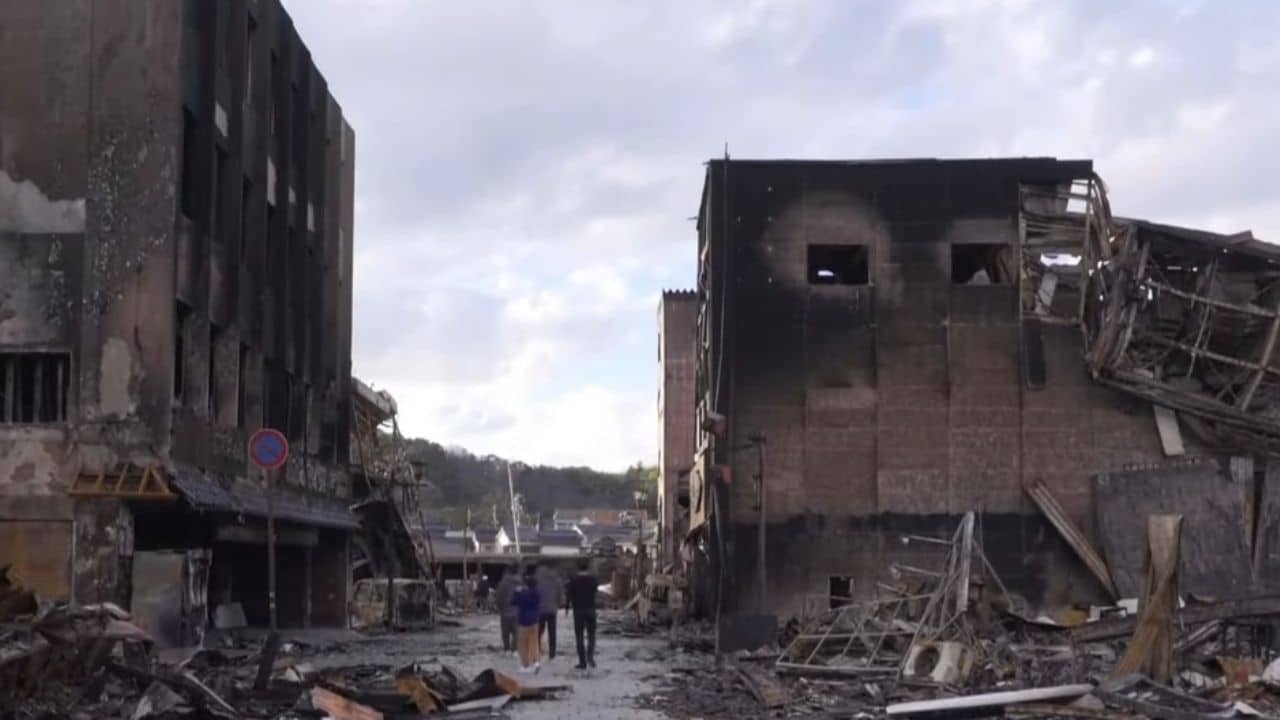
Are you aware of the risk of a possible earthquake in Bangladesh? It is estimated that a major 8-9 magnitude quake could occur on the Richter scale soon. Do you know if Bangladesh is ready to face such an event?
This blog post will provide insights on earthquake preparation in Bangladesh and also the earthquake disaster situation.
In this article, we’ll unearth the issue and discuss historical data related to past quakes, vulnerable areas, and initiatives taken by stakeholders for improved seismic safety.
So let’s find out together – Is Bangladesh Prepared To Face The Rage Of An Earthquake?
Content Highlights
- Bangladesh’s geographical position, population density, and city expansions put it at risk for earthquakes.
- Historical earthquakes like the 1897 Assam Earthquake, the 1950 Assam – Tibet Earthquake, and the 2003 Chittagong earthquake have had catastrophic effects on the country.
- Areas such as Dhaka City, other major cities, and coastal regions are particularly vulnerable to strong seismic activity due to liquefaction of soils and poor building structures.
- Disaster preparedness techniques such as Early Warning Systems (EWS), and Risk Identification and preparedness (RIP) planning need to be implemented in order to help reduce destruction by future quakes.
Related Articles: Burmese Tectonic Plate and The Risk of a Massive Earthquake in Bangladesh and India
Why Earthquakes Are a Concern in Bangladesh?
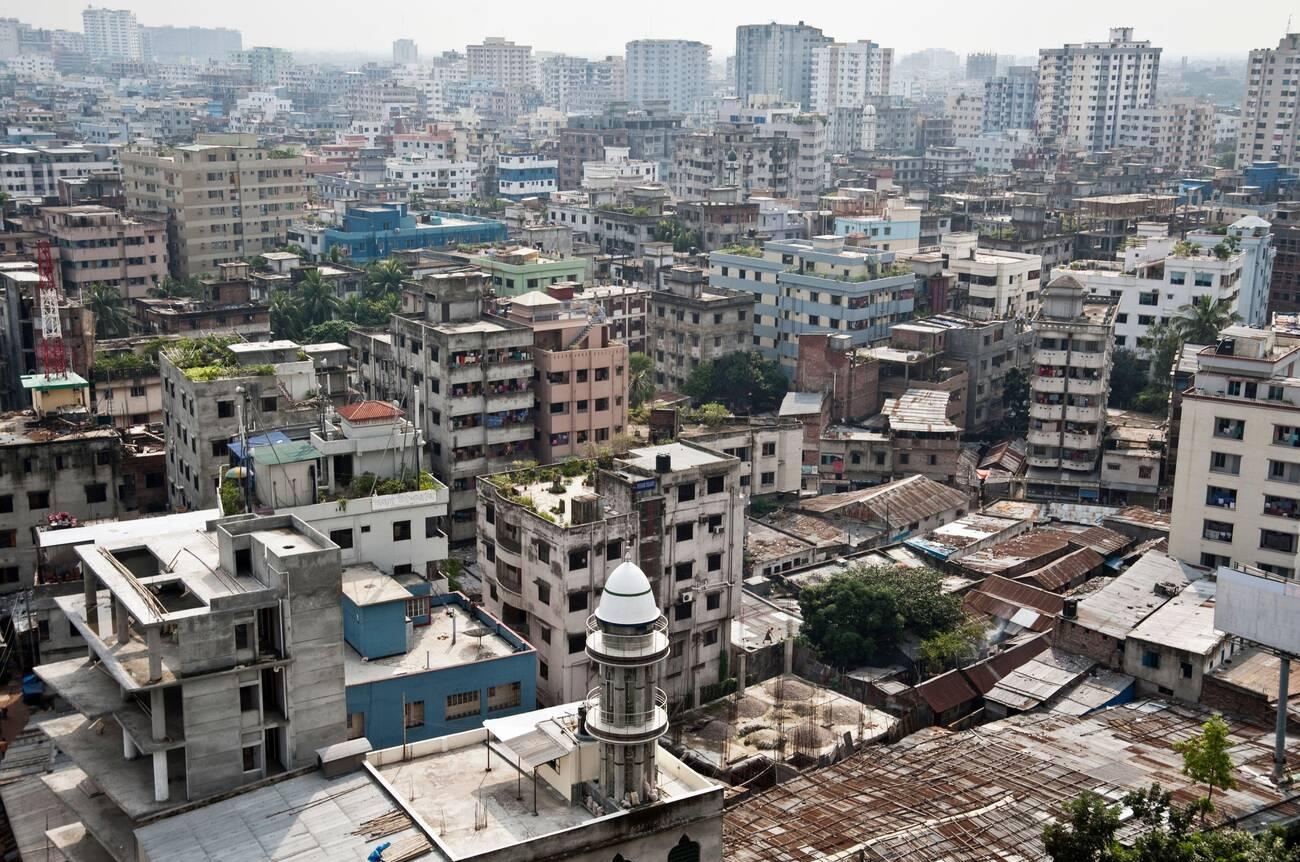

Bangladesh is particularly vulnerable to earthquakes due to its geographical location, the expansion of cities, high population density, and the impacts of liquefaction.
Geographical Location
Bangladesh is located in a seismically active region between several distinct and separate seismic zones within its borders and the adjacent regions of India, Myanmar, and Nepal.
This fragile territory lies at the intersection of three tectonic plates – Eurasia, Indian-Australia plate, and Sunda Plate – making it extremely vulnerable to deadly earthquakes. Bangladesh’s geographical position has been highlighted by a Modified Mercalli Intensity map which indicates the areas most susceptible to tremor effects from an earthquake if it happens there.
The nation possesses an abundant number of poorly constructed buildings that can collapse quickly during even a mildly strong tremor or moderate quake shock wave, further accentuating its vulnerability to devastating natural disasters like earthquakes.
Expansion of Cities
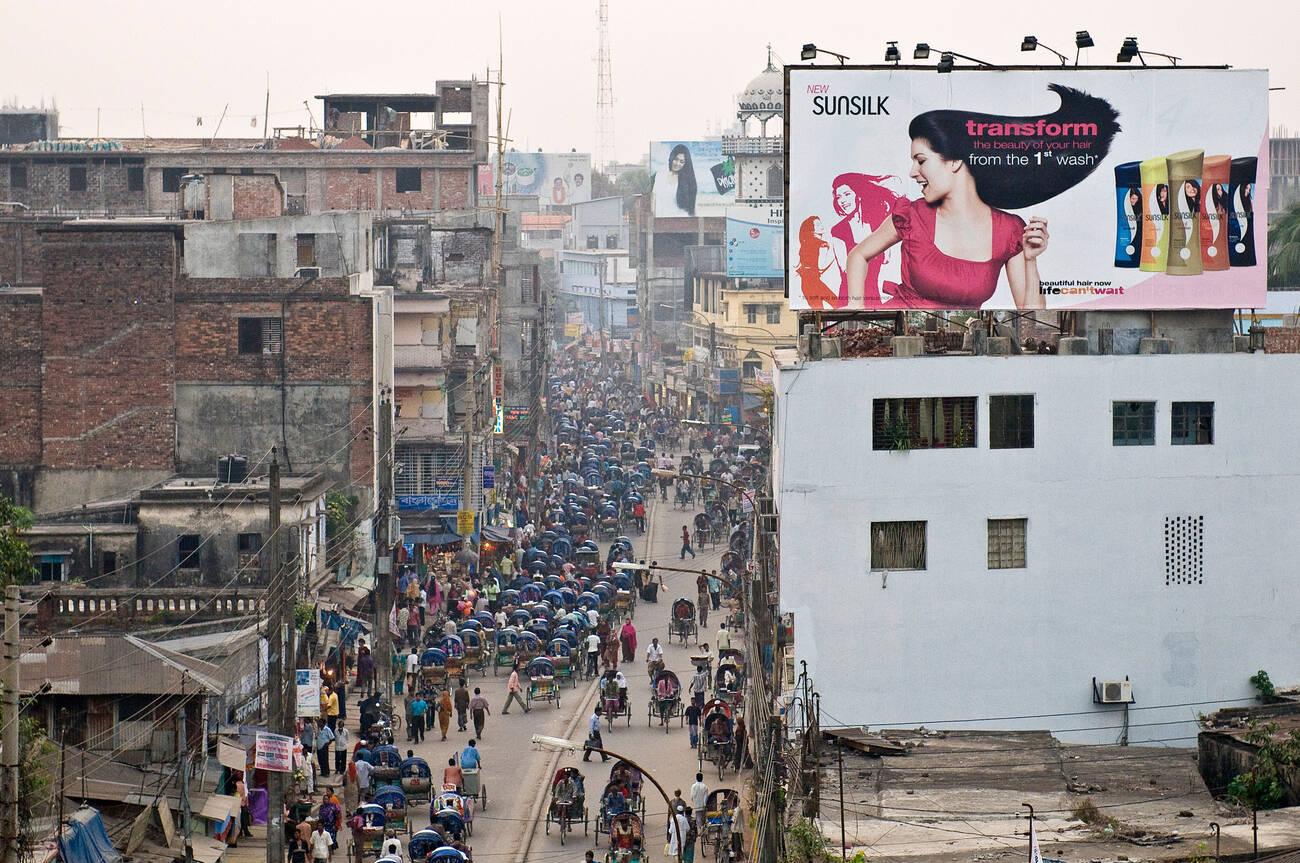
The expansion of cities in Bangladesh has been growing exponentially, with Dhaka city being at the forefront. As urban areas become denser and broader, they are more vulnerable to earthquakes.
This is because an expanding area requires constantly shifting soil substrate, amplifying ground shaking due to seismic activity. The ever-growing population density in these cities means that more lives will be impacted if saturated soils liquefy during a quake, causing further destruction and casualties thereafter.
Furthermore, without proper planning or preventive regulations imposed for building codes and geotechnical assessments at foundation levels prior to projects taking place can aggravate damages when an earthquake does hit as buildings may collapse from lack of safe support systems implemented beneath them.
High Population Density
here are some of the most earthquake-vulnerable cities in the world, including Dhaka, with their population and population density per km2.
|
City |
Population |
Population Density (per km2) |
|
Manila, Philippines |
1,846,513 |
42,857 |
|
Kathmandu, Nepal |
1,442,000 |
29,161 |
|
Dhaka, Bangladesh |
23,209,616 |
23,234 |
|
Jakarta, Indonesia |
18,400,000 |
14,464 |
|
Tehran, Iran |
24,839,000 |
13,800 |
|
New Delhi, India |
29,399,141 |
11,297 |
|
Lima, Peru |
21,035,504 |
8,001 |
|
Tokyo, Japan |
37,435,191 |
6,158 |
|
Istanbul, Turkey |
15,519,267 |
6,042 |
|
Mexico City, Mexico |
21,581,000 |
5,540 |
|
Quito, Ecuador |
1,957,000 |
5,500 |
|
Beirut, Lebanon |
2,000,000 |
3,500 |
|
Los Angeles, United States |
3,898,747 |
3,295 |
Among the earthquake-vulnerable cities worldwide, Dhaka presents a distinctive concern due to its significantly high population density of 23,234 people per square kilometer.
When compared to other cities on the list, such as Jakarta, Tokyo, and Beirut, Dhaka’s population density is notably higher, making it particularly susceptible to the devastating impact of a major earthquake. This emphasizes the urgent need for Dhaka and similar high-density cities to prioritize earthquake preparedness and mitigation strategies to safeguard their populations in the event of seismic activity.
In addition, the dense population throughout the Ganges Basin places people at greater risk from other natural disasters, such as tornadoes. Due to limited resources and over-population within these areas, there is an increased strain on responding to disaster relief efforts which can be difficult or even impossible depending on the scale of damage caused by an earthquake.
Poorly constructed buildings are also more likely to crumble during a quake in highly populated areas than in rural locations, thus leading to higher casualty rates if an earthquake does occur, challenging emergency response teams even further when trying to provide aid and support during a crisis situation.
Impacts of Liquefaction
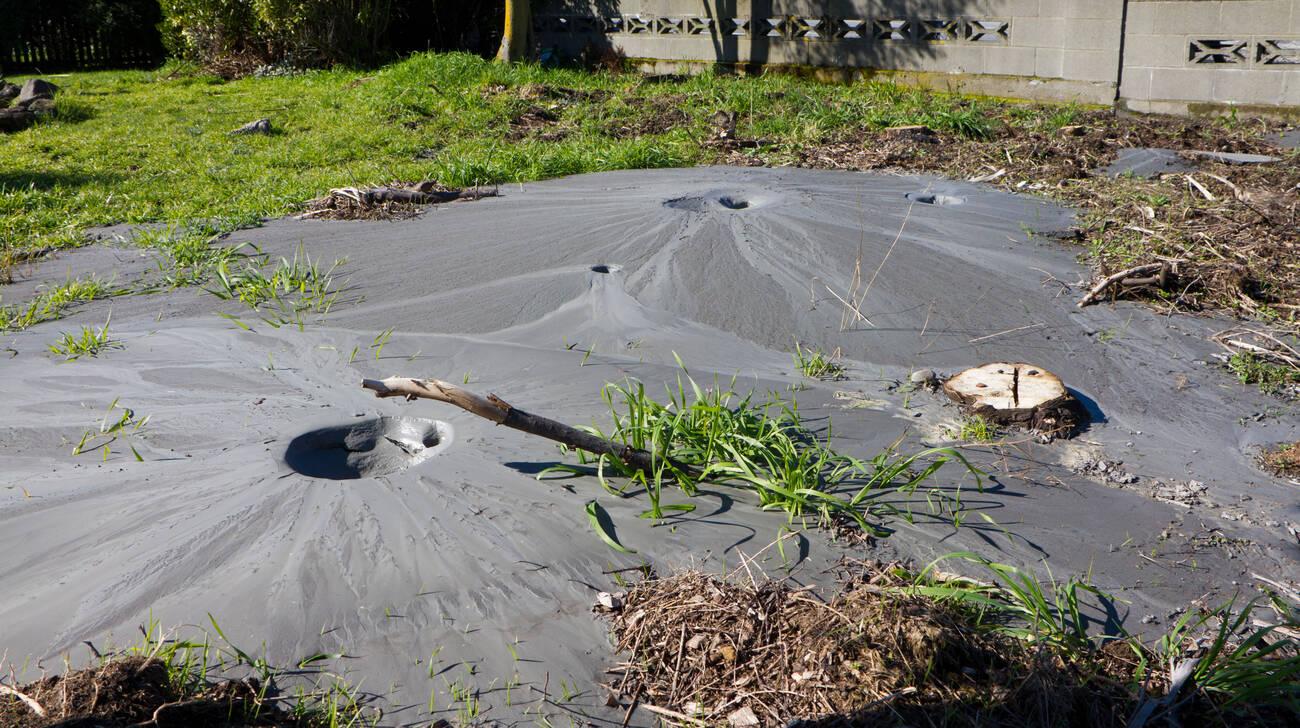

Liquefaction is a process by which the soil loses strength during an earthquake, causing it to behave like a liquid and resulting in significant damage to infrastructure and buildings.
Bangladesh’s dense population and lack of preparedness increase its vulnerability to liquefaction from earthquakes. Dhaka city’s expansion towards the east and southwest has made it particularly vulnerable due to unwanted changes in local geology.
The 1950 Assam-Tibet Earthquake was an example of this type of destruction when more than 1,500 people died due to the collapse of structures caused by increased liquefaction at Mirzapur village near Mymensingh district.
In addition, liquefied sand found over 30 feet above sea level in the Jhenaidah district also indicates this phenomenon after the 1997 National Jadeen Fulchari earthquake, as indicated in Important Facts.
Historical Earthquakes in Bangladesh
Bangladesh has faced powerful earthquakes in the past, such as the 1897 Assam Earthquake and the 1950 Assam-Tibet Earthquake. Read further to learn more about how this affects today’s population of Bangladesh.
1897 Assam Earthquake
The 1897 Assam Earthquake is considered one of the deadliest earthquakes in world history and was significant by big magnitude. On June 12, 1897, the Assam earthquake hit with an estimated moment magnitude of 8.2-8.3 and had far-reaching impacts on the region today known as India and Bangladesh.
This devastating quake shook a vast area of approximately 600 km stretching from Sadiya in Arunachal Pradesh to Jaintia Hills in present Meghalaya state., triggering landslides that damaged roads leading to difficult rescue operations carried out by officials later on.
Additionally, widespread destruction was seen throughout Assam, Meghalaya, and Bangladesh regions due to this destructive quake. Eight villages were destroyed within a couple of minutes, killing more than 15,000 people instantly, while march casualties rose up to 20,000 people, including other related death tolls such as disease epidemics caused by seismic waves due to severe famine prevailing at that time of year.
1950 Assam-Tibet Earthquake
On August 15, 1950, the Assam-Tibet Earthquake occurred with a moment magnitude of 8.7. Located in Assam, eastern India, this right-lateral strike-slip earthquake caused significant damage to the region.
The resulting seismic waves were felt all over, and seismographs recorded it from as far away as Tokyo. The intense shaking shattered cement houses and trembles while creating deep fissures in roads and railway lines in some parts of Assam that few remained useable until repairs had been made.
In addition to property destruction, hundreds of lives were lost due to collapsing buildings or landslides triggered by the quake’s intensity near steep hillsides along its path of destruction.
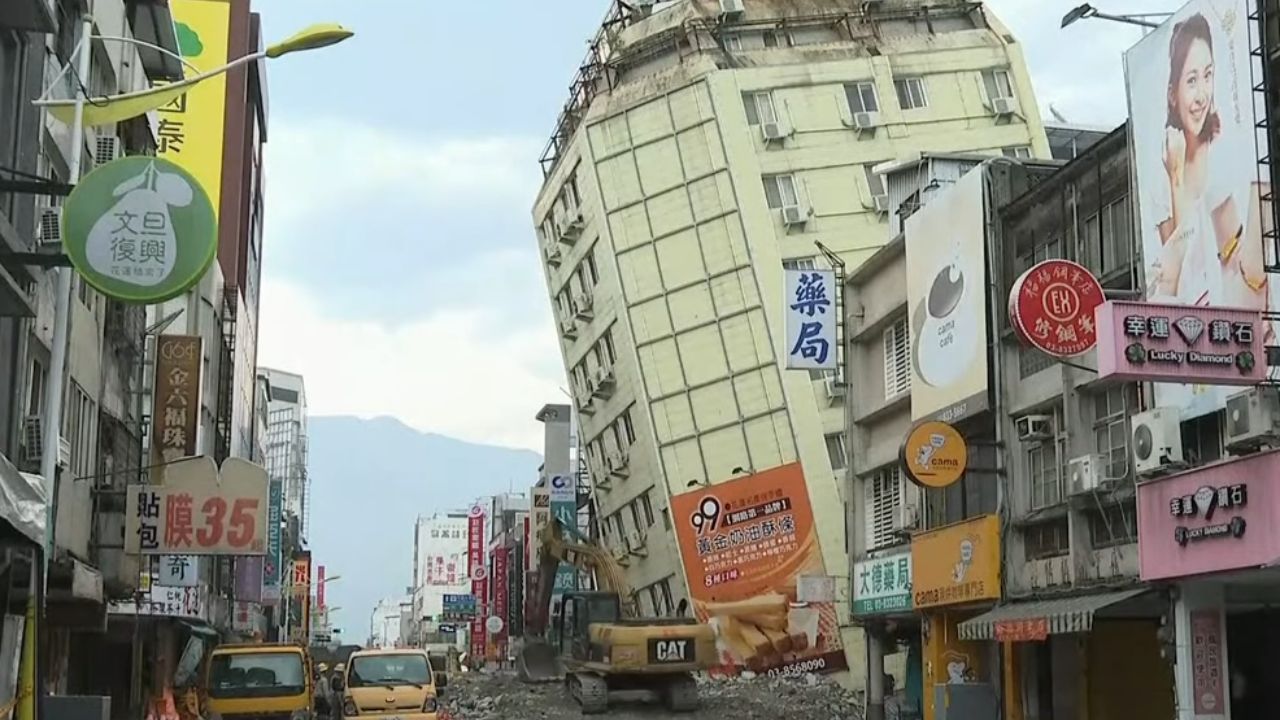
2003 Chittagong Earthquake
The 2003 Chittagong Earthquake was one of the most destructive earthquakes to ever hit Bangladesh, with a magnitude of 7.8 on the Richter scale. It caused significant destruction and loss of life due to its epicenter near the Myanmar border, generating tremors strongly felt as far as Dhaka, the capital city of Bangladesh.
This earthquake is associated with two other historical earthquakes in Assam and Tibet (in 1897 & 1950, respectively) that also had severe effects on Bangladesh, along with highlighting vulnerability issues such as rapid expansion in urban areas, high population density, liquefaction effect on soils, etc., all renewed conversations regarding disaster preparedness and safety precautions for the entire country.
Vulnerable Areas in Bangladesh
Dhaka City and other major cities such as Rajshahi, Chittagong, Barisal, and Sylhet as well as areas along the coastal strip, are prone to high seismic activity.
Dhaka City
Dhaka, the capital of Bangladesh, faces a high risk of earthquakes due to its geography and population density. Approximately 23,209,616 people live in a 300 square kilometer area, making Dhaka one of the world’s densest cities.
Additionally, slums are widespread throughout the city, and poverty rates are high; these issues can make it difficult for those living in low-income areas to prepare for disasters like earthquakes adequately.
To add insult to injury, experts have warned that many buildings within Dhaka were not designed with earthquake resistance standards due to the lack of consensus among national architectural authorities.
Mymensingh
Mymensingh, situated in the most earthquake-vulnerable zone of Bangladesh, faces significant seismic risks. The region is encircled by multiple fault lines, including the Madhupur Blind Fault, exacerbating the earthquake threat. With a population density that demands attention, preparedness and mitigation efforts become paramount, particularly considering the potential impact on vulnerable communities residing in low-income areas.
Sylhet
Sylhet, in northeastern Bangladesh, along with portions of Chittagong and the Chittagong Hill Tracts, is also acknowledged as an earthquake-prone zone. These areas need to be vigilant about earthquake preparedness, considering their geographical susceptibility. Similar to Dhaka, ensuring the resilience of buildings in these regions is of utmost importance, given the known seismic risks in the country.
Other Major Cities
In Bangladesh, other major cities, such as Chittagong, Khulna, and Rajshahi, are also vulnerable to seismic activity. These metropolitan areas experience high levels of population density with overcrowded buildings and a lack of proper planning for potential disasters.
As most structures are built on or near fault lines, there is an increased risk of destruction in the event of an earthquake. The shallow depth of coastal plains also increases coastal vulnerability, as evidenced by the extensive damages caused by the 2003 Chittagong Earthquake, devastatingly impacting these cities.
Additionally, regions close to major riverbeds and bridges can suffer from liquefaction, as witnessed during past earthquakes like that in the 1950 Assam-Tibet Earthquake took its toll on major infrastructure across Bangladesh, including highways, roads, and bridges.
To mitigate this hazard, it is important to take proactive measures such as reinforcing existing building codes or introducing strict regulations for newer constructions in order to ensure protection against seismic activity.
Coastal Areas
Located near the Bay of Bengal, Bangladesh is vulnerable to natural hazards such as cyclones and floods. Coastal areas, in particular, are prone to strong winds and heavy downpours, which can cause widespread destruction when coupled with rising sea levels.
In addition, poor sanitation also impacts the severity of cyclone-related disasters – open latrines and waste sitting on land surfaces lead to further contamination if they become submerged in water.
Infrastructure components ranging from communication networks, public service systems, roads, and drainage networks must be increased and strengthened for these areas before any expected natural disaster to help reduce their vulnerability risk.
Current Disaster Preparedness in Bangladesh
To ensure disaster preparedness, the government of Bangladesh has established some initiatives such as early warning systems, earthquake drills, and capacity building for local authorities.
Government Initiatives
- The government of Bangladesh has implemented initiatives for earthquake preparedness and increased attention to cyclone preparedness.
- It promulgated the Disaster Management Act 2012 and Disaster Management Policy 2015, establishing a national framework for disaster risk reduction.
- Bangladesh has been a member of the International Strategy for Disaster Reduction (IDSR) since 1998, enabling it to reduce the risk by sharing and exchanging information on disasters with other countries.
- Bangladeshi governments are leading major infrastructure projects such as seismic-microzonation in Dhaka City, which involves gathering data through geological surveys to model locations most vulnerable to earthquakes.
- Community-based initiatives have been established to educate people about disaster management, safe building construction techniques, and evacuation planning.
Role of NGOs and Community Organizations
NGOs (Non-Governmental Organizations) and community groups have a vital role in disaster readiness in Bangladesh. They help assess the risk of disasters in advance and boost the community’s ability to prepare, respond, and recover.
These organizations engage in various activities, including running programs, offering micro-credits for development projects, and providing essential family planning services and human rights services. Their active participation also aids the government of Bangladesh in fulfilling its duty to protect the population from disasters.
For instance, international NGOs like Action Aid provide funding for relief operations during floods or climate-induced emergencies across the country.
Additionally, local organizations conduct public awareness campaigns to educate communities on what to do during emergencies, especially regarding earthquake preparedness. NGOs also contribute to creating accurate databases that are crucial for efficient disaster mapping efforts before an earthquake or other disaster strikes a specific area.
Building Codes and Regulations
In Bangladesh, buildings and structures are required to follow the guidelines outlined in the Bangladesh National Building Code (BNBC) 2015. These codes ensure that appropriate earthquake-resistant measures are taken during the planning and construction process of a building to reduce its vulnerability to earthquakes.
Furthermore, local municipalities must comply with these building codes while granting projects’ licenses; they also inspect existing buildings for code compliance on a regular basis.
Challenges in Disaster Preparedness
Challenges in Bangladesh’s earthquake preparedness exist, such as scarce resources and inadequate knowledge. Learn more to understand the gravity of this issue.
Lack of Resources
The lack of resources is a major challenge to earthquake preparedness in Bangladesh. In Dhaka, the capital city of Bangladesh, rapid urbanization has added an extra load on its infrastructure.
Poverty and limited financial resources are preventing seismic retrofitting, which could help strengthen existing buildings and infrastructure against future earthquakes. The cost of disaster mitigation measures, such as installing early warning systems, is still prohibitively high for most local governments and individuals living in rural areas.
Besides this, inadequate educational opportunities limit the public’s access to knowledge about how to respond before, during, or after an earthquake event. This can put them at greater risk of harm if any disaster strikes their area due to a lack of awareness about important safety tips and procedures.
Corruption and Mismanagement
When it comes to Bangladesh and its battle with disaster management, corruption, and mismanagement are some of the main obstacles that have long hindered effective preparedness. Weak governance in the country is a major driver of disaster risk, including financial fraud and the transgression of regulations meant to ensure building safety codes.
The collapse of the Rana Plaza after an eight-story building caved in on thousands of textile workers highlighted the direct consequences of inadequate infrastructure standards due to building violations or bribing practices among those responsible for approving such constructions.
Furthermore, political instability within recent years has further hampered efforts towards crisis prevention as there continues to be a lack of resources allocated by government organizations due to poor decision-making where key funding streams are largely misspent while only organizational personnel benefit from them instead.
Lack of Knowledge and Awareness
For Bangladesh, a lack of knowledge and awareness of disaster preparedness is one of the biggest challenges. This lack of understanding comes from structural factors such as poverty, lack of resources, and education, along with cultural practices that brush aside lessons learned from earthquakes in other parts of the world.
To compound matters further, information on seismic activity within Bangladesh is not widely available or documented so people are often unaware how much they should be prepared for an Earthquake.
Knowledge management plays an essential role in improving disaster preparedness by shifting the focus onto identifying local capacities and ensuring that those actively involved in response efforts possess a comprehensive understanding of what may happen as well as skill sets to respond quickly and appropriately when it does occur.
This requires constant research to remain familiar with advanced earthquake science, learning more about how particular settlements interact seismically, and analyzing data on past events to determine cause-and-effect relationships between human activities provides insight into possible strategies for mitigation while also providing a foundation upon which emergency plans can be prepared.
Improving Earthquake Preparation in Bangladesh
Enhancing infrastructure, investing in regular drills and simulations, and educating communities at large about earthquake preparedness measures are some of the key steps that Bangladesh needs to prioritize to manage earthquakes better.
Regular Drills and Simulations
Regular drills and simulations are key components of disaster preparedness. These exercises can help individuals, communities, and organizations practice safety measures during earthquakes and develop emergency response plans.
The DEEP project in Bangladesh is one example of how regular drills and simulations were used to strengthen the resilience of affected communities. Through simulated quake scenarios, citizens better understood what to do if an earthquake happened.
They also learned about evacuation routes and emergency supplies needed in case such an event occurs.
Besides preparing for earthquakes, regular drills are instrumental in raising awareness among people on what actions must be taken before and after an earthquake.
By regularly practicing appropriate responses through these exercises, individuals gain confidence which helps them respond quickly if a real crisis situation arises due to seismic activity or any other natural hazard phenomenon.
Strengthening Infrastructure
Strengthening infrastructure in Bangladesh is key to better preparing against the threat of earthquakes. Resilient infrastructure can minimize the impacts felt by a population, allowing for prompt access and response to earthquake-affected areas.
Infrastructure such as buildings need to be retrofitted or restored using improved technologies, while road networks and utilities should also be upgraded wherever necessary.
Retrofitting existing buildings with new seismic protection measures, training engineers about seismic design techniques, and ensuring proper maintenance of roads and bridges are important steps that can drastically improve preparedness toward minimizing damage caused due to earthquakes in Bangladesh.
Additionally, adopting new building standards such as certification schemes would help raise awareness and encourage more proprietors and builders alike to increase safety features in their structures based on modern standards set up for densely populated areas like Dhaka city, where people’s lives are especially at risk.
Educating Individuals and Communities
The importance of community and individual awareness about disaster preparedness cannot be overstated. With ever-increasing seismic activity, Bangladesh must take proactive steps to reduce the likelihood and severity of an earthquake’s impact.
Educating individuals and communities on earthquake preparedness measures can help them become better informed about earthquake risks and ensure appropriate response to any aftermath that may result from tremors or forces produced by seismic activity.
Important topics include teaching people how to identify potential hazards in each room before a quake occurs, reinforcing structures so that they are more likely to withstand shaking, putting together contingency plans in case of aftershocks or extended power outages, stocking emergency supplies such as food water and batteries, becoming familiar with proper evacuation methods if necessary.
Education also focuses on helping people cope with the psychological effects of disasters. Earthquake-related education should involve active participation from local communities through drills and simulations wherever possible.
International Support for Disaster Preparedness
To mitigate the impacts of seismic activity, international assistance is essential and must include initiatives such as learning from other earthquake-prone countries’ strategies for prevention, financing for preparedness measures, technological exchange programs, humanitarian aid, and collaboration.
Lessons From Other Earthquake-Prone Countries
The international community has learned valuable lessons about disaster preparedness and response from seismically active areas around the world. Countries in Southeast Asia, like Indonesia, have implemented a range of measures to strengthen their disaster risk reduction capacity, including enhanced risk identification and analysis, increased investment in disaster risk reduction education and skills development, and improved access to insurance against large-scale disasters.
The crisis response to the 2015 Nepal earthquake offers lessons applicable to other disaster-prone countries dealing with natural hazards such as floods, cyclones, or earthquakes.
Some of these best practices include making information on operational planning available for public use beforehand; establishing early warning systems that reach remote communities directly via SMS messages; improving coordination among government bodies; strengthening evacuation plans according to need by conducting detailed surveys prior to an expected event; increasing data collection during disasters for improved decision-making purposes afterward; and reinstating infrastructure through post reconstruction activities.
In Bangladesh, particular emphasis should be laid on investing in more reliable weather forecasting systems as well as long-term measures with resilient construction techniques, especially when it comes to protecting cultural heritage sites which are vulnerable due largely in part to poor maintenance over time.
Funding and Aid for Disaster Management
Bangladesh is an all too familiar victim of natural disasters, with its vulnerable low-lying geography located at the junction between three tectonic plates in the Ganges Delta. This makes it highly prone to both earthquakes and floods.
The government has undertaken many initiatives to improve disaster preparedness against such calamities; however, resources are limited, and the population density is high – making prevention difficult without proper funding.
International aid plays a key role in helping Bangladesh strengthen its resilience towards natural disasters.
In 2018, USAID’s programs helped nearly 3 million poor Bangladeshis by adapting infrastructure for better disaster risk management, raising their awareness and training them on emergency response plans.
Similarly, The World Bank approved a credit of $500 Million to help Bangladesh cope with flooding incidents. This enabled numerous initiatives ranging from building embankments to creating early warning systems across affected areas within the country, reducing potential damages by millions each year.
Collaborative Efforts
Collaboration is increasingly being recognized as an effective way to improve disaster preparedness in Bangladesh. Inter-agency collaboration has played a crucial role in mainstreaming disaster management into development planning and providing support for vulnerable communities in responding to disasters.
For instance, after the 2005 earthquake, numerous non-governmental organizations (NGOs), relief groups, and donor agencies collaborated with the Bangladesh government, ensuring that early recovery and risk reduction projects were successful. And when it comes to disaster recovery, many things can often go wrong.
USAID/BHA provided over $28.5 million in funding for partner organizations conducting activities related to early recovery, risk reduction, and resilience-building measures within affected locations nationwide.
The German Red Cross also led a project in Dhaka that used simulated evacuation exercises to prepare local communities and authorities for efficient emergency response capabilities during seismic events or natural disasters.
Moreover, various countries like India have responded positively whenever help was requested from them after earthquakes by sending troops or offering financial assistance for rebuilding damaged infrastructures quickly to minimize further damages caused by such calamities.
Importance of Timely Response
The importance of a timely response to an earthquake should not be underestimated, as these can save lives and help provide aid for those affected.
Search and Rescue Efforts
Search and rescue teams provide one of the most vital services to reduce casualties during an earthquake. Trained professionals such as firefighters, police officers, medical personnel, and search-and-rescue specialists are often dispatched to affected areas to locate survivors trapped under debris or collapsed buildings.
According to a published report from The United Nations Office for Disaster Risk Reduction (UNDRR), emergency response teams, including heavy lifting units, must reach hard-hit areas within 72 hours of an earthquake to effectively rescue people trapped beneath rubble that has not yet begun settling.
National disaster management response forces across Bangladesh, India, and Pakistan deploy specialized teams equipped with tools like axes, flaw detectors, stretchers, and litter for rescue operations while Germany’s Red Cross project equips local training centers with simulations on how best assist people in times of distress due rapid onset earthquakes like those common throughout Africa & Asia Pacific regions.
Providing Aid and Support
During disasters in Bangladesh, providing timely aid and support is essential to minimize the damage caused by earthquakes. Organizations such as the Bangladesh Fire Service and Civil Defense (BFSCD) are well-trained and equipped to provide efficient disaster response, but often prevention becomes hampered due to traffic congestion and other logistical issues.
The Rohingya crisis has also added a lot of strain on Bangladeshi resources, with nearly 1 million refugees living in multiple camps throughout the country. To tackle these hindrances, there is already a National Plan for Disaster Management in place as endorsed by the World Health Organization (WHO).
This plan includes specific strategies for searching and rescuing victims, providing relief materials, access to safe drinking water, shelter management, healthcare services, and improving hygiene practices among affected communities.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Here are some frequently asked questions for your reference.
1. Is Bangladesh At Risk of Earthquakes?
Bangladesh is in an active seismic zone and prone to moderate to large earthquakes.
2. Are There Any Prevention Measures Put in Place By The Bangladesh Government?
Yes, the government has taken steps such as rigorous building regulations, frequent quake drills, and constructing flood-proof shelters to help protect people from potential damage caused by future earthquakes.
3. How Can I Prepare for an Earthquake If I Live in Bangladesh?
You should become informed about safe practices during a quake and create an emergency plan with your family members on where to assemble after the shaking ends. It’s also important to have supplies like a flashlight, batteries, and a first aid kit in emergencies.
Final Words
The current state of earthquake preparedness in Bangladesh is far from satisfactory, as highlighted by the research conducted by organizations like the German Red Cross and other independent studies.
People’s awareness about an upcoming quake must be improved, and wide-ranging initiatives must be taken immediately to prepare for a potential disaster. The government must urgently address issues such as lack of resources, mismanagement, and corruption before any major catastrophe occurs.
Bangladesh should look at international support provided by experienced earthquake-prone countries to understand how overarching issues can be holistically addressed using fundamental techniques such as Early Warning Systems (EWS), Risk Identification and preparedness (RIP) planning, etc. Timely response during emergencies is crucial; otherwise, losses could have catastrophic consequences.
Thus, communities must exercise frequent emergency drills with due training on search and rescue operations being mandatory for all stakeholders, along with aid management plans to equip the local authorities with accurate information on prompt relief measures.