Tax management can be a daunting task for self-employed professionals in Finland, but with the right strategies, it can become an effortless process.
This comprehensive guide is designed to help you understand the Finnish tax system and master the essential tax tips for self-employed professionals in Finland.
By implementing these insights, you can save time, reduce stress, and focus on growing your business.
Understanding the Finnish Tax System
Before diving into specific tax tips for self-employed professionals in Finland, it’s essential to understand the foundational elements of Finland’s tax system. Familiarity with these basics helps you navigate your obligations more effectively and avoid unnecessary penalties.
Overview of Tax Obligations in Finland
In Finland, self-employed individuals are required to pay income tax, social security contributions, and potentially value-added tax (VAT). Here’s a brief breakdown:
- Income Tax: Taxed progressively, with rates increasing based on income levels. Understanding your tax bracket is crucial for accurate tax planning.
- Social Security Contributions: These include pensions, unemployment insurance, and health insurance payments, essential for financial security.
- Value-Added Tax (VAT): Applicable if your annual turnover exceeds €15,000, VAT compliance is vital for maintaining legal and financial integrity.
| Tax Type | Description |
| Income Tax | Progressive rates based on income |
| Social Security | Includes pension and health contributions |
| Value-Added Tax (VAT) | Applies if turnover exceeds €15,000 |
Importance of Accurate Record-Keeping
Maintaining accurate records is not only a legal requirement but also a cornerstone for maximizing deductions. Ensure all income, expenses, and receipts are well-documented and easily accessible for audits. Organized record-keeping also simplifies tax preparation and reduces the likelihood of errors.
Practical Tips for Record-Keeping:
- Use cloud-based accounting tools for real-time updates.
- Create digital backups of receipts using scanning apps.
- Categorize expenses monthly to avoid end-of-year stress.
Tax Deadlines and Penalties
The Finnish tax year aligns with the calendar year. Filing deadlines typically fall in March or April. Missing these deadlines can result in penalties and interest on unpaid taxes. To stay compliant, mark critical dates on your calendar and set reminders.
| Key Tax Deadlines | Description |
| March 1–15 | Annual tax filing for self-employed |
| Quarterly (if VAT-registered) | VAT returns |
| Monthly (if applicable) | Prepayments on income tax |
Essential Tax Tips for Self-Employed Professionals
Mastering your taxes starts with actionable strategies tailored to Finland’s regulations. These 12 tax tips for self-employed professionals in Finland will help you stay compliant while maximizing your savings.
1. Separate Personal and Business Expenses
Mixing personal and business finances complicates tax filing and can lead to errors. Open a dedicated business bank account to ensure clear separation and accurate tracking of business-related expenses. This practice simplifies bookkeeping and creates a transparent financial trail.
| Action | Benefit |
| Use separate accounts | Easier to identify deductible expenses |
| Track expenses weekly | Prevents oversight of smaller transactions |
| Automate payments | Reduces manual errors and improves accuracy |
2. Leverage Home Office Deductions
If you work from home, you can claim deductions for a portion of your rent, utilities, and maintenance costs. Calculate the percentage of your home used exclusively for work to determine eligible expenses. For instance, if 20% of your home is used for your business, you can claim 20% of these costs.
| Expense Type | Deductible Portion |
| Rent or mortgage | Proportion used for work |
| Electricity & heating | Based on office space usage |
| Internet & phone bills | Proportion used for business communication |
3. Utilize Travel and Vehicle Expense Deductions
Expenses incurred for business travel, including public transportation, fuel, and vehicle maintenance, are deductible. Keep detailed mileage logs and receipts to support your claims. For instance, if you drive 10,000 km annually for business purposes, calculate deductions accordingly.
| Travel Expense | Eligibility |
| Business meetings | Fully deductible |
| Commuting to clients | Deductible if work-related |
| Parking fees | Deductible for business-related trips |
4. Claim Education and Training Costs
Investing in professional development can reduce your taxable income. Courses, certifications, and workshops related to your field are often deductible. For example, a graphic designer taking an advanced Photoshop course can claim the tuition fee and study materials.
Examples of Deductible Training:
- Online courses on industry trends.
- Software training workshops.
- Professional certifications relevant to your field.
5. Understand VAT (Value-Added Tax) Responsibilities
Register for VAT if your turnover exceeds €15,000 annually. File VAT returns quarterly and deduct the VAT paid on business expenses from the VAT collected on sales. Keeping a detailed record of VAT transactions is crucial to avoid discrepancies.
| VAT Component | Details |
| Registration Threshold | €15,000 annual turnover |
| Filing Frequency | Quarterly (or monthly for larger businesses) |
| Deductible VAT | Applies to business-related purchases |
6. Make Use of Depreciation
Assets like equipment, vehicles, or furniture can be depreciated over time. This reduces your taxable income and spreads the cost of high-value items over several years. For example, if you purchase a €3,000 laptop, you might depreciate it over three years, claiming €1,000 annually.
| Asset Type | Depreciation Period |
| Computers & electronics | 3–5 years |
| Office furniture | 7 years |
| Vehicles | 5 years |
7. Plan for Social Security Contributions
Self-employed individuals are responsible for their pension insurance (YEL) payments. Calculate these contributions carefully to avoid underpayment and ensure adequate coverage. Contributions also affect your future pension benefits.
| Income Level | Contribution Rate |
| Low income (<€10,000) | Lower minimum contribution |
| Average income (€30,000) | Standard YEL rates apply |
| High income (€60,000+) | Higher pension contributions |
8. Consider Hiring an Accountant
A professional accountant can help you navigate complex tax regulations, identify deductions, and ensure accurate filings. Their expertise often saves more money than their fees cost. Additionally, accountants can provide insights into financial planning and tax-saving opportunities.
Benefits of an Accountant:
- Tailored tax strategies based on your industry.
- Assistance with VAT registration and compliance.
- Support during audits or tax disputes.
9. Explore Retirement Savings Options
Contributions to private pension plans or long-term savings accounts can provide tax benefits while securing your financial future. Research government-approved retirement plans to maximize benefits.
Examples of Retirement Options:
- Private pension insurance.
- Investment funds with tax-deferred growth.
10. Keep Up with Tax Law Changes
Finland’s tax laws evolve regularly. Stay informed by subscribing to newsletters, attending seminars, or consulting your accountant to adapt your strategy. For instance, recent green tax incentives encourage sustainable business practices.
11. Take Advantage of Tax Credits and Incentives
The Finnish government offers various tax credits for businesses, such as incentives for hiring employees or investing in environmentally friendly equipment. Researching available credits can significantly lower your tax burden.
| Incentive | Eligibility |
| Hiring Credits | For employing new staff |
| Green Investments | For adopting energy-efficient technologies |
12. File Taxes Electronically for Faster Processing
Using Finland’s online tax portal, MyTax, simplifies the filing process. It’s user-friendly, ensures faster processing, and reduces the likelihood of errors. Additionally, electronic filing keeps all your records in one accessible location.
Tools and Resources for Tax Management
Leveraging the right tools can make tax management more efficient. Below are some recommendations to streamline the process.
Recommended Accounting Software
- Procountor: Popular for its VAT reporting and expense tracking features.
- Talenom: Designed for Finnish tax regulations.
- QuickBooks: Offers invoicing and financial management tools for self-employed professionals.
| Software | Features |
| Procountor | VAT reporting, financial insights |
| Talenom | Finnish tax compliance |
| QuickBooks | Expense tracking, invoicing |
Online Resources and Government Portals
- MyTax Portal: Finland’s official online platform for tax filing.
- Finnish Tax Administration Website: A comprehensive source of up-to-date information on tax policies and deadlines.
Common Tax Mistakes to Avoid
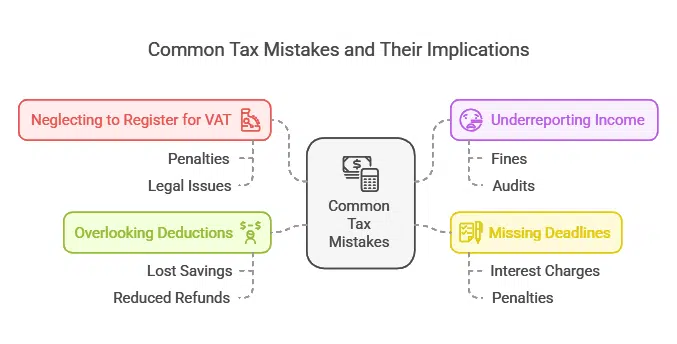
Even seasoned professionals can make errors that cost time and money. Avoid these common pitfalls:
- Neglecting to Register for VAT: If required, failing to register can lead to penalties.
- Underreporting Income: Always declare all income to avoid fines.
- Missing Deadlines: Late filings can result in interest and penalties.
- Overlooking Deductions: Ensure you claim all eligible expenses.
Takeaways
Managing taxes as a self-employed professional in Finland doesn’t have to be overwhelming. By implementing these tax tips for self-employed professionals in Finland, you can simplify your tax process, maximize deductions, and focus on growing your business.
Remember to stay informed, leverage the right tools, and seek professional help when needed. Empower yourself with knowledge and make tax season stress-free.