data effectively. For instance, a query like `SELECT Name, Salary FROM employees ORDER BY Salary DESC;` lists employees by their salary from highest to lowest.
By default, it arranges data in ascending order unless you specify otherwise.
You can combine the ORDER BY clause with multiple columns for detailed sorting. For example, `SELECT Name, Department FROM employees ORDER BY Department ASC, Name ASC;` first organizes by department alphabetically and then by employee name within each department.
Use this tool to make relational database management more efficient and clear during analysis.
Use Joins to Combine Data from Multiple Tables
SQL joins help merge data from different tables in a relational database. INNER JOIN fetches matching records from both tables, often using shared columns like foreign keys. For example, joining an “orders” table with a “customers” table retrieves orders linked to their respective customer details.
LEFT JOIN pulls all rows from the left table and matched ones from the right; unmatched rows show NULL values. RIGHT JOIN works similarly but prioritizes the right table. FULL OUTER JOIN fetches everything, with NULLs filling gaps where matches do not exist.
Combining multiple joins can extract data spanning three or more tables efficiently for comprehensive queries.
Group Data with GROUP BY
The GROUP BY clause organizes rows by one or more columns. It works well for data aggregation in relational databases. For example, you can sum orders per customer using this query: `SELECT customer_id, SUM(order_amount) AS total_order_amount FROM orders GROUP BY customer_id;`.
This groups all rows with the same `customer_id` and calculates totals.
You can group data on multiple columns to enhance detail. For instance, break down sales by both year and month using functions like YEAR() and MONTH(). Use the HAVING clause to filter grouped results based on conditions post-grouping.
Aggregate functions such as COUNT(), AVG(), MAX(), MIN(), or STDDEV simplify analysis during query execution plans in relational database management systems (RDBMS).
Insert New Records into a Table
Use the `INSERT INTO` statement to add new records in SQL tables. Specify the table name, columns, and values you want to insert. For example: `INSERT INTO employees (Name, Department, Salary) VALUES (‘John Smith’, ‘HR’, 60000);`.
Confirm that data types match column definitions and follow primary key or unique key constraints.
Ensure data integrity by respecting foreign key constraints and other rules. Adding correct information improves database management and prevents errors. In web development, inserting user profiles or transaction logs into relational databases is a frequent task handled through SQL commands like this one.
Update Existing Records in a Table
The `UPDATE` command changes data in existing records within a relational database. It pinpoints specific rows using a condition in the `WHERE` clause. For example, modifying an employee’s salary can look like this: `UPDATE employees SET Salary = 50000 WHERE Name = ‘John’;`.
Without the `WHERE` clause, every record in the table will change.
Testing updates on a staging database ensures safety and accuracy. SQL performance optimization also improves with proper conditions to avoid unnecessary updates. Always verify your query before running it on live systems.
Delete Records from a Table
SQL DELETE statements remove specific rows from a table while keeping its structure intact. Omitting the WHERE clause deletes all records, which can lead to accidental data loss. For example, running `DELETE FROM orders;` wipes every entry in the “orders” table.
To target specific entries safely, always pair DELETE with a WHERE condition. A safer query would look like: `DELETE FROM orders WHERE order_id = 5;`.
Wrap deletion queries within transactions to allow rollbacks if errors occur. For instance, using `BEGIN TRANSACTION; DELETE FROM users WHERE user_role = ‘guest’; ROLLBACK;` restores data if needed during troubleshooting or testing.
This approach ensures data integrity and avoids permanent mistakes in relational databases like MySQL or MS SQL Server. Always test these commands first in a development environment before executing them on live systems!
Use Subqueries for Advanced Data Retrieval
Subqueries simplify advanced data retrieval in relational databases by nesting one query inside another. Use them to solve complex problems like correlating data from multiple tables or performing calculations.
For example, a subquery within the SELECT clause can fetch customer names and their total order counts. Subqueries in the WHERE clause filter product names based on matching product IDs from specific orders.
Correlated subqueries dynamically match rows, improving SQL performance optimization for detailed analysis tasks. These are crucial for relational database management systems (RDBMS) when working with large datasets or linked tables using primary and unique keys.
Avoid redundancy by applying subqueries strategically, ensuring clean and efficient database queries under acid compliance rules.
Limit Results with TOP or LIMIT
The SELECT TOP clause helps limit the number of records in SQL Server or MS Access. For instance, `SELECT TOP 5 * FROM Customers` retrieves only the first five rows. MySQL uses LIMIT instead, as shown in `SELECT * FROM Orders LIMIT 10`, which fetches ten results.
Oracle handles this differently with FETCH FIRST or ROWNUM depending on its version. A query like `SELECT * FROM Employees FETCH FIRST 3 ROWS ONLY` restricts output to three rows. These methods improve data retrieval efficiency and streamline performance across relational databases.
Takeaways
Mastering these SQL queries will sharpen your database skills. They help you retrieve, manipulate, and manage data efficiently. Web developers use them daily to handle real-world projects.
Focus on learning each query step by step for better results. Strong SQL knowledge sets a solid foundation for working with relational databases confidently.
FAQs on Essential SQL Queries Every Web Developer Should Know
1. What are SQL queries, and why are they important for web developers?
SQL queries are commands used to interact with relational databases. They help web developers retrieve, manipulate, and manage data efficiently in database management systems like RDBMS.
2. What is the purpose of using joins in SQL?
Joins, such as inner join, left join, right join, and full outer join, combine data from multiple tables based on related columns. They simplify working with relational databases by connecting meaningful datasets.
3. How can I filter data effectively in SQL?
You can use the WHERE clause or pattern matching techniques to filter specific rows that meet your conditions within a table or query result.
4. Why is query optimization essential for web development?
Query optimization improves SQL performance by making data retrieval faster and reducing server load. Techniques like indexing (IDX), prepared statements, and proper use of parameters enhance efficiency.
5. What role do primary keys play in database integrity?
Primary keys ensure each row in a table is unique while maintaining referential integrity between linked tables in relational database management systems.